Training_AERE radiation worker_2018.ppt
- 1. Basic of Nuclear and Radiological Emergency Preparedness and Response Training Course on Radiation Protection for Radiation Workers and RCOs of BAEC, Medical Facilities and Industries TI, AERE, 05 -0 9 August 2018 Shampa Paul Shampa Paul Senior Engineer, HPRWMU Senior Engineer, HPRWMU INST, AERE, Savar INST, AERE, Savar
- 2. 1. Introduction 1. Introduction 2. Nuclear/Radiological Accident 2. Nuclear/Radiological Accident 3. Nuclear/Radiological Emergency Basics 3. Nuclear/Radiological Emergency Basics 4. Emergency types, response planning 4. Emergency types, response planning and responsibility and responsibility 5. Emergency Management Organization 5. Emergency Management Organization and Infrastructure and Infrastructure 6. Bangladesh Perspectives 6. Bangladesh Perspectives 7. Future Plan 7. Future Plan Contents Contents
- 3. Emergency Management Emergency Management is the application of the necessary resources to mitigate consequences of an emergency and protect workers, the public, the environment, and national security. It consists of key activities: planning, preparedness, readiness assurance and response. Emergency An emergency is any unwanted operational (large scale accidents), civil (mass agitation), natural calamities (earthquake, cyclone, flood), or security occurrence (war situation) that could endanger or adversely affect the health and safety of workers, the public, and/or the environment. 1. Introduction 1. Introduction
- 4. Introduction.. Introduction.. Preparedness Refers to various actions of planning, organizing, training, and exercising (with proper equipment and personnel) that are taken in advance at normal times and can be adopted promptly upon the occurrence of an emergency. Response Refers to measures to be taken upon the occurrence of an emergency with various actions of preventing continual deterioration of the situation and protecting the safety, health properties of the public and the environment.
- 5. (a) (a) Nuclear emergencies may occur at: Nuclear emergencies may occur at: ŌĆö Nuclear Power Reactors; ŌĆö Large irradiation facilities (e.g., industrial irradiators); ŌĆö Nuclear reactors (research reactors, ship etc.); ŌĆö Storage facilities for large quantities of spent fuel ŌĆö Fuel cycle facilities (e.g. fuel processing plants); ŌĆö Industrial facilities (e.g. facilities of radiopharmaceuticals); ŌĆö Research or medical facilities with large fixed sources. Two Types of Emergencies: 1. Nuclear 1. Nuclear (arise in nuclear installations) (arise in nuclear installations) 2. Radiological 2. Radiological (related to radioactive sources) Introduction.. Introduction..
- 6. (b) Radiological emergencies include: (b) Radiological emergencies include: 1. Sources ŌĆö Uncontrolled (abandoned or lost) dangerous sources; ŌĆö Misuse of industrial and medical dangerous sources; ŌĆö Detection of medical over-exposure; ŌĆö Public exposures and contamination; ŌĆö Nuclear weapons; ŌĆöRe-entry of a satellite containing radioactive material. 2. Transport emergencies 3. Serious overexposures 4. Terrorist threats and/or criminal activities Introduction.. Introduction..
- 7. Major Nuclear and radiological Incidents happened all over the world Nuclear 1. Fukushima (Japan, 2011) 2. Chernobyl (USSR, 1986) 2. Three Mile Island (USA, 1979) Radiological 1. Mexico City (Mexico, 1962, lost source, 8 deaths) 2. Ohio (USA, 1974, radiotherapy source, 10 deaths) 3. Goiania (Brazil, 1987, lost radiography source, 5 deaths) 4. Zaragoza (Spain, 1990, radiotherapy accident, 18 deaths) 5. Panama City (Panama, radiotherapy accident, 17 deaths) 2. Nuclear Power Reactor and Accident 2. Nuclear Power Reactor and Accident
- 8. Nuclear Power Reactor and Accident.. Nuclear Power Reactor and Accident.. I. Nuclear Accident: I. Nuclear Accident: Chernobyl, USSR, 1986 Chernobyl, USSR, 1986
- 9. Aftermath of Nuclear Accident: Aftermath of Nuclear Accident: Chernobyl, USSR, 1986 Chernobyl, USSR, 1986 Fact sheet on Chernobyl Fact sheet on Chernobyl Disaster Disaster Place: Chernobyl, Ukrane, USSR Time: 26 April, 1986 Accident Type: Explosion of Reactor Direct Death: 237 suffered from acute dose and 31 died within a month Cancer Induced Death: 4000 Total exposure: 600000 Resettled: 336000 Affected area: Western S. Union, Whole of Europe and most affected states are Belarus and Ukraine. About 60% of the fallout landed in Belarus. Map of radiation levels in 1996 around Chernobyl.
