Transistor notes
Download as PPTX, PDF13 likes16,645 views
A transistor is a semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and power by using a voltage or current applied to one pair of terminals to control the current through another pair of terminals. It is composed of semiconductor material with three terminals - the emitter, base, and collector. Transistors use a sandwich of p-type and n-type semiconductor materials and can be NPN or PNP types. They are commonly used in integrated circuits and have replaced vacuum tubes in most modern electronics due to being more durable, having a longer life, consuming less power, and not requiring a heating element.
1 of 15
Downloaded 458 times












Recommended
Presentation of transistor



Presentation of transistorSohag Babu
Ěý
The document discusses transistors, including:
- Transistors are electronic devices made of three layers of semiconductor material that can act as insulators or conductors.
- The first transistor was invented in 1947 by John Bardeen and Walter Brattain.
- There are several types of transistors including BJT, UJT, FET, and MOS transistors. BJTs use both electrons and holes, while FETs use only one type of carrier.
- Transistors have wide applications as switches, amplifiers, and in digital circuits. Recent developments include 3D transistors made using tri-gate technology for improved performance and efficiency.Transistor



TransistorTouqeer Jumani
Ěý
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaTransistor basics



Transistor basicsAtheenaPandian Enterprises
Ěý
The study of the basics of electronics can be studied through the link http://bit.ly/2PPv0mv
The transistor is a semiconductor device with three connections, capable of amplification in addition to rectificationMagnetic Circuits



Magnetic CircuitsChetan Patil
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to magnetic circuits, including key definitions:
- Magnet provides magnetic property, magnetic flux is the number of field lines passing through a closed surface.
- Magnetic flux density B and field intensity H are defined, with units of tesla and ampere/meter respectively.
- Magneto motive force (MMF) is the force that causes flux to flow, measured in ampere-turns. Reluctance is the opposition to flux flow, measured in ampere-turns/weber.
- Permeance is the reciprocal of reluctance. Permeability is the ability of a material to allow flux flow.
- Series and parallel magnetic circuits are discussed, behaving similarly to electricDiode ,its types & its Application



Diode ,its types & its ApplicationSUFYAN SATTAR
Ěý
1. The document discusses diodes, their structure and types including PN junction diode, LED, photodiode, and Zener diode.
2. It explains how diodes allow current to flow in one direction during forward bias when positive voltage is applied to the p-type side, and restricts current in reverse bias.
3. Applications of diodes discussed include different types of rectifiers (half wave, full wave, bridge) which convert AC to DC, and clippers which shape input waveforms.An introduction to electronic components



An introduction to electronic componentsMaria Romina Angustia
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to basic electronic components. It discusses two types of components - passive components (resistors, capacitors, inductors) and active components (tube devices, semiconductor devices). Resistors oppose current flow, capacitors store electrical energy, and inductors produce inductance. Semiconductor devices like chips are now replacing tube devices due to their smaller size, lower power needs, and longer life. The document provides details on interpreting color codes for resistors and markings for other components.Transistor Fundamentals



Transistor FundamentalsJay Baria
Ěý
- The document summarizes transistor fundamentals, including the invention of the transistor, its basic construction and operation, and different transistor configurations like common-base, common-emitter, and common-collector.
- It discusses key transistor parameters like current gain (β), maximum voltage and current ratings, and biasing requirements to operate transistors in the active region.
- Simulation results are presented to demonstrate a transistor functioning as an amplifier in the common-emitter configuration.Digital storage ocilloscope



Digital storage ocilloscopekajal8899
Ěý
dso is use for measurement ac as well as dc voltage and current.
and also use for faulty components in various circuit .it stored wave form in digital memory.it easy to operate. cursor measurement is possible. Cro cathode ray oscilloscope working and applications



Cro cathode ray oscilloscope working and applicationsEdgefxkits & Solutions
Ěý
The document discusses the cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO), which is an electronic test instrument used to observe changing electrical signals over time. It describes the key components of a CRO including the cathode ray tube, vertical/horizontal controllers, triggers, and displays. The document explains how a CRO works by amplifying input signals and using electron beams to produce waveforms on the screen. Various sweep modes, synchronization methods, and applications of CROs for measuring voltage, current, and examining waveforms are also covered.Transistor biasing 



