Traffic volume study
- 1. Topic on: traffic volume study Presented by :- Kalpataru Das 120101cel062
- 2. OUTLINE 1. Objectives 2. Scope 3. Definition 4. Methodology 5. Data presentation 6. Purpose 7. Conclusion
- 3. OBJECTIVE  Counting is the most fundamental measurement in traffic engineering: vehicles, passenger etc.  Counting technique to produce estimates of volume, rate flow, demand and capacity.  The purposes of carrying out traffic volume count are designing, improving traffic system, planning, management etc.  Traffic volume study is used in plan.
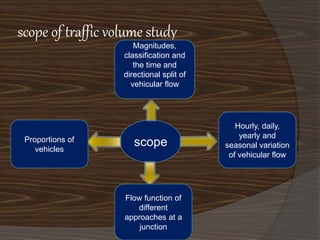
- 4. scope of traffic volume study Magnitudes, classification and the time and directional split of vehicular flow Proportions of scope vehicles Flow function of different approaches at a junction Hourly, daily, yearly and seasonal variation of vehicular flow
- 5. DEFINATION  Traffic volume study is producer to determine mainly the volume of traffic moving on roads on a particular section during a particular time.  AADT: Average annual daily traffic obtain by adding daily traffic count in one year divided by 365.  ADT: Average daily traffic is the volume of traffic total counted on the roadway(two way) over a given time period(greater than one day but less than one year) divided by the number of days in that time period.
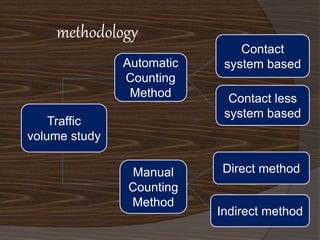
- 6. methodology Traffic volume study Automatic Counting Method Manual Counting Method Contact system based Contact less system based Direct method Indirect method
- 7. Automatic counting method  In this method, vehicles are counted automatically without any human involvement.  There are two techniques of automatic counting  Contact system based:-  It is based on pneumatic, mechanical, magnetic or piezo-electric method.  Contactless system based:-  It is based on electrical/optical, ultrasound/infrared radar, micro wave, CCTV/video image processing method.
- 8. equipments used for automatic counting methods Bending plate
- 9. equipments used for automatic counting methods ÔÇû Vehicles numbers are recorder using ultrasound, light beam or other infrared technology.
- 10. ELECTRONIC COUNTING BOARDS ÔÇû Electronic counting board are battery-operated , lighter, more compact, and easier to handle. They have an internal clock that automatically separates the data by time interval.
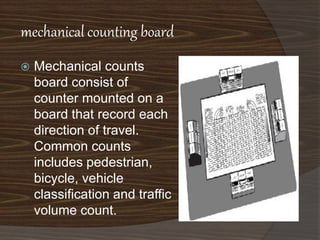
- 11. mechanical counting board ÔÇû Mechanical counts board consist of counter mounted on a board that record each direction of travel. Common counts includes pedestrian, bicycle, vehicle classification and traffic volume count.
- 12. manual counting method  There are two types of manual counting  Direct method  Indirect method  Direct method: Data is counted by using hand tally manual counter.  Indirect method: In this method, data is collected using video camera. Video is captured for long time and data is collected later by rewinding.
- 13. Instruments used in direct method Hand counter Instrument to measure distance
- 14. Instrument used in indirect method ÔÇû Video cameras are mounted to record the traffic condition on road.
- 16. Data presentation ÔÇûThe collect from traffic volume counts may be presented in the several ways depending on the type of count conducted and primary use of the data.
- 17. continue…  Trend chart showing volume trends over period of years are prepared. These data useful for planning future expansion, design and regulation.  Variation chart showing hourly,daily and seasonal variations are also prepared. these help in deciding the facilities and regulation needed during peak traffic periods.  Traffic flow maps along the routes are drawn.These helps to find the traffic volume distribution at glance.
- 18. continue…  Volume flow diagram at intersection either drawn to a certain scale or indicating traffic volume as shown in this figure and it showing the details of crossing and turning traffic, these data is needed for intersection design.
- 19. purposes ÔÇû Estimating of highway usage ÔÇû Measurement of current demand of facility ÔÇû Economic feasibility evaluation ÔÇû Computation of accident rates ÔÇû Improvement purpose ÔÇû Planning purpose ÔÇû Traffic management purpose
- 20. conclusion ÔÇû Light vehicles(car,jeep,etc) occupied 64% of total vehicle ÔÇû Percentage of auto rickshaw is relatively high ÔÇû Percentage of public transport is very low