Transport systems in plants.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes69 views
This document discusses the transport systems in dicotyledonous plants. It describes the three main tissue types - dermal, vascular, and ground tissues. The dermal tissue provides an outer protective covering. The vascular tissue, made up of xylem and phloem, transports water, minerals and organic nutrients throughout the plant. The ground tissue fills the internal space. Secondary growth in woody plants is driven by the vascular cambium, which produces secondary xylem and phloem. Water and minerals enter the roots through three pathways - transmembrane, symplastic, and apoplastic. They are then transported through the xylem to the leaves. In the leaves, transpiration creates a pulling force that draws
1 of 40
Download to read offline





















Ad
Recommended
Unit 5 support and transport in plants
Unit 5 support and transport in plantsObey Maduna
╠²
1. The document discusses plant anatomy and transport systems. It describes the basic tissues and organs of dicotyledonous plants including dermal, vascular and ground tissues. It also discusses secondary growth in stems and roots.
2. The document explains how water and minerals are taken up by roots through transmembrane, symplastic and apoplastic pathways, and transported through the xylem. Environmental factors like transpiration pull water up from the roots and through the stems and leaves.
3. The products of photosynthesis are transported from source to sink tissues through the phloem. Sucrose moves from leaves to areas of storage or growth through phloem translocation.Ls2 afet unit 5 support and transport in plants
Ls2 afet unit 5 support and transport in plantsThabo Bafana
╠²
The document discusses plant transport systems. It describes that plants have dermal, vascular and ground tissues that make up their basic organs - roots, stems and leaves. Transport of water and minerals occurs through the xylem, moving from the roots upward. Transpiration creates a pulling force that draws water through the xylem. Photosynthates are transported through the phloem from sugar sources like leaves to sugar sinks like roots, moving downward.Support And Transport Systems In Plants
Support And Transport Systems In PlantsLebohang Potsane
╠²
The document discusses plant transport systems. It describes that plants have dermal, vascular and ground tissues that make up their basic organs - roots, stems and leaves. The vascular tissues include xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards, while phloem transports organic nutrients between source and sink tissues. Secondary growth in woody plants involves vascular cambium that produces secondary xylem and phloem. Water and minerals enter roots via transmembrane, symplastic or apoplastic routes. They are then transported upwards via root pressure, cohesion-tension and transpiration. Photosynthates are translocated from source to sink tissues through the phloem.support and transport in plants
support and transport in plantsThabang Mokoena
╠²
Plants have evolved three basic organs - roots, stems and leaves - that are organized into root and shoot systems. Each organ contains dermal, vascular and ground tissues. Secondary growth in woody plants occurs due to the vascular cambium, producing secondary xylem and phloem. Water and minerals enter roots through cell walls and membranes by transmembrane, symplastic or apoplastic routes. They move upwards via root pressure, cohesion-adhesion-tension and transpiration. Transpiration is influenced by environmental factors and causes guttation. Photosynthates are translocated from source leaves to sinks through the phloem sieve tubes via sucrose molecules moving from high to low concentration.9.2 transport in angiospermophytes
9.2 transport in angiospermophytescartlidge
╠²
The root system provides a large surface area for water and mineral uptake through branching and root hairs. Mineral ions move to the roots through diffusion, fungal hyphae, or mass flow in water. Plants absorb minerals through active transport against a concentration gradient. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from leaves and stems, which creates a pull carrying water and minerals through xylem vessels. Transpiration is regulated by guard cells and affected by light, temperature, wind and humidity. Phloem transports sugars and amino acids between plant parts.Cambridge AS Biology plant revision
Cambridge AS Biology plant revisionGuerillateacher
╠²
Plants need transport systems to move water, minerals, and sugars throughout their tissues since roots absorb water and minerals from the soil while leaves produce sugars through photosynthesis. Xylem tissue transports water and minerals upward from the roots to the leaves, having dead cells with thick lignified walls that form continuous tubes. Phloem tissue transports sugars downward from the leaves to all parts of the plant using living sieve tube cells and companion cells. Transport occurs via mass flow driven by water potential gradients between sources and sinks.How plants survive grade 11
How plants survive grade 11majoydrew
╠²
Plants need transport systems to move water, minerals, and sugars throughout their tissues since roots absorb water and minerals from the soil while leaves produce sugars through photosynthesis. Xylem tissue transports water and minerals upward from the roots to the leaves, while phloem tissue transports sugars downward from the leaves to all other plant parts. Xylem is made of dead water-conducting cells called vessels while phloem is made of living sieve tube elements that transport sugars with the help of companion cells.Transport in plants
Transport in plantsHoang Phuong Linh
╠²
Monocots and dicots are classified based on the number of seed leaves, with monocots having one and dicots having two. They differ in various structural aspects including leaf vein patterns, floral parts, and root systems. Additionally, the document discusses the vascular tissue organization in stems and roots, explaining how water and nutrients are transported within plants.11. Transport in Plants
11. Transport in PlantsNavodaya Vidyalaya Samiti
╠²
1. Multicellular plants need transport systems to move water, minerals, and sugars throughout their large structures since single cells rely on diffusion.
2. Xylem tissue transports water and minerals up from the roots through the stem and into leaves. Phloem tissue transports sugars made in leaves to other plant parts.