Transistor biasing Anisur Rahman
Ěý
There are four main methods of transistor biasing: base resistor method, emitter bias method, biasing with collector feedback resistor, and voltage-divider bias method. The document then focuses on explaining the base resistor method and voltage-divider bias method in more detail. For the base resistor method, a resistor is used to provide base current, but it has poor stability. For the voltage-divider bias method, two resistors are used to provide stable biasing of the transistor by controlling the base-emitter voltage. This method is widely used due to its stability from the emitter resistor preventing changes in collector current.Transistor and it's working principle



Transistor and it's working principleEkram Bin Mamun
Ěý
A slide on Transistor and it's working principle for the course Research Methodology under International Islamic University Chittagong.Transistor , NPN & PNP Transistor



Transistor , NPN & PNP TransistorPreston University
Ěý
A transistor is a small electronic device that controls the flow of electric current. It acts like a switch that can open and close many times per second. There are two main types of transistors - NPN and PNP - which differ in how they allow or block the flow of electric current between three terminals: the base, collector, and emitter. The base terminal controls the flow of current between the collector and emitter terminals.Transistor 



Transistor Ikhlas Rahman
Ěý
Here you find the information about Transistors. And know about
-> Type Of Transistor:
->Region of Transistor:
->P-N Junction Diodes
->Transistor application
->Transistor Connections
Limitation:
->Future of transistor:
Transistor



TransistorUnsa Shakir
Ěý
Transistors are electronic devices made of semiconductor material that can act as both an insulator and conductor. They have three layers - an emitter, base, and collector - and come in two types: NPN and PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). BJTs use both holes and electrons as charge carriers. Transistors have different operating regions - cutoff, linear, and saturation - and can be used as electronic switches or amplifiers by controlling the base current to mimic an input signal with greater amplitude at the collector. Common transistor types include BJTs, JFETs, FETs, and MOS transistors.Push pull amplifier (class b power amplifier)



Push pull amplifier (class b power amplifier)hepzijustin
Ěý
This document describes the push-pull amplifier circuit. A push-pull amplifier uses two transistors connected in a way that one transistor amplifies the positive half of the input signal while the other amplifies the negative half. This results in an output signal that is an amplified replica of the input signal with less distortion compared to a single transistor amplifier. The key components are two transistors, input and output transformers, and biasing resistors. The transistors are biased at cutoff so that they only conduct during one half of the input signal cycle. This alternating amplification of the signal halves is what gives the circuit its name - it "pushes" the signal high during one half and "pulls" it low during the other half.Semiconductor Devices

Semiconductor DevicesRajesh Kumar
Ěý
This presentation gives a lot of information about
Semiconductor Devices.This is presented by Rajesh Kumar Sangani from Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies,Basar Dist
Adilabad,A.P,India.Active and passive



Active and passiveSUneel Gupta
Ěý
The document discusses active and passive components in electronics. It defines passive components as circuit elements that receive and store energy in electric or magnetic fields, but cannot continuously deliver power. Passive components mentioned include capacitors, inductors, and transformers. Active components are defined as having gain or ability to control voltage/current, and include transistors and integrated circuits. The document provides examples of capacitors, inductors, and transformers as passive elements, and contrasts them with transistors as active elements.3.bipolar junction transistor (bjt)



3.bipolar junction transistor (bjt)firozamin
Ěý
Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) are three-terminal semiconductor devices consisting of two pn junctions. There are two types, NPN and PNP, depending on the order of doping. BJTs can operate as amplifiers and switches by controlling the flow of majority charge carriers through the base terminal. Proper biasing is required to operate the transistor in its active region between cutoff and saturation. Common configurations include common-base, common-emitter, and common-collector, each with different input and output characteristics. Maximum ratings like power dissipation and voltages must be considered for circuit design and temperature derating.CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE (CRO)



CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE (CRO)KumarSUshilSINGH
Ěý
The document discusses the cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO). It begins with an introduction that describes a CRO as an electronic device that uses a cathode ray tube to generate visible patterns and graphs on a screen. It then provides details about the basic blocks of a CRO including the vertical and horizontal amplifiers, trigger circuit, time-base generator, and cathode ray tube. Applications of CROs include viewing waveforms, measuring frequency and voltage, and circuit design and testing. Advantages include high resolution and contrast while disadvantages include size, power consumption, and complexity.Oscilloscope