- 10. II. Nuclear Accident: TMI, USA, 1989 II. Nuclear Accident: TMI, USA, 1989 Statistics of TMI Accident Place: Three Mile Island, Middletown, Pennsylvania, USA Date: March 28, 1979 Accident Type: Core Meltdown Direct Death: No Acute Exposure: No Hazard Type: Noble gas and I-131 Evacuation: 140000 TMI plant before accident TMI plant after accident (Unit-2, left)
- 11. Radioactive Waste Transport Accident Nuclear Weapon Test Scenarios of Radiological Incident Scenarios of Radiological Incident Radioactive Material Transport and Accident
- 12. Effect of Nuclear Accident Effect of Nuclear Accident Health and Environmental Hazards The plume of radiation released by Chernobyl accident settled on trees killing areas of pine trees what is now called the Red Forest. The health and environmental effects of Nuclear incidents occur in much larger scale. However, the effects of radiological incidents are much lower than the nuclear incidents. Children suffered from the thyroid cancer after Chernobyl accident
- 13. Two questions arises from two historic severe nuclear accidents: (1) Why, as a result of the Chernobyl release, did 1000 or more children suffer from thyroid cancer that could have been easily avoided? (2) Why were actions of the operators partly the cause of the melting of the core during the accident at Three Mile Island? The answer to the first question is that the authorities under-reacted because of lack of preparedness. The answer to the second question is that the operators were not trained for the conditions they faced. In both cases, the basic cause was that no one thought it was worth preparing in advance for such low probability emergencies. 3. Nuclear/Radiological Emergency Basics 3. Nuclear/Radiological Emergency Basics
- 14. Response goal is: ŌĆö To mitigate accident at the scene ŌĆö To prevent the occurrence of deterministic health effects ŌĆö To render first aid and to manage the treatment of injuries ŌĆö To reasonably reduce the stochastic health effects ŌĆö To protect the property and the environment ŌĆö To prepare for the resumption of normal social and economic activity Objectives: Emergency Preparedness and Response Objectives: Emergency Preparedness and Response Preparedness goal is: ŌĆö To ensure that arrangements are in place to protect ’ü▒ Public health ’ü▒ Public welfare and the environment ŌĆö To develop and implement ’ü▒ Justified and optimized countermeasures in a timely, managed, controlled, coordinated and effective way Emergency preparedness helps to build confidence that an emergency response would be managed, controlled and coordinated effectively.
- 15. Types of Health Effects in Emergencies Types of Health Effects in Emergencies Deterministic Effect: ’āśIs a fatal or life threatening or results in a permanent injury ’āśHas a threshold level of dose ’āśThreshold differs for different organs ’āśThresholds are one or more Gys Stochastic Effect ’āśThe probability of occurrence increases with dose ’āśNo threshold level of dose ’āśCause cancers and hereditary effects