3. In roots, xylem forms a cross-shape in the center with phloem between the arms. In stems, xylem and phloem bundles are arranged around the edges. In leaves, xylem is closer to the top surface and phloem is below.BIO 2203 Lecture 3 WATER TRANSPORT or TRANSLOCATION.pptx
BIO 2203 Lecture 3 WATER TRANSPORT or TRANSLOCATION.pptxAmatiRonald
╠²
Water transport in plants occurs through xylem tissue. Water moves upwards through the plant via transpiration pull and cohesion-tension forces. Evaporation from leaves creates negative pressure that pulls water upwards from the roots. Water adheres to itself through hydrogen bonding, allowing columns of water to form. Transpiration is regulated by stomata opening and closing in response to environmental conditions. Xerophytic plants have adaptations like reduced stomata to minimize water loss through transpiration.Notes .pptx
Notes .pptxAmatiRonald
╠²
Water transport in plants occurs through xylem vessels. Transpiration creates a pulling force that draws water up from the roots through the stem and into the leaves. This transpirational pull is facilitated by the cohesive forces between water molecules and adhesive forces between water and vessel walls. Opening and closing of stomata controls the rate of transpiration and water loss from the leaves. Together, root pressure and transpirational pull drive the absorption and ascent of water through the xylem vessels against gravity to heights of over 100 meters in tall plants.Notes .pptx
Notes .pptxAdomatiOresto
╠²
Water transport in plants occurs through xylem tissue. Transpiration creates a pulling force that draws water up from the roots through the xylem. Transpiration occurs as water evaporates from the leaves and exits through stomata, creating negative pressure. Cohesion between water molecules and adhesion of water to cell walls allows the water column to remain intact over great heights. Together, root pressure and transpirational pull drive the absorption and movement of water through the xylem from roots to leaves.9. Transport in Plants.pptx
9. Transport in Plants.pptxsahibzadamohsinbaloc
╠²
The document summarizes transport in plants. It describes that transport is carried out by vascular tissues called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards from roots to stems and leaves, providing mechanical support. Phloem transports sugars and amino acids throughout the plant. Transpiration pull is the driving force to transport water upwards, while translocation transports sugars via the phloem. Plant adaptations help maximize transport and minimize water loss.Biology Form 5 chapter 1.7 & 1.8 (Transport in Plants)
Biology Form 5 chapter 1.7 & 1.8 (Transport in Plants)mellina23
╠²
This document summarizes transport in plants. It discusses the two types of vascular tissue - xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals up the plant, while phloem transports organic substances downward and outward. Both are found in roots, stems, and leaves. The document describes the structure and function of roots, stems, leaves, xylem, phloem, and the processes of transpiration and transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant.cape biology unit 2-_transport_systems_in_plants
cape biology unit 2-_transport_systems_in_plantsHilton Ritch
╠²
Plants have sophisticated transport systems to move water and nutrients throughout the plant. Water and dissolved minerals are transported up the xylem vessel through root, stem, and into the leaves. Transpiration through leaf stomata creates a pulling force that draws water up the xylem. Sugars produced by photosynthesis are actively transported down the phloem to areas in need, such as roots and growing parts. The mass flow mechanism uses energy from active transport and transpiration to circulate fluids between the xylem and phloem.9.2 transport in angiospermophytes
9.2 transport in angiospermophytescartlidge
╠²
The root system provides a large surface area for uptake of water and minerals through branching and root hairs. Minerals move into the root through diffusion, fungal hyphae, or mass flow with water and are absorbed into roots by active transport. Terrestrial plants support themselves with thickened cell walls, turgor pressure, and lignified xylem. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from leaves and stems, which establishes a transpiration stream that transports water and minerals through the xylem.transport in plants
transport in plantsKhadijaparekh93
╠²
The document summarizes transport systems in plants. It describes that xylem transports water and minerals up the plant and provides mechanical support, while phloem transports sugars and amino acids. Xylem cells are dead and hollow, strengthened by lignin, whereas phloem is made of living sieve tube cells that transport sugars with help from companion cells. Water moves into roots by osmosis and up the plant via root pressure, capillary action and transpiration pull through the xylem. The rate of transpiration is affected by temperature, humidity, light, wind and carbon dioxide levels.9_ Transport in Plants.ppt
9_ Transport in Plants.pptMahdAli3
╠²
The document discusses transport in plants. There are two main transport tissues in flowering plants: xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and mineral salts upwards from the roots through hollow tubes reinforced with lignin. Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids throughout the plant through sieve tubes and companion cells. Water is absorbed into the roots through osmosis and transported upwards through the plant via root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration pull. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from leaves and creates a pulling force. Various environmental factors like temperature, humidity, light intensity, and wind affect the rate of transpiration.Chapter 9 transport in plants lecture
Chapter 9 transport in plants lectureXu Jia Xian
╠²
1) Water and minerals are transported from the roots to the leaves through xylem tissue. Water enters root hair cells through osmosis and moves cell to cell through the root cortex and xylem vessels up the stem.
2) Photosynthates are transported from the leaves to the rest of the plant through phloem tissue. Phloem is made of sieve tube cells that transport sugars and amino acids.
3) Xylem and phloem are arranged in vascular bundles in stems and leaves, and alternate with each other in roots. Transpiration through the stomata of leaves creates a transpiration pull that draws water up the xylem against gravity.AS Level Biology - 7) Plant Transport
AS Level Biology - 7) Plant TransportArm Punyathorn
╠²
The document discusses plant transport systems, detailing the structure and function of various plant tissues involved in transport, including xylem and phloem. It explains the mechanisms of water and nutrient movement within plants, highlighting processes such as transpiration, osmosis, and the pathways through which water and nutrients are absorbed and distributed. Additionally, it describes adaptations that enhance efficiency in water transport and nutrient translocation in different plant types.Transportation in plant
Transportation in plantSantosh Kumar Kar
╠²
1. The document discusses the transport structures in plants, including xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards from the roots to the leaves, while phloem transports food like sugar downward from leaves to other plant parts.