OscilloscopeUniversity of Technology
Ěý
The document discusses oscilloscopes, including:
1) An oscilloscope is a visual voltmeter that displays voltage patterns over time using a cathode ray tube (CRT) similar to a television screen.
2) There are several types of oscilloscopes including analog, digital storage, digital phosphor, and digital sampling oscilloscopes.
3) Oscilloscopes are used to measure signals and analyze waveforms, and can display different waveforms like sine waves. They have applications in measuring light intensity from a photocell and other signals.Bio-polar junction transistor (edc)



Bio-polar junction transistor (edc)Abhinay Potlabathini
Ěý
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) consists of two PN junctions formed by sandwiching either a p-type or n-type semiconductor between two opposite types. It has three sections - the emitter, base, and collector. Current flows due to both electrons and holes, making it a bipolar device. The base is lightly doped and very thin to allow charge carriers to easily move from the emitter to the collector. BJTs can be used as amplifiers because the collector current is controlled by the base current.Function generator



Function generatorBhavin Mangukiya
Ěý
This document describes different types of waveforms that can be generated by a function generator. It discusses how triangular, square, and sine waves are produced. For triangular waves, the function generator charges and discharges a capacitor to produce a linear ramp waveform. A square wave is created using an integrator circuit that causes the output to switch between saturation voltages. Sine waves can be approximated from triangular waves using a resistor-diode network to nonlinearly scale the output.Types of transistors



Types of transistorsUnsa Shakir
Ěý
There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and field effect transistors (FET). BJTs use both holes and electrons as current carriers and include NPN and PNP types, while FETs use only one carrier type and include JFETs and MOSFETs. MOSFETs are particularly important as they can be easily integrated into circuits. MOSFETs operate in different modes depending on the voltage applied to the gate and include depletion, enhancement, linear, and saturation modes.Transistors ppt by behin



Transistors ppt by behinBehin anben
Ěý
The document discusses transistors, including their history and evolution. It describes how the transistor was invented in 1947 and became the building block of electronics. Moore's Law, which predicted transistors would double every two years, driving down costs, is also mentioned. The key types of transistors - bipolar junction transistors and field effect transistors - are defined. Their basic construction, symbols, operation, and applications as switches and amplifiers are outlined. New developments in transistor technology like 3D transistors are also summarized.Electrical instruments ppt



Electrical instruments pptAmey Waghmare
Ěý
This document provides an overview of electrical measurement and measuring instruments. It discusses the essential requirements of indicating instruments, which are deflecting torque, controlling torque, and damping torque. Controlling torque methods include spring control and gravity control. Damping torque is achieved through air friction or eddy current damping. Moving iron, permanent magnet moving coil, and electrodynamic instruments are described in terms of their construction and working principles. DC ammeters and voltmeters are also briefly discussed.Photo diode



Photo diodeDEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
Ěý
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in the photodiode. Photodiodes may contain optical filters, built-in lenses, and may have large or small surface areas.
TRANSISTORS



TRANSISTORSAJAL A J
Ěý
The document discusses the history and operation of transistors, beginning with the point-contact transistor invented in 1947 by Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley at Bell Labs. It then covers the basic structure and types of bipolar junction transistors, including NPN and PNP, as well as their operating regions and usage as switches and amplifiers. New developments in transistor technology include 3D transistors using tri-gate designs for improved power efficiency and performance.Semiconductor diode

Semiconductor diodeRAMPRAKASHT1
Ěý
This document provides an overview of semiconductor diodes, including PN junction diodes. It discusses intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, doping to create N-type and P-type materials, the PN junction, depletion region and built-in voltage calculations. Forward and reverse bias characteristics are examined along with current equations. Energy band diagrams are presented for the PN junction under zero, forward and reverse bias. Other topics covered include drift and diffusion current densities, transition and diffusion capacitances, switching characteristics and breakdown mechanisms in PN junction diodes. Ratings for diodes such as maximum current and voltage are also defined.Transistors



