Tracing scaffolding in technology-enhanced inquiry learning activities by exploiting a digital platform.
- 1. Maria Margoudi1, Zacharoula Smyrnaiou 1 1 Educational Technology Lab, School of Philosophy, Department of Pedagogy, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece mariamar@ppp.uoa.gr , zsmyrnaiou@ppp.uoa.gr Tracing scaffolding in technology- enhanced inquiry learning activities by exploiting a digital platform.
- 2. Theoretical Background ? Problem: Scaffolding practices cannot find effective application in today's classrooms ? Solution: Technology ? Computer-based Scaffolds (Davis and Miyake, 2004)
- 3. Theoretical Background ? Question: Types and purposes of scaffolding? ? Answer: Moore et al. (2014) ? Propose a common framework of scaffolding types
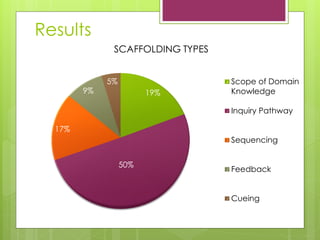
- 4. 5 scaffolding types: Scope of Domain Knowledge Inquiry Pathway SequencingFeedback Cueing Moore et al. (2014)
- 5. Explicit vs. Implicit instructional guidance ? Explicit ? Implicit (Podolefsky et al., 2013) ,(Smyrnaiou et al, 2013)
- 6. Inquiry-Based Science Learning (IBSL) ? innovative approach to science education ? use of computer-based learning environments ? virtual scaffolding possibilities (Moore et al., 2014)
- 7. Methodology ? Aim: Tracing both implicit and explicit scaffolding techniques used during the experimentation of students with this scientific microworld, while engaging in an inquiry-based activity.
- 8. Methodology ? Research Questions: 1. The role and significance each of the five scaffolding types during an inquiry learning process that integrates the engagement with an e-slate scientific microworld? 2. What is the interaction between implicit and explicit scaffolding techniques in an Inquiry- Based Science Learning (IBSL) activity for science education?
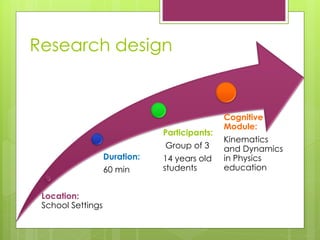
- 9. Research design Location: School Settings Duration: 60 min Participants: Group of 3 14 years old students Cognitive Module: Kinematics and Dynamics in Physics education
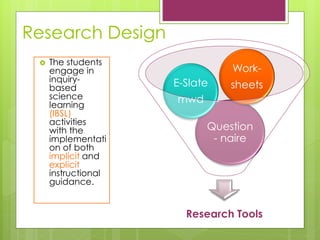
- 10. Research Design ? The students engage in inquiry- based science learning (IBSL) activities with the implementati on of both implicit and explicit instructional guidance. Research Tools Question - naire E-Slate mwd Work- sheets
- 11. Procedure E-SLATE platform is a source of Preman ufacture d educati onal software , called microwo rlds. The students were asked to engage with the microworldĪ»s activities, while working as team. During this process they received instructional guidance by a teacher and a researcher. Variation toolsStage Question buttons Logo button
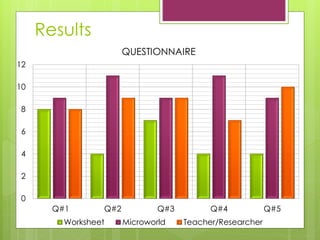
- 12. Data Collection Procedure ? A voiceover of the procedure (screen recording software). ? A questionnaire answered by each student, assessing what helped them the most during the activities (worksheet, microworld, teacher/researcher) on a scale from 1 (not helpful at all) to 4 (very helpful).
- 13. 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Q#1 Q#2 Q#3 Q#4 Q#5 QUESTIONNAIRE Worksheet Microworld Teacher/Researcher Results
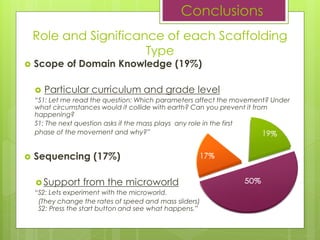
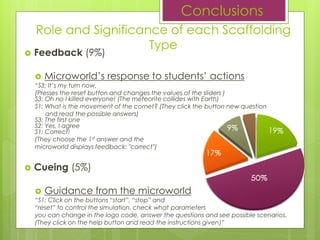
- 14. 19% 50% 17% 9% 5% SCAFFOLDING TYPES Scope of Domain Knowledge Inquiry Pathway Sequencing Feedback Cueing Results
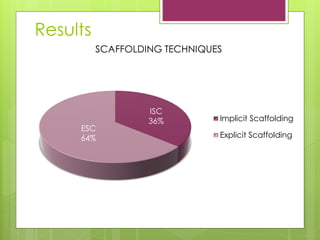
- 15. ISC 36% ESC 64% SCAFFOLDING TECHNIQUES Implicit Scaffolding Explicit Scaffolding Results
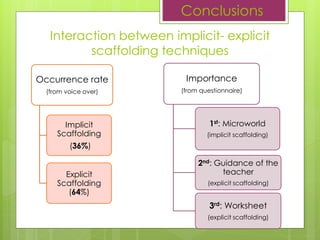
- 16. Interaction between implicit- explicit scaffolding techniques Conclusions Occurrence rate (from voice over) Implicit Scaffolding (36%) Explicit Scaffolding (64%) Importance (from questionnaire) 1st: Microworld (implicit scaffolding) 2nd: Guidance of the teacher (explicit scaffolding) 3rd: Worksheet (explicit scaffolding)
- 17. ? Inquiry Pathway (50%) ? Cognitive issues (laws of physics): Ī░T: You can play the simulation again if you want, in order to find out what type of motion we are looking for or you may use the physics laws you already know.Ī▒ ? Coordination of the students): Ī░R: Let's begin then, you all have instructions in front of you. The first step is to run the software which you will find on the computerĪ»s desktop.Ī▒ Conclusions Role and Significance of each Scaffolding Type
- 18. ? Scope of Domain Knowledge (19%) ? Particular curriculum and grade level Ī░S1: Let me read the question: Which parameters affect the movement? Under what circumstances would it collide with earth? Can you prevent it from happening? S1: The next question asks if the mass plays any role in the first phase of the movement and why?Ī▒ ? Sequencing (17%) ? Support from the microworld Ī░S2: Lets experiment with the microworld. (They change the rates of speed and mass sliders) S2: Press the start button and see what happens.Ī▒ Conclusions Role and Significance of each Scaffolding Type
- 19. ? Feedback (9%) ? MicroworldĪ»s response to studentsĪ» actions Ī░S3: ItĪ»s my turn now. (Presses the reset button and changes the values ??of the sliders ) S3: Oh no I killed everyone! (The meteorite collides with Earth) S1: What is the movement of the comet? (They click the button new question and read the possible answers) S3: The first one S2: Yes, I agree S1: Correct! (They choose the 1st answer and the microworld displays feedback: "correct") ? Cueing (5%) ? Guidance from the microworld Ī░S1: Click on the buttons Ī░startĪ▒, Ī░stopĪ▒ and Ī░resetĪ▒ to control the simulation, check what parameters you can change in the logo code, answer the questions and see possible scenarios. (They click on the help button and read the instructions given)Ī▒ Conclusions Role and Significance of each Scaffolding Type
- 20. Any Questions?