2. Transpiration is the process where water evaporates from the leaves and creates a transpiration pull that draws water up the xylem. Factors like temperature, light intensity, and humidity affect the transpiration rate.
3. Capillary action and adhesion between water and xylem vessels walls helps push water upwards against gravity, along with root pressure and transpiration pull. Together these forces facilitate the movement of water through the plant.Transport in vascular_plants..
Transport in vascular_plants..Shihab Kaniyadukam
╠²
Transport in plants occurs through two main tissues: xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals up from the roots through the stem and leaves using a combination of root pressure and transpiration pull. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from leaves, which creates a negative water potential that pulls water up through the xylem vessels and tracheids. Phloem transports sugars made during photosynthesis from leaves to areas of growth or storage through pressure flow, where sugars move from high pressure source tissues to low pressure sink tissues.Transport in plant slides
Transport in plant slidesAlex Chiam
╠²
The document discusses the transport structures and processes in plants. It describes how xylem transports water and minerals upwards from the roots to the leaves, driven by transpiration pull. Phloem transports food substances manufactured in the leaves to all parts of the plant through sieve tubes and companion cells. Experiments using aphids, ringing, and radioisotopes demonstrate phloem transport.Transport in flowering plants (self created)
Transport in flowering plants (self created)Alex Chiam
╠²
This document discusses the structure and function of xylem in flowering plants. It aims to explain how water is transported from roots to leaves through vascular bundles, which contain xylem and phloem. Xylem consists of hollow tubes reinforced with lignin that transport water and minerals upwards. Water movement occurs through root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration pull. Transpiration pull is the dominant force driving water transport in tall plants, where water loss from leaves creates suction that pulls water upwards.plant anatomy and physiology notes.ppt-ŌĆ£Structure correlates to functionŌĆØ
plant anatomy and physiology notes.ppt-ŌĆ£Structure correlates to functionŌĆØnyagahwanjiru
╠²
The lecture covers plant anatomy and physiology, focusing on the structure and function of plant cells, tissues, and organs including roots, stems, and leaves. It highlights the types of plant tissues: dermal, vascular, and ground, as well as essential processes such as water and sugar transport within plants. Key concepts of plant hormones and their effects on growth and development are also introduced.Lec3_PlantAnat.ppt
Lec3_PlantAnat.pptValeriaTavares21
╠²
This document summarizes a plant anatomy and physiology lecture. It discusses plant cells, tissues and organs. It describes the three main tissue types - dermal, vascular and ground tissues. It explains the roles of xylem and phloem in transporting water and sugars respectively. Key plant organs - roots, stems and leaves - are outlined. Their structures and functions are summarized. The processes of transpiration and phloem translocation are briefly explained. The major plant hormones and their functions are also introduced.Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptx
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptxSourav Kr Podder
╠²
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Celebration QuizMore Related Content
Similar to Transport systems in plants.pptx (20)
11. Transport in Plants
11. Transport in PlantsNavodaya Vidyalaya Samiti
╠²
1. Multicellular plants need transport systems to move water, minerals, and sugars throughout their large structures since single cells rely on diffusion.
2. Xylem tissue transports water and minerals up from the roots through the stem and into leaves. Phloem tissue transports sugars made in leaves to other plant parts.
3. In roots, xylem forms a cross-shape in the center with phloem between the arms. In stems, xylem and phloem bundles are arranged around the edges. In leaves, xylem is closer to the top surface and phloem is below.BIO 2203 Lecture 3 WATER TRANSPORT or TRANSLOCATION.pptx
BIO 2203 Lecture 3 WATER TRANSPORT or TRANSLOCATION.pptxAmatiRonald
╠²
Water transport in plants occurs through xylem tissue. Water moves upwards through the plant via transpiration pull and cohesion-tension forces. Evaporation from leaves creates negative pressure that pulls water upwards from the roots. Water adheres to itself through hydrogen bonding, allowing columns of water to form. Transpiration is regulated by stomata opening and closing in response to environmental conditions. Xerophytic plants have adaptations like reduced stomata to minimize water loss through transpiration.Notes .pptx
Notes .pptxAmatiRonald
╠²
Water transport in plants occurs through xylem vessels. Transpiration creates a pulling force that draws water up from the roots through the stem and into the leaves. This transpirational pull is facilitated by the cohesive forces between water molecules and adhesive forces between water and vessel walls. Opening and closing of stomata controls the rate of transpiration and water loss from the leaves. Together, root pressure and transpirational pull drive the absorption and ascent of water through the xylem vessels against gravity to heights of over 100 meters in tall plants.Notes .pptx
Notes .pptxAdomatiOresto
╠²
Water transport in plants occurs through xylem tissue. Transpiration creates a pulling force that draws water up from the roots through the xylem. Transpiration occurs as water evaporates from the leaves and exits through stomata, creating negative pressure. Cohesion between water molecules and adhesion of water to cell walls allows the water column to remain intact over great heights. Together, root pressure and transpirational pull drive the absorption and movement of water through the xylem from roots to leaves.9. Transport in Plants.pptx