TransistorsSAMYAKKHADSE
Ěý
In this presentation there are different types of transistors and are they are well explained. It can be used in school, college purposesBasic Fundamental Of Transistors by D-Sarda



Basic Fundamental Of Transistors by D-SardaDinesh Sarda
Ěý
Transistors are the building blocks of electronics and come in two types - intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure while extrinsic have impurities added. The first transistor was invented in 1947 by Bardeen and Brattain. Moore's Law predicted transistors in integrated circuits would double every two years. A transistor is a three-layer semiconductor device that can conduct or insulate electricity and comes in bipolar and field effect varieties.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Cro cathode ray oscilloscope working and applications



Cro cathode ray oscilloscope working and applicationsEdgefxkits & Solutions
Ěý
The document discusses the cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO), which is an electronic test instrument used to observe changing electrical signals over time. It describes the key components of a CRO including the cathode ray tube, vertical/horizontal controllers, triggers, and displays. The document explains how a CRO works by amplifying input signals and using electron beams to produce waveforms on the screen. Various sweep modes, synchronization methods, and applications of CROs for measuring voltage, current, and examining waveforms are also covered.Transistor biasing 



Transistor biasing Anisur Rahman
Ěý
There are four main methods of transistor biasing: base resistor method, emitter bias method, biasing with collector feedback resistor, and voltage-divider bias method. The document then focuses on explaining the base resistor method and voltage-divider bias method in more detail. For the base resistor method, a resistor is used to provide base current, but it has poor stability. For the voltage-divider bias method, two resistors are used to provide stable biasing of the transistor by controlling the base-emitter voltage. This method is widely used due to its stability from the emitter resistor preventing changes in collector current.Transistor and it's working principle



Transistor and it's working principleEkram Bin Mamun
Ěý
A slide on Transistor and it's working principle for the course Research Methodology under International Islamic University Chittagong.Transistor , NPN & PNP Transistor



Transistor , NPN & PNP TransistorPreston University
Ěý
A transistor is a small electronic device that controls the flow of electric current. It acts like a switch that can open and close many times per second. There are two main types of transistors - NPN and PNP - which differ in how they allow or block the flow of electric current between three terminals: the base, collector, and emitter. The base terminal controls the flow of current between the collector and emitter terminals.Transistor 



Transistor Ikhlas Rahman
Ěý
Here you find the information about Transistors. And know about
-> Type Of Transistor:
->Region of Transistor:
->P-N Junction Diodes
->Transistor application
->Transistor Connections
Limitation:
->Future of transistor:
Transistor



TransistorUnsa Shakir
Ěý
Transistors are electronic devices made of semiconductor material that can act as both an insulator and conductor. They have three layers - an emitter, base, and collector - and come in two types: NPN and PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). BJTs use both holes and electrons as charge carriers. Transistors have different operating regions - cutoff, linear, and saturation - and can be used as electronic switches or amplifiers by controlling the base current to mimic an input signal with greater amplitude at the collector. Common transistor types include BJTs, JFETs, FETs, and MOS transistors.Push pull amplifier (class b power amplifier)



Push pull amplifier (class b power amplifier)hepzijustin
Ěý
This document describes the push-pull amplifier circuit. A push-pull amplifier uses two transistors connected in a way that one transistor amplifies the positive half of the input signal while the other amplifies the negative half. This results in an output signal that is an amplified replica of the input signal with less distortion compared to a single transistor amplifier. The key components are two transistors, input and output transformers, and biasing resistors. The transistors are biased at cutoff so that they only conduct during one half of the input signal cycle. This alternating amplification of the signal halves is what gives the circuit its name - it "pushes" the signal high during one half and "pulls" it low during the other half.Semiconductor Devices

Semiconductor DevicesRajesh Kumar
Ěý
This presentation gives a lot of information about
Semiconductor Devices.This is presented by Rajesh Kumar Sangani from Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies,Basar Dist
Adilabad,A.P,India.Active and passive



Active and passiveSUneel Gupta
Ěý
The document discusses active and passive components in electronics. It defines passive components as circuit elements that receive and store energy in electric or magnetic fields, but cannot continuously deliver power. Passive components mentioned include capacitors, inductors, and transformers. Active components are defined as having gain or ability to control voltage/current, and include transistors and integrated circuits. The document provides examples of capacitors, inductors, and transformers as passive elements, and contrasts them with transistors as active elements.3.bipolar junction transistor (bjt)