- 16. ŌĆö External exposure from contact with or being in proximity to a source of radiation (e.g. a source, a plume containing radioactive material or ground contamination); ŌĆö External gamma radiation from the plume, called cloud shine; ŌĆö External gamma radiation from radioactive material deposited on the ground, called ground shine; ŌĆö Inhalation of radioactive material contained in the plume; ŌĆö Ingestion of contaminated food, milk or water; ŌĆö To a lesser extent, deposition of radioactive material on the skin. Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents
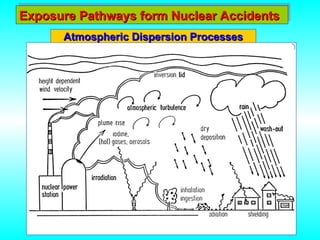
- 17. Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents Atmospheric Dispersion Processes Atmospheric Dispersion Processes
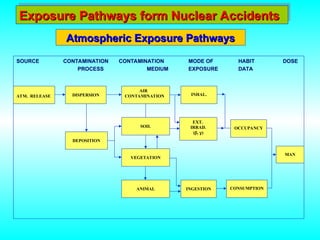
- 18. Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents Atmospheric Exposure Pathways Atmospheric Exposure Pathways SOURCE CONTAMINATION CONTAMINATION MODE OF HABIT DOSE PROCESS MEDIUM EXPOSURE DATA ATM. RELEASE DISPERSION AIR CONTAMINATION INHAL. SOIL VEGETATION ANIMAL EXT. IRRAD. (’üó, ’ü¦) INGESTION DEPOSITION OCCUPANCY CONSUMPTION MAN
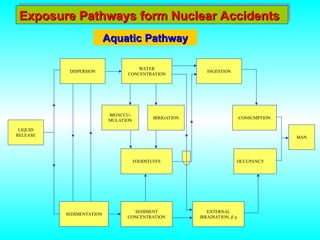
- 19. Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents Exposure Pathways form Nuclear Accidents DISPERSION SEDIMENTATION LIQUID RELEASE WATER CONCENTRATION BIOACCU- MULATION IRRIGATION FOODSTUFFS SEDIMENT CONCENTRATION INGESTION EXTERNAL IRRADIATION, ’üó ’ü¦ CONSUMPTION OCCUPANCY MAN Aquatic Pathway Aquatic Pathway
- 20. International Nuclear Event Scale International Nuclear Event Scale 4. Emergency Types, Response Planning and 4. Emergency Types, Response Planning and Responsibility Responsibility
- 21. Emergency Types, Response Planning and Emergency Types, Response Planning and Responsibility.. Responsibility.. General Emergency General Emergency Site Area Emergency Site Area Emergency Plant Emergency Plant Emergency Standby Emergency Standby Emergency Four types of radiation emergency situations may arise in nuclear installations I. Standby Emergency (Alert) II. Plant Emergency (Local/Facility) III. Site Area Emergency IV. General Emergency I. Standby Emergency: The emergency situation in which events are in progress or have occurred indicate a potential degradation of safety at facility. Staff members are put on stand-by and all agencies monitor the situation. This may arise in nuclear and radiological facilities. II. Plant Emergency: The emergency situation in which radiological consequences are likely to be confined to a limited area of the facility. This may arise in nuclear and radiological facilities. Emergency agencies are notified and asked to stay in touch.
- 22. Emergency Types.. Emergency Types.. III. Site Area Emergency: The emergency situation involving an accidental release of radioactive material extending beyond the plant boundary. Site area emergency is declared if there is problem with the plant safety system. Members of public should be alerted. This may arise in nuclear facilities. IV. General Emergency: The emergency situation in which consequences of the emergency extend beyond the site boundary. A general emergency is declared when an event at the plant has caused a loss of several safety systems that could lead to release of radiation. This may arise in nuclear facilities. All agencies and organizations involved in radiological emergency preparedness are notified, all emergency operation centers are activated, and all pre-designated agency personnel and resources are deployed.