9. Transport in Plants.pptxsahibzadamohsinbaloc
╠²
The document summarizes transport in plants. It describes that transport is carried out by vascular tissues called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards from roots to stems and leaves, providing mechanical support. Phloem transports sugars and amino acids throughout the plant. Transpiration pull is the driving force to transport water upwards, while translocation transports sugars via the phloem. Plant adaptations help maximize transport and minimize water loss.Biology Form 5 chapter 1.7 & 1.8 (Transport in Plants)
Biology Form 5 chapter 1.7 & 1.8 (Transport in Plants)mellina23
╠²
This document summarizes transport in plants. It discusses the two types of vascular tissue - xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals up the plant, while phloem transports organic substances downward and outward. Both are found in roots, stems, and leaves. The document describes the structure and function of roots, stems, leaves, xylem, phloem, and the processes of transpiration and transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant.cape biology unit 2-_transport_systems_in_plants
cape biology unit 2-_transport_systems_in_plantsHilton Ritch
╠²
Plants have sophisticated transport systems to move water and nutrients throughout the plant. Water and dissolved minerals are transported up the xylem vessel through root, stem, and into the leaves. Transpiration through leaf stomata creates a pulling force that draws water up the xylem. Sugars produced by photosynthesis are actively transported down the phloem to areas in need, such as roots and growing parts. The mass flow mechanism uses energy from active transport and transpiration to circulate fluids between the xylem and phloem.9.2 transport in angiospermophytes
9.2 transport in angiospermophytescartlidge
╠²
The root system provides a large surface area for uptake of water and minerals through branching and root hairs. Minerals move into the root through diffusion, fungal hyphae, or mass flow with water and are absorbed into roots by active transport. Terrestrial plants support themselves with thickened cell walls, turgor pressure, and lignified xylem. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from leaves and stems, which establishes a transpiration stream that transports water and minerals through the xylem.transport in plants
transport in plantsKhadijaparekh93
╠²
The document summarizes transport systems in plants. It describes that xylem transports water and minerals up the plant and provides mechanical support, while phloem transports sugars and amino acids. Xylem cells are dead and hollow, strengthened by lignin, whereas phloem is made of living sieve tube cells that transport sugars with help from companion cells. Water moves into roots by osmosis and up the plant via root pressure, capillary action and transpiration pull through the xylem. The rate of transpiration is affected by temperature, humidity, light, wind and carbon dioxide levels.9_ Transport in Plants.ppt
9_ Transport in Plants.pptMahdAli3
╠²
The document discusses transport in plants. There are two main transport tissues in flowering plants: xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and mineral salts upwards from the roots through hollow tubes reinforced with lignin. Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids throughout the plant through sieve tubes and companion cells. Water is absorbed into the roots through osmosis and transported upwards through the plant via root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration pull. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from leaves and creates a pulling force. Various environmental factors like temperature, humidity, light intensity, and wind affect the rate of transpiration.Chapter 9 transport in plants lecture
Chapter 9 transport in plants lectureXu Jia Xian
╠²
1) Water and minerals are transported from the roots to the leaves through xylem tissue. Water enters root hair cells through osmosis and moves cell to cell through the root cortex and xylem vessels up the stem.
2) Photosynthates are transported from the leaves to the rest of the plant through phloem tissue. Phloem is made of sieve tube cells that transport sugars and amino acids.
3) Xylem and phloem are arranged in vascular bundles in stems and leaves, and alternate with each other in roots. Transpiration through the stomata of leaves creates a transpiration pull that draws water up the xylem against gravity.AS Level Biology - 7) Plant Transport
AS Level Biology - 7) Plant TransportArm Punyathorn
╠²
The document discusses plant transport systems, detailing the structure and function of various plant tissues involved in transport, including xylem and phloem. It explains the mechanisms of water and nutrient movement within plants, highlighting processes such as transpiration, osmosis, and the pathways through which water and nutrients are absorbed and distributed. Additionally, it describes adaptations that enhance efficiency in water transport and nutrient translocation in different plant types.Transportation in plant
Transportation in plantSantosh Kumar Kar
╠²
1. The document discusses the transport structures in plants, including xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards from the roots to the leaves, while phloem transports food like sugar downward from leaves to other plant parts.
2. Transpiration is the process where water evaporates from the leaves and creates a transpiration pull that draws water up the xylem. Factors like temperature, light intensity, and humidity affect the transpiration rate.
3. Capillary action and adhesion between water and xylem vessels walls helps push water upwards against gravity, along with root pressure and transpiration pull. Together these forces facilitate the movement of water through the plant.Transport in vascular_plants..