3.bipolar junction transistor (bjt)firozamin
Ěý
Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) are three-terminal semiconductor devices consisting of two pn junctions. There are two types, NPN and PNP, depending on the order of doping. BJTs can operate as amplifiers and switches by controlling the flow of majority charge carriers through the base terminal. Proper biasing is required to operate the transistor in its active region between cutoff and saturation. Common configurations include common-base, common-emitter, and common-collector, each with different input and output characteristics. Maximum ratings like power dissipation and voltages must be considered for circuit design and temperature derating.CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE (CRO)



CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE (CRO)KumarSUshilSINGH
Ěý
The document discusses the cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO). It begins with an introduction that describes a CRO as an electronic device that uses a cathode ray tube to generate visible patterns and graphs on a screen. It then provides details about the basic blocks of a CRO including the vertical and horizontal amplifiers, trigger circuit, time-base generator, and cathode ray tube. Applications of CROs include viewing waveforms, measuring frequency and voltage, and circuit design and testing. Advantages include high resolution and contrast while disadvantages include size, power consumption, and complexity.Oscilloscope



OscilloscopeUniversity of Technology
Ěý
The document discusses oscilloscopes, including:
1) An oscilloscope is a visual voltmeter that displays voltage patterns over time using a cathode ray tube (CRT) similar to a television screen.
2) There are several types of oscilloscopes including analog, digital storage, digital phosphor, and digital sampling oscilloscopes.
3) Oscilloscopes are used to measure signals and analyze waveforms, and can display different waveforms like sine waves. They have applications in measuring light intensity from a photocell and other signals.Bio-polar junction transistor (edc)



Bio-polar junction transistor (edc)Abhinay Potlabathini
Ěý
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) consists of two PN junctions formed by sandwiching either a p-type or n-type semiconductor between two opposite types. It has three sections - the emitter, base, and collector. Current flows due to both electrons and holes, making it a bipolar device. The base is lightly doped and very thin to allow charge carriers to easily move from the emitter to the collector. BJTs can be used as amplifiers because the collector current is controlled by the base current.Function generator



Function generatorBhavin Mangukiya
Ěý
This document describes different types of waveforms that can be generated by a function generator. It discusses how triangular, square, and sine waves are produced. For triangular waves, the function generator charges and discharges a capacitor to produce a linear ramp waveform. A square wave is created using an integrator circuit that causes the output to switch between saturation voltages. Sine waves can be approximated from triangular waves using a resistor-diode network to nonlinearly scale the output.Types of transistors



Types of transistorsUnsa Shakir
Ěý
There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and field effect transistors (FET). BJTs use both holes and electrons as current carriers and include NPN and PNP types, while FETs use only one carrier type and include JFETs and MOSFETs. MOSFETs are particularly important as they can be easily integrated into circuits. MOSFETs operate in different modes depending on the voltage applied to the gate and include depletion, enhancement, linear, and saturation modes.Transistors ppt by behin



Transistors ppt by behinBehin anben
Ěý
The document discusses transistors, including their history and evolution. It describes how the transistor was invented in 1947 and became the building block of electronics. Moore's Law, which predicted transistors would double every two years, driving down costs, is also mentioned. The key types of transistors - bipolar junction transistors and field effect transistors - are defined. Their basic construction, symbols, operation, and applications as switches and amplifiers are outlined. New developments in transistor technology like 3D transistors are also summarized.Electrical instruments ppt



Electrical instruments pptAmey Waghmare
Ěý
This document provides an overview of electrical measurement and measuring instruments. It discusses the essential requirements of indicating instruments, which are deflecting torque, controlling torque, and damping torque. Controlling torque methods include spring control and gravity control. Damping torque is achieved through air friction or eddy current damping. Moving iron, permanent magnet moving coil, and electrodynamic instruments are described in terms of their construction and working principles. DC ammeters and voltmeters are also briefly discussed.Photo diode



Photo diodeDEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
Ěý
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in the photodiode. Photodiodes may contain optical filters, built-in lenses, and may have large or small surface areas.
TRANSISTORS