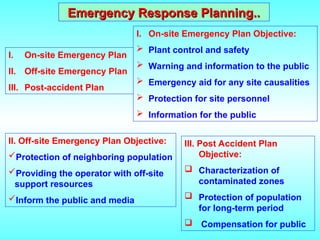
- 23. Emergency Response Planning.. Emergency Response Planning.. I. On-site Emergency Plan II. Off-site Emergency Plan III. Post-accident Plan I. On-site Emergency Plan Objective: ’āś Plant control and safety ’āś Warning and information to the public ’āś Emergency aid for any site causalities ’āś Protection for site personnel ’āś Information for the public II. Off-site Emergency Plan Objective: ’ā╝Protection of neighboring population ’ā╝Providing the operator with off-site support resources ’ā╝Inform the public and media III. Post Accident Plan Objective: ’ü▒ Characterization of contaminated zones ’ü▒ Protection of population for long-term period ’ü▒ Compensation for public
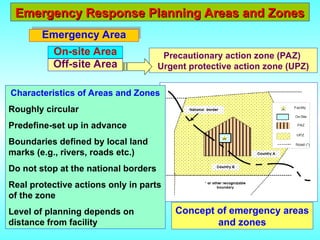
- 24. Emergency Response Planning Areas and Zones Emergency Response Planning Areas and Zones Emergency Area Characteristics of Areas and Zones Roughly circular Predefine-set up in advance Boundaries defined by local land marks (e.g., rivers, roads etc.) Do not stop at the national borders Real protective actions only in parts of the zone Level of planning depends on distance from facility Precautionary action zone (PAZ) Urgent protective action zone (UPZ) Concept of emergency areas and zones On-site Area Off-site Area
- 25. Emergency Response Planning Areas and Zones Emergency Response Planning Areas and Zones On-site Area Area under the control of the operator or first responders. For nuclear facilities the on-site area is the area surrounding the facility within the security perimeter, fence or other designated property marker. Off-site Area Area beyond that area under the control of the facility, operator or first responders. It applies for the nuclear facilities only. Applies to nuclear facilities and is the area within which arrangements should be made to implement precautionary urgent protective actions before or shortly after a major release with the aim of preventing the occurrence of severe deterministic effects. Precautionary action zone (PAZ)
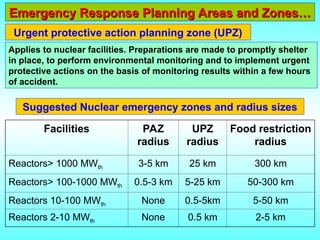
- 26. Emergency Response Planning Areas and ZonesŌĆ” Emergency Response Planning Areas and ZonesŌĆ” Applies to nuclear facilities. Preparations are made to promptly shelter in place, to perform environmental monitoring and to implement urgent protective actions on the basis of monitoring results within a few hours of accident. Urgent protective action planning zone (UPZ) Facilities PAZ radius UPZ radius Food restriction radius Reactors> 1000 MWth 3-5 km 25 km 300 km Reactors> 100-1000 MWth 0.5-3 km 5-25 km 50-300 km Reactors 10-100 MWth None 0.5-5km 5-50 km Reactors 2-10 MWth None 0.5 km 2-5 km Suggested Nuclear emergency zones and radius sizes
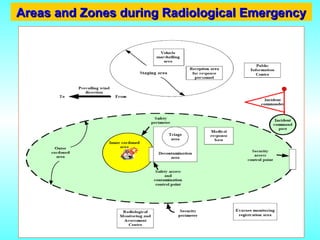
- 27. Areas and Zones during Radiological Emergency Areas and Zones during Radiological Emergency
- 28. Responsibility during Nuclear Emergency Responsibility during Nuclear Emergency Responsibilities are typically assigned at three levels: 1. On-site 2. Off-site and 3. International 1. The operator is responsible for on-site area under emergency. The responsibilities are: Ō¢Ā Identifying and/or detecting an emergency or hazard; Ō¢Ā Taking immediate action to mitigate the consequences; Ō¢Ā Protecting individuals on the site; Ō¢Ā Declaring the class of the emergency; Ō¢Ā Notifying off-site officials and providing them technical assistance; Ō¢Ā Establishing communication with off-site officials; Ō¢Ā Assisting the off-site officials in keeping the public informed; Ō¢Ā Providing initial radiological monitoring and technical advice.
- 29. Responsibility during Nuclear EmergencyŌĆ” Responsibility during Nuclear EmergencyŌĆ” 2. Local or National officials are responsible for off-site area under emergency. The responsibilities include: ’üČ Implement urgent protective action within the emergency zones; ’üČ Conduct environmental monitoring; ’üČ Control consumption of contaminated food; ’üČ Provide emergency services to the facility; ’üČ Provide medical treatment for the affected; ’üČ Instruct the public and the media of the risks; ’üČ Report transnational emergencies to the IAEA; ’üČ Request IAEA assistance when needed. 3. The international level consists of organizations responsible for providing technical, humanitarian or medical assistance in the event of an emergency such as: IAEA, WHO, FAO etc.