Transport in vascular_plants..Shihab Kaniyadukam
╠²
Transport in plants occurs through two main tissues: xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals up from the roots through the stem and leaves using a combination of root pressure and transpiration pull. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from leaves, which creates a negative water potential that pulls water up through the xylem vessels and tracheids. Phloem transports sugars made during photosynthesis from leaves to areas of growth or storage through pressure flow, where sugars move from high pressure source tissues to low pressure sink tissues.Transport in plant slides
Transport in plant slidesAlex Chiam
╠²
The document discusses the transport structures and processes in plants. It describes how xylem transports water and minerals upwards from the roots to the leaves, driven by transpiration pull. Phloem transports food substances manufactured in the leaves to all parts of the plant through sieve tubes and companion cells. Experiments using aphids, ringing, and radioisotopes demonstrate phloem transport.Transport in flowering plants (self created)
Transport in flowering plants (self created)Alex Chiam
╠²
This document discusses the structure and function of xylem in flowering plants. It aims to explain how water is transported from roots to leaves through vascular bundles, which contain xylem and phloem. Xylem consists of hollow tubes reinforced with lignin that transport water and minerals upwards. Water movement occurs through root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration pull. Transpiration pull is the dominant force driving water transport in tall plants, where water loss from leaves creates suction that pulls water upwards.plant anatomy and physiology notes.ppt-ŌĆ£Structure correlates to functionŌĆØ
plant anatomy and physiology notes.ppt-ŌĆ£Structure correlates to functionŌĆØnyagahwanjiru
╠²
The lecture covers plant anatomy and physiology, focusing on the structure and function of plant cells, tissues, and organs including roots, stems, and leaves. It highlights the types of plant tissues: dermal, vascular, and ground, as well as essential processes such as water and sugar transport within plants. Key concepts of plant hormones and their effects on growth and development are also introduced.Lec3_PlantAnat.ppt
Lec3_PlantAnat.pptValeriaTavares21
╠²
This document summarizes a plant anatomy and physiology lecture. It discusses plant cells, tissues and organs. It describes the three main tissue types - dermal, vascular and ground tissues. It explains the roles of xylem and phloem in transporting water and sugars respectively. Key plant organs - roots, stems and leaves - are outlined. Their structures and functions are summarized. The processes of transpiration and phloem translocation are briefly explained. The major plant hormones and their functions are also introduced.Recently uploaded (20)
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptx
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptxSourav Kr Podder
╠²
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Celebration QuizTanja Vujicic - PISA for Schools contact Info
Tanja Vujicic - PISA for Schools contact InfoEduSkills OECD
╠²
Tanja Vujicic, Senior Analyst and PISA for SchoolŌĆÖs Project Manager at the OECD spoke at the OECD webinar 'Turning insights into impact: What do early case studies reveal about the power of PISA for Schools?' on 20 June 2025
PISA for Schools is an OECD assessment that evaluates 15-year-old performance on reading, mathematics, and science. It also gathers insights into studentsŌĆÖ learning environment, engagement and well-being, offering schools valuable data that help them benchmark performance internationally and improve education outcomes. A central ambition, and ongoing challenge, has been translating these insights into meaningful actions that drives lasting school improvement. INDUCTIVE EFFECT slide for first prof pharamacy students
INDUCTIVE EFFECT slide for first prof pharamacy studentsSHABNAM FAIZ
╠²
The inductive effect is the electron-withdrawing or electron-donating effect transmitted through sigma (Žā) bonds in a molecule due to differences in electronegativity between atoms.
---
¤ö╣ Definition:
The inductive effect is the permanent shifting of electrons in a sigma bond caused by the electronegativity difference of atoms, resulting in partial charges within the molecule.How to use search fetch method in Odoo 18
How to use search fetch method in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
The search_fetch is a powerful ORM method used in Odoo for some specific addons to combine the functionality of search and read for more efficient data fetching. It might be used to search for records and fetch specific fields in a single call. It stores the result in the cache memory.Filipino 9 Maikling Kwento Ang Ama Panitikang Asiyano
Filipino 9 Maikling Kwento Ang Ama Panitikang Asiyanosumadsadjelly121997
╠²
Filipino 9 Maikling Kwento Ang Ama Panitikang AsiyanoIIT KGP Quiz Week 2024 Sports Quiz (Prelims + Finals)
IIT KGP Quiz Week 2024 Sports Quiz (Prelims + Finals)IIT Kharagpur Quiz Club
╠²
The document outlines the format for the Sports Quiz at Quiz Week 2024, covering various sports & games and requiring participants to Answer without external sources. It includes specific details about question types, scoring, and examples of quiz questions. The document emphasizes fair play and enjoyment of the quiz experience.Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: IshiguroŌĆÖs Fiction and the Rise of ŌĆ£Godi...
Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: IshiguroŌĆÖs Fiction and the Rise of ŌĆ£Godi...Rajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Dive into a captivating analysis where Kazuo IshiguroŌĆÖs nuanced fiction meets the stark realities of postŌĆæ2014 Indian journalism. Uncover how ŌĆ£Godi MediaŌĆØ turned from watchdog to lapdog, echoing the moral compromises of IshiguroŌĆÖs protagonists. WeŌĆÖll draw parallels between restrained narrative silences and sensationalist headlinesŌĆöare our media heroes or traitors? DonŌĆÖt forget to follow for more deep dives!
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 107: The Twentieth Century Literature: From World War II to the End of the Century
Submitted Date: April 4, 2025
Paper Name: The Twentieth Century Literature: From World War II to the End of the Century
Topic: From Watchdog to Lapdog: IshiguroŌĆÖs Fiction and the Rise of ŌĆ£Godi MediaŌĆØ in Post-2014 Indian Journalism
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/kIEqwzhHJ54
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/from-watchdog-to-lapdog-ishiguro-s-fiction-and-the-rise-of-godi-media-in-post-2014-indian-journalism.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#GodiMedia #Ishiguro #MediaEthics #WatchdogVsLapdog #IndianJournalism #PressFreedom #LiteraryCritique #AnArtistOfTheFloatingWorld #MediaCapture #KazuoIshiguro
Keyword Tags:
Godi Media, Ishiguro fiction, post-2014 Indian journalism, media capture, Kazuo Ishiguro analysis, watchdog to lapdog, press freedom India, media ethics, literature and media, An Artist of the Floating WorldRomanticism in Love and Sacrifice An Analysis of Oscar WildeŌĆÖs The Nightingal...
Romanticism in Love and Sacrifice An Analysis of Oscar WildeŌĆÖs The Nightingal...KaryanaTantri21
╠²
The story revolves around a college student who despairs not having a red rose as a condition for dancing with the girl he loves. The nightingale hears his complaint and offers to create the red rose at the cost of his life. He sang a love song all night with his chest stuck to the thorns of the rose tree. Finally, the red rose grew, but his sacrifice was in vain. The girl rejected the flower because it didnŌĆÖt match her outfit and preferred a jewellery gift. The student threw the flower on the street and returned to studying philosophyLDMMIA Yoga S10 Free Workshop Grad Level
LDMMIA Yoga S10 Free Workshop Grad LevelLDM & Mia eStudios
╠²
This is complete for June 17th. For the weekend of Summer Solstice
June 20th-22nd.