TRANSISTORSAJAL A J
Ěý
The document discusses the history and operation of transistors, beginning with the point-contact transistor invented in 1947 by Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley at Bell Labs. It then covers the basic structure and types of bipolar junction transistors, including NPN and PNP, as well as their operating regions and usage as switches and amplifiers. New developments in transistor technology include 3D transistors using tri-gate designs for improved power efficiency and performance.Semiconductor diode

Semiconductor diodeRAMPRAKASHT1
Ěý
This document provides an overview of semiconductor diodes, including PN junction diodes. It discusses intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, doping to create N-type and P-type materials, the PN junction, depletion region and built-in voltage calculations. Forward and reverse bias characteristics are examined along with current equations. Energy band diagrams are presented for the PN junction under zero, forward and reverse bias. Other topics covered include drift and diffusion current densities, transition and diffusion capacitances, switching characteristics and breakdown mechanisms in PN junction diodes. Ratings for diodes such as maximum current and voltage are also defined.Similar to Transistor notes (20)
Transistors



TransistorsSAMYAKKHADSE
Ěý
In this presentation there are different types of transistors and are they are well explained. It can be used in school, college purposesBasic Fundamental Of Transistors by D-Sarda



Basic Fundamental Of Transistors by D-SardaDinesh Sarda
Ěý
Transistors are the building blocks of electronics and come in two types - intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure while extrinsic have impurities added. The first transistor was invented in 1947 by Bardeen and Brattain. Moore's Law predicted transistors in integrated circuits would double every two years. A transistor is a three-layer semiconductor device that can conduct or insulate electricity and comes in bipolar and field effect varieties.Module II- Part 01.pptx



Module II- Part 01.pptxssuseraaa4d6
Ěý
This document provides information about the course "20EC201 & ELECTRON DEVICES" taught at SRI RAMAKRISHNA ENGINEERING COLLEGE. The course covers concepts of semiconductor devices including bipolar junction transistors. It discusses transistor basics such as types, terminals, configurations, characteristics and parameters. Common configurations covered are common base, common collector and common emitter. Key concepts explained are current and voltage gains, input and output resistances, and early effect.Rectifiers



RectifiersMadhu Sudana
Ěý
Rectifiers play an important role in the x-ray circuit, this presentation gives a brief idea about rectifiers, generators and transformers. PHY-Presentation.pptx



PHY-Presentation.pptxMveTm
Ěý
This is about BJT Transistor Operation.. that is for BSCS students.
This is very help ful .. but I'm writing this because i wanna download the presentation from this platform.. just chill Field effect transistors and MOSFET's



Field effect transistors and MOSFET'sPraveen Kumar
Ěý
introduction, types & structure of MOSET ,turn ON and OFF of device, working, I-V characteristics of MOSFET,Different regions of operations,applications, adv & disadvantagesSSD.pptx



SSD.pptxUniversity of Malakand
Ěý
This document provides an overview of solid-state devices and semiconductor components. It discusses intrinsic and doped semiconductors, n-type and p-type materials, and how p-n junctions are formed. Common solid-state devices are then described, including diodes, transistors, and capacitors. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction, while transistors can amplify signals. Capacitors store electrical energy in an electric field. The document explains key concepts such as forward and reverse biasing of diodes. In summary, it introduces fundamental building blocks of electronics like semiconductors and reviews important passive and active solid-state components.Electromagnetic induction



Electromagnetic inductionUgyenNamgay4
Ěý
1. Electromagnetic induction occurs when a changing magnetic field induces a current in a conductor. This can be generated by moving a magnet near a coil or changing the current in a neighboring circuit.
2. Faraday's law states that an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in a conductor whenever the magnetic flux through the conductor changes. The magnitude of the induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of flux.
3. Transformers use electromagnetic induction to change the voltage of alternating current. A step-up transformer increases voltage by having fewer turns in the primary coil, while a step-down transformer decreases voltage with more turns in the primary coil.Electronic components