- 30. Basic Emergency Management Program Elements ’ü▒TECHNICAL PLANNING BASIS Hazards Survey/Hazards Assessment ’ü▒PROGRAMMATIC (ŌĆ£ongoingŌĆØ activities) Program Administration Training and Drills Exercises ’ü▒RESPONSE (ŌĆ£standbyŌĆØ activities) Emergency Response Organization (ERO) Offsite Response Interfaces Emergency Facilities and Equipment Categorization and Classification Communication and Notification Consequence Assessment Protective Actions and Reentry Emergency Medical Support Emergency Public Information Termination of Emergency and Recovery 5. Emergency Management Organization and Infrastructure 5. Emergency Management Organization and Infrastructure
- 31. Concept of Emergency Response Organization Concept of Emergency Response Organization
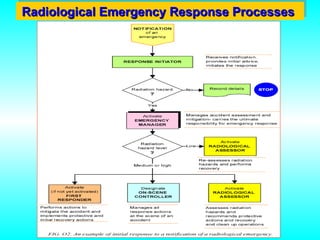
- 32. Radiological Emergency Response Processes Radiological Emergency Response Processes
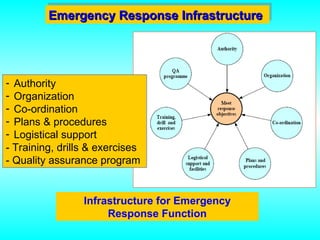
- 33. Emergency Response Infrastructure Emergency Response Infrastructure - Authority - Organization - Co-ordination - Plans & procedures - Logistical support - Training, drills & exercises - Quality assurance program Infrastructure for Emergency Response Function
- 34. Emergency Logistic Support Emergency Logistic Support Emergency Response Centre with Necessary Facility Radiological Emergency Equipment
- 35. ’üČInternal and National level & with Predefined frequency. ’üČThe objective of which is: Training, Drill and Exercise Training 1. Personnel should be trained to ensure efficient and effective role in implementation of emergency plan 2. Help familiarization & understanding of emergency and hands-on training in use of equipment. Drills and Exercise 1. To check the effectiveness of the emergency plans establish the basis of its review. 2. To check the effectiveness of the personnel emergency training and hence review the training program if required. 3. To check the effectiveness of the plant personnel training in their particular response during emergency. 4. To check the effectiveness of the on-site and off-site emergency plan and organization.
- 36. Training, Drill and Exercise Internal Level
- 37. 6. Bangladesh Perspectives 6. Bangladesh Perspectives Sources of Probable Nuclear and Radiological Emergency in Bangladesh ŌĆó Research reactor ŌĆó Hospitals & NMCsŌĆō using radioactive sources ŌĆó Commercial irradiator (e.g., IRPT) ŌĆó Industries and research institutes ŌĆó Space debris from nuclear powered satellites ŌĆó Transportation of radioactive materials or wastes ŌĆó Sabotage or nuclear terrorism such as dirty bomb ŌĆó Nuclear powered carrier or submarine when berths at harbour Industrial Radiography Gauging Medical Sources Research Reactor
- 38. Legal Basis for Emergency Management Legal Basis for Emergency Management ŌĆó In Bangladesh: ŌĆó There are nuclear safety and radiation control Act-1993 and Rules-1997 but have no integrated national emergency management program. ŌĆó There are safety analysis report (SAR) for the research reactor (RR) which includes preparedness and response program for RR. ŌĆó National Nuclear and Radiological Emergency Response (NNRER) Plan draft has been formulated.
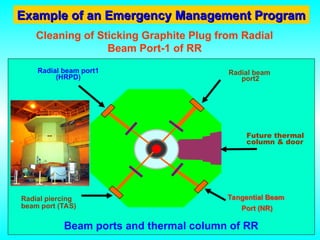
- 39. Radial beam port2 Radial beam port1 (HRPD) Radial piercing beam port (TAS) Future thermal column & door Beam ports and thermal column of RR Tangential Beam Port (NR) Example of an Emergency Management Program Example of an Emergency Management Program Cleaning of Sticking Graphite Plug from Radial Beam Port-1 of RR
- 40. ’ü▒ Sticking of the Inner Shielding Plug (Graphite Plug) in the Radial Beam Port1(RBP1) of RR in 2008-2009. Thank You Very Much! Thank You Very Much! ’ā╝ Conduction of Integrated Emergency Preparedness and Response Program at National Level ’ā╝ Establishment of National Nuclear and Radiological Emergency Control Center 7. Future Plan 7. Future Plan