6/17/25: ŌĆ£My now Grads, YouŌĆÖre doing well. I applaud your efforts to continue. We all are shifting to new paradigm realities. Its rough, thereŌĆÖs good and bad days/weeks. However, Reiki with Yoga assistance, does work.ŌĆØ
6/18/25: "For those planning the Training Program Do Welcome. Happy Summer 2k25. You are not ignored and much appreciated. Our updates are ongoing and weekly since Spring. I Hope you Enjoy the Practitioner Grad Level. There's more to come. We will also be wrapping up Level One. So I can work on Levels 2 topics. Please see documents for any news updates. Also visit our websites. Every decade I release a Campus eMap. I will work on that for summer 25. We have 2 old libraries online thats open. https://ldmchapels.weebly.com "
Our Monthly Class Roster is 7,141 for 6/21.
ALL students get privacy naturally. Thx Everyone.
As a Guest Student,
You are now upgraded to Grad Level.
See Uploads for ŌĆ£Student CheckinsŌĆØ & ŌĆ£S9ŌĆØ. Thx.
Happy Summer 25.
These are also timeless.
Thank you for attending our workshops.
If you are new, do welcome.
For visual/Video style learning see our practitioner student status.
This is listed under our new training program. Updates ongoing levels 1-3 this summer. We just started Session 1 for level 1.
These are optional programs. I also would like to redo our library ebooks about Hatha and Money Yoga. THe Money Yoga was very much energy healing without the Reiki Method. An updated ebook/course will be done this year. These Projects are for *all fans, followers, teams, and Readers. TY for being presenting.List View Components in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs
List View Components in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In Odoo, there are many types of views possible like List view, Kanban view, Calendar view, Pivot view, Search view, etc.
The major change that introduced in the Odoo 18 technical part in creating views is the tag <tree> got replaced with the <list> for creating list views. Sustainable Innovation with Immersive Learning
Sustainable Innovation with Immersive LearningLeonel Morgado
╠²
Prof. Leonel and Prof. Dennis approached educational uses, practices, and strategies of using immersion as a lens to interpret, design, and planning educational activities in a sustainable way. Rather than one-off gimmicks, the intent is to enable instructors (and institutions) to be able to include them in their regular activities, including the ability to evaluate and redesign them.
Immersion as a phenomenon enables interpreting pedagogical activities in a learning-agnostic way: you take a stance on the learning theory to follow, and leverage immersion to envision and guide your practice.Intellectual Property Right (Jurisprudence).pptx
Intellectual Property Right (Jurisprudence).pptxVishal Chanalia
╠²
Intellectual property corresponds to ideas owned by a person or a firm and thus subjected to legal protection under the law.
The main purpose of intellectual property is to give encouragement to the innovators of new concepts by giving them the opportunity to make sufficient profits from their inventions and recover their manufacturing costs and efforts. University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students SanctionedKweku Zurek
╠²
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
How to Customize Quotation Layouts in Odoo 18
How to Customize Quotation Layouts in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
Customizing quotation layouts in Odoo 18 allows businesses to personalize their quotations to match branding or specific requirements. This can include adding logos, custom fields, or modifying headers and footers. Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. In this slide try to present the brief history of Chaulukyas of Gujrat up to Kumarpala To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
Chaulukya or Solanki was one of the Rajputs born from Agnikul. In the Vadnagar inscription, the origin of this dynasty is told from Brahma's Chauluk or Kamandalu. They ruled in Gujarat from the latter half of the tenth century to the beginning of the thirteenth century. Their capital was in Anahilwad. It is not certain whether it had any relation with the Chalukya dynasty of the south or not. It is worth mentioning that the name of the dynasty of the south was 'Chaluky' while the dynasty of Gujarat has been called 'Chaulukya'. The rulers of this dynasty were the supporters and patrons of Jainism.Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02Mauricio Alexandre Silva
╠²
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
F-BLOCK ELEMENTS POWER POINT PRESENTATIONS
F-BLOCK ELEMENTS POWER POINT PRESENTATIONSmprpgcwa2024
╠²
F-block elements are a group of elements in the periodic table that have partially filled f-orbitals. They are also known as inner transition elements. F-block elements are divided into two series:
1.Lanthanides (La- Lu) These elements are also known as rare earth elements.
2.Actinides (Ac- Lr): These elements are radioactive and have complex electronic configurations.
F-block elements exhibit multiple oxidation states due to the availability of f-orbitals.
2. Many f-block compounds are colored due to f-f transitions.
3. F-block elements often exhibit paramagnetic or ferromagnetic behavior.4. Actinides are radioactive.
F-block elements are used as catalysts in various industrial processes.
Actinides are used in nuclear reactors and nuclear medicine.
F-block elements are used in lasers and phosphors due to their luminescent properties.
F-block elements have unique electronic and magnetic properties.K12 Tableau User Group virtual event June 18, 2025
K12 Tableau User Group virtual event June 18, 2025dogden2
╠²
National K12 Tableau User Group: June 2025 meeting slidesThis is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...Kweku Zurek
╠²
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Service PIN codes (LIST)Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: IshiguroŌĆÖs Fiction and the Rise of ŌĆ£Godi...
Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: IshiguroŌĆÖs Fiction and the Rise of ŌĆ£Godi...Rajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
Ad
Transport systems in plants.pptx
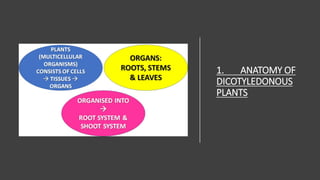
- 1. UNIT 5: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS
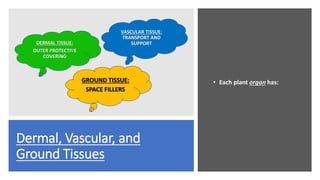
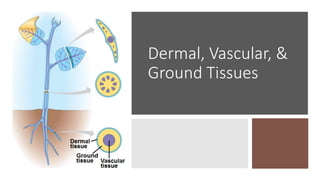
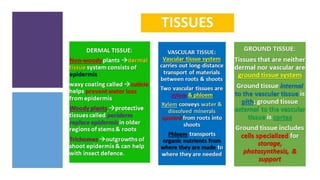
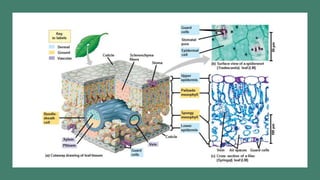
- 4. Dermal, Vascular, and Ground Tissues ŌĆó Each plant organ has: DERMAL TISSUE: OUTER PROTECTIVE COVERING VASCULAR TISSUE: TRANSPORT AND SUPPORT GROUND TISSUE: SPACE FILLERS
- 5. Dermal, Vascular, & Ground Tissues
- 7. Dermal tissue Non-woody plants ’āĀdermal tissue system consists of epidermis ŌĆó waxy coating called ’āĀcuticle helps prevent water loss from epidermis Woody plants ’āĀprotective tissues called periderm replace epidermis in older regions of stems & roots ŌĆó Trichomes ’āĀoutgrowths of shoot epidermis & can help with insect defence.
- 8. Vascular Tissues Vascular tissue system carries out long-distance transport of materials between roots & shoots Two vascular tissues are xylem & phloem Xylem conveys water & dissolved minerals upward from roots into shoots Phloem transports organic nutrients from where they are made to where they are needed
- 9. Ground Tissues Tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular are ground tissue system Ground tissue internal to the vascular tissue is pith; ground tissue external to the vascular tissue is cortex Ground tissue includes cells specialized for storage, photosynthesis, & support
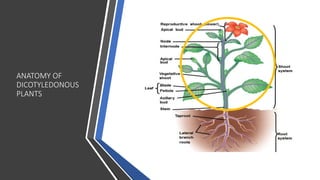
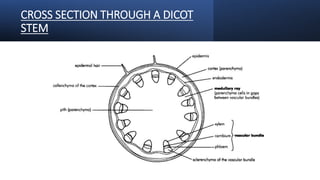
- 11. CROSS SECTION THROUGH A DICOT STEM
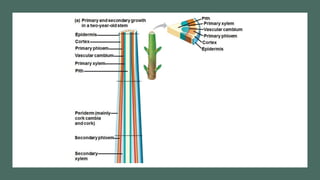
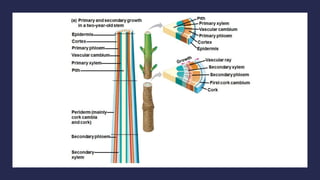
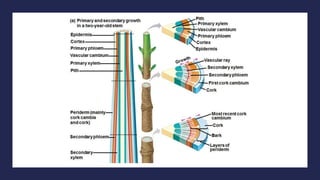
- 14. 2. SECONDARY GROWTH Secondary growth occurs in stems & roots of woody plants ’āĀ rarely in leaves Secondary plant body consists of tissues produced by vascular cambium & cork cambium
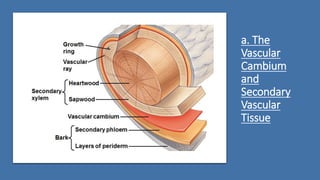
- 18. a. The Vascular Cambium and Secondary Vascular Tissue The vascular cambium is cylinder of meristematic cells 1 cell layer thick ŌĆó develops from undifferentiated parenchyma cells Secondary xylem accumulates as wood (consists of tracheids, vessel elements & fibers. ŌĆó Early wood ’āĀ formed in spring ’āĀ has thin cell walls to maximize water delivery. ŌĆó Late wood ’āĀ formed in late summer ’āĀ has thick-walled cells & contributes more to stem support.
- 19. Tree rings ’āĀ visible where late & early wood meet ’āĀ can be used to estimate a treeŌĆÖs age Dendrochronology ’āĀ analysis of tree ring growth patterns ’āĀ can be used to study past climate change. As a tree or woody shrub ages ’āĀ older layers of secondary xylem (heartwood) ’āĀ no longer transport water & minerals. Outer layers (sapwood) ’āĀ still transport materials through xylem.
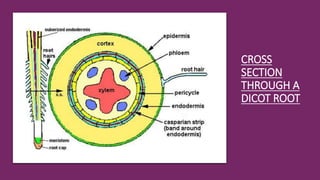
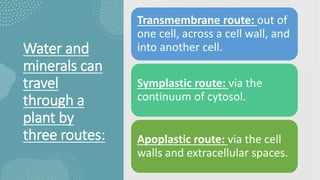
- 21. 3. UPTAKE OF WATER AND MINERALS INTO THE ROOTS The plasma membrane directly controls the traffic of molecules into and out of the cell. In most plant tissues, the cell wall and cytosol are continuous from cell to cell. The cytoplasmic continuum is called the symplast. The cytoplasm of neighbouring cells is connected by channels called plasmodesmata. The apoplast is the continuum of cell walls and extracellular spaces.