Electronic componentsUnsa Shakir
Ěý
This document provides an overview of key electrical concepts including:
- Voltage is the potential difference measured in volts that causes current to flow. Current is the rate of flow of electric charge measured in amperes.
- Ohm's law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. Power is defined as voltage multiplied by current and describes the rate of energy transfer.
- Common circuit components are described including resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, and how they are connected using printed circuit boards. Direction of electron and conventional currents are also discussed.a6.pptxsadqwqwdcsdsdqwdazcscdsvsdvsdqwcs



a6.pptxsadqwqwdcsdsdqwdazcscdsvsdvsdqwcsvikknaguem
Ěý
Potential difference (voltage) enables the flow of charge (current) through conductors. Voltage is measured in volts, current in amperes, and their relationship is defined by Ohm's law. Circuits allow current to flow in a closed path, and their basic components - resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors - each control current in different ways. Integrated circuits combine many transistors to process electronic signals and power. Printed circuit boards provide a platform to connect these components via conductive pathways.NPN and PNP Transistors: Structure and Function



NPN and PNP Transistors: Structure and FunctionMahmud Hasan Tanvir
Ěý
This presentation provides an introduction to NPN and PNP transistors, their terminals, and essential facts about their functions. It covers the working principles of both transistor types and explores their applications in circuits, offering a solid foundation for anyone studying electronics. Perfect for students, hobbyists, and professionals looking to understand the role of transistors in modern electronics.Unit 2 semiconductors 



Unit 2 semiconductors Abhinay Potlabathini
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to semiconductors. It discusses how semiconductors can behave as either conductors or insulators depending on doping, and describes the crystal lattice structure of semiconductors. It also explains intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, detailing how doping with trivalent or pentavalent impurities creates N-type or P-type materials respectively. The document concludes by discussing diode operation under forward and reverse bias conditions.Electronic devices



Electronic devicesZeeshanChoudhary4
Ěý
This document provides an overview of basic electronic devices and components. It introduces diodes, transistors, rectifiers, and amplifiers. The document is presented by 6 students and contains their names and a table of contents. It defines electronic devices and discusses semiconductors, intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, PN junctions, diode biasing and types of diodes. It also explains transistors, rectifiers including half wave and full wave rectification, and different types of amplifiers such as weak-signal and power amplifiers.Type of pn junction & rectifiers plus Transistor



Type of pn junction & rectifiers plus TransistorMuhammad Adeel Shakir
Ěý
The document discusses PN junction diodes, rectifiers, and bridge rectifiers. It begins by explaining the history and workings of PN junction diodes, including the depletion region and forward/reverse biasing. It then covers half-wave and full-wave rectifiers for converting AC to DC. Finally, it describes bridge rectifiers, including their types, working principle, advantages of higher output voltage and efficiency over center-tap rectifiers, and applications in power supplies.Transistor s06



Transistor s06SUneel Gupta
Ěý
This document summarizes different types of transistors, including Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT), Unijunction Transistors (UJT), Field Effect Transistors (FET), Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFET), FinFETs, and Dualgate transistors. It describes the basic structure and functioning of BJTs, including PNP and NPN types, and provides information on UJTs, FETs including n-channel and p-channel types, MOSFETs, FinFETs which use a 3D "fin" design, and Dualgate transistors which incorporate more than one gate.DELD Unit 1 BJT



DELD Unit 1 BJTKanchanPatil34
Ěý
The transistor is a semiconductor device with three terminals - the emitter, base, and collector. Current flowing into the base terminal controls the flow of current between the emitter and collector terminals, allowing transistors to function as amplifiers or switches. Transistors come in two main types - bipolar junction transistors (BJT) which use both electrons and holes as current carriers, and field effect transistors (FET) which use an electric field to control the flow of electrons or holes in a channel. BJTs contain two pn junctions and come in npn or pnp varieties, while FETs use a gate to modulate the conductivity of a channel between source and drain terminals.semiconductor ,n- p type semiconductor ,forward biased and reverse biased

semiconductor ,n- p type semiconductor ,forward biased and reverse biasedSHRI RAM KRISHNA GUIDANCE CENTER
Ěý
semiconductor ,n- p type semiconductor ,forward biased and reverse biased TRANSISTOR.pptx