- 22. Water and minerals can travel through a plant by three routes: Transmembrane route: out of one cell, across a cell wall, and into another cell. Symplastic route: via the continuum of cytosol. Apoplastic route: via the cell walls and extracellular spaces.
- 23. Water and minerals can travel through a plant by three routes:
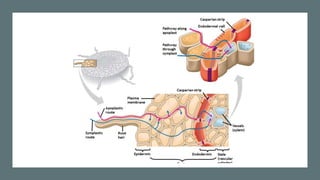
- 24. Pathway 1: Transmembrane route Water and minerals move from soil (high WP) through cell wall, plasmamembra ne & into cytoplasm of roothair. 01 Through cell wall, plasma membrane & into cytoplasm of cortex cells. 02 Through cell wall, plasma membrane & into cytoplasm of endodermis 03 Through cell wall, plasma membrane & into cytoplasm of pericycle. 04 Through cell wall, plasma membrane & into xylem of plant. 05
- 26. Pathway 2: symplastic route Water and minerals flow from high WP in soil, through cell wall, plasma membrane & into cytoplasm of roothair. Through plasmodesmata linking cytoplasm of cells into cytoplasm of the cortex cells. Flowing through plasmodesmata into cytoplasm of endodermis cells & pericycle & into xylem.
- 27. Pathway 3: Apoplastic route During Apoplastic route water & minerals travel along cell walls of roothairs, cortical cells, and endodermis, Endodermis has Casparian strips that prevent further movement of water, therefore water enter cytoplasm of endodermal cells and then take: symplastic route (through cytoplasm & plasmodesmata that link cytoplasm of cells) into xylem of root.
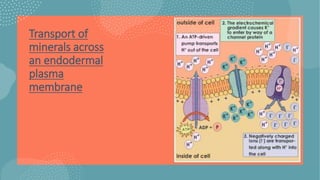
- 29. Transport of minerals across an endodermal plasma membrane Minerals follow same routes as water when it moves through roothair & cortex cells. But when it moves through the endodermal plasma membrane it does it in the following way: ŌĆó An ATP driven pump removes hydrogen ions from cell. ŌĆó This establishes an electrochemical gradient that allows potassium ions & other positively charged ions to cross the membrane via a channel protein. ŌĆó Negatively charged mineral ions can cross the membrane by bonding to a carrier (hydrogen ions) which are diffusing down their concentration gradient.
- 30. CELLS THROUGH WHICH WATER MOVE ROOTHAIR. CORTEX CELLS. ENDODERMIS PERICYCLE. XYLEM ATP driven pump
- 31. Transport of minerals across an endodermal plasma membrane
- 32. 3. TRANSPORT OF WATER AND MINERALS TO THE LEAVES ŌĆó What makes upward movement of water in xylem of stems & leaves possible? ’āś Root pressure ’āś Cohesion-adhesion-tension ’āś Transpiration
- 33. I) Root pressure ŌĆó Water entering root cells creates positive pressure called root pressure. ŌĆó It occurs at night & push xylem sap upwards.
- 34. II) Cohesion- adhesion- tension model Upward movement of water requiring no energy. Cohesion- Tendency of water molecules cling together & form continuous water column. Adhesion- Tendency of water molecules to cling to the sides of the container (xylem) they are in. It gives water column extra strength & prevents it from slipping back
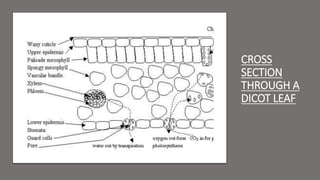
- 35. III) Transpiration Transpiration is loss of water vapour through stomata of leaf. Water molecules that evaporate from cells into intercellular airspaces are replaced by other water molecules from leaf xylem. Because water molecules are cohesive, transpiration exerts a pulling force / tension, that draws water column through xylem to replace water lost by stomata. ŌĆó This is also a mechanism by which minerals are transported throughout plant body.
- 36. Environmental factors that influence the speed of transpiration High temperature ŌĆō faster transpiration High light intensity ŌĆō faster transpiration Windy ŌĆō faster transpiration High humidity ŌĆō slower transpiration
- 37. What is guttation and what causes it? ’ü▒ Root pressure is responsible for guttation. ’ü▒ Guttation is when drops of water are forced out of the vein endings along the edges of leaves called hydathodes.
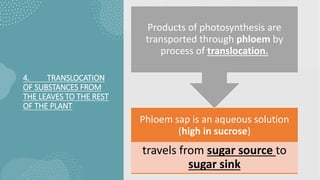
- 38. 4. TRANSLOCATION OF SUBSTANCES FROM THE LEAVES TO THE REST OF THE PLANT Phloem sap is an aqueous solution (high in sucrose) travels from sugar source to sugar sink Products of photosynthesis are transported through phloem by process of translocation.
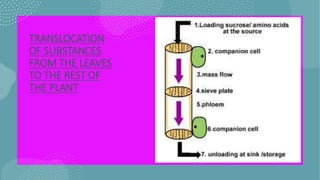
- 39. ŌĆó Sugar source (organ producing sugar (mature leaves) Sugar ŌĆó Sugar sink (organ that stores sugar (net consumer ) Sugar ŌĆó Sugar loaded into sieve-tube elements of phloem. ŌĆó Sugar moves by symplastic or both (symplastic and apoplastic) pathways. Sugar ŌĆó At the sink, sugar molecules diffuse from phloem to sink tissues & are followed by water. Sugar
- 40. TRANSLOCATION OF SUBSTANCES FROM THE LEAVES TO THE REST OF THE PLANT