TRANSISTOR.pptxSyedSaifuddin30
Ěý
Transistors are three-terminal electronic components made of semiconductor material that control the flow of current in circuits. There are two main types: NPN transistors, which have two blocks of N-type semiconductor and one block of P-type; and PNP transistors, which have one block of N-type and two blocks of P-type. Transistors have three terminals - the emitter supplies charge carriers to the base, the collector collects carriers from the base, and the base controls the flow. Transistors are used in many applications like oscillators, compact discs, hearing aids, switches, and as the basic building blocks of computer processors. Modern computer processors can contain billions of transistors on a single chip.Transistor, its working and Applications



Transistor, its working and ApplicationsSajawalNawaz2
Ěý
The document discusses transistors, their working, types, and applications. A transistor is an electronic component that uses semiconductors to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. It has three terminals called the emitter, base, and collector. Transistors come in different types like bipolar junction, field effect, etc. and are classified as NPN or PNP depending on the arrangement of N-type and P-type semiconductors. The document describes how NPN and PNP transistors work by controlling the flow of current between the emitter and collector using the base. Finally, it lists some common applications of transistors like as a switch, circuit element, and amplifier.Assignment_3.1_BJT and BJT Amplifiers.pptx



Assignment_3.1_BJT and BJT Amplifiers.pptxGABRIELABRAMJOPIA1
Ěý
The document discusses the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) including its history, working principle, types (PNP and NPN), and biasing techniques. Key points:
- BJTs were invented in 1947 and replaced vacuum tubes, making electronics smaller and more reliable. They consist of P-type and N-type semiconductor materials.
- In a BJT, the base terminal controls the flow of current between the emitter and collector. It works by having one junction forward biased and the other reverse biased.
- The two types are PNP, where the emitter is more positive than the base and collector, and NPN, where the connections are reversed.
- BJT biassemiconductor ,n- p type semiconductor ,forward biased and reverse biased

semiconductor ,n- p type semiconductor ,forward biased and reverse biasedSHRI RAM KRISHNA GUIDANCE CENTER
Ěý
Transistor notes
- 1. Transistor Made by - priyank jain
- 3. introduction • A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current flowing through another pair of terminals., a transistor can amplify a signal. found embedded in integrated circuits.
- 4. Transistor • Transistor are electrical device, which utilize a sandwich of p and n type of semi conductor materials. • It can be NPN or PNP types
- 5. Transistor • It has got 3 parts : • emitter • Base • Collector.
- 6. • One of the n type at the left is emitter • Right is collector • And central p type is the base
- 7. • When contact is being made between materials in case of NPN transistor PD develops at their junction and the emitter and collector being positive relative to the base.
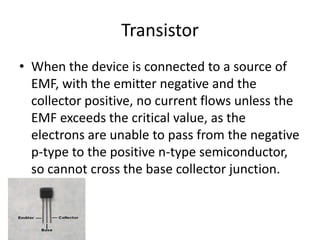
- 8. Transistor • When the device is connected to a source of EMF, with the emitter negative and the collector positive, no current flows unless the EMF exceeds the critical value, as the electrons are unable to pass from the negative p-type to the positive n-type semiconductor, so cannot cross the base collector junction.
- 9. Transistor • A second source of EMF is connected to the base and the emitter, the base being positive relative to the emitter. • The electron can pass from the negative n type to the positive p-type • So the current flows across the base collector junction.
- 10. Transistor • In the circuit’ there is a thick layer of n-type semiconductor, a thin layer of p-type semiconductor’ so the current consist largely of the movement of electrons from the emitter soon pass into the base
- 11. Transistor • The base has now an adequate supply of electrons, and as it is very thin these come close to the base collector junction, and are attracted into the collector, to replace those that had migrated into the base.
- 12. Transistor • This reduces the barrier effect across the base-collector junction, and current flows across the transistor. • Thus a current fed into he base current, causes greater variation of current flowing across the transistor.
- 13. Transistor • In this respect the current fed into the base of the transistor has an effect, comparable to that of a positive charge applied to the grid of a triode valve.
- 14. Transistor • Uses of transistor • Transistor are used in preference to the valve in most modern equipment, as they are durable, have a long life, consume less power and need no heating device. • As the power output is limited they are suitable for use in the production of low frequency but fail to produce high frequency currents e.g. SWD
- 15. Thank you Priyank jain
