Treating Obesity: The Way Forward
- 8. The Common Ground Approach Impact of MODEST weight loss on obesity-related comorbidi%es (% weight loss associated with improvement of di’¼Ćerent condi0ons) Weight loss and Obesity Related Comorbidi0es 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Metabolic syndrome Pre-diabetes T2 diabetes Hypertension NAFLD OSA Asthma Urinary incon0nence Weight loss rela0ve to baseline Garvey et al. End Prac:ce 2016
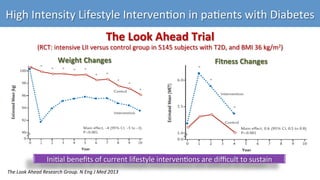
- 13. The Look Ahead Trial (RCT: intensive LII versus control group in 5145 subjects with T2D, and BMI 36 kg/m2) High Intensity Lifestyle Interven0on in pa0ents with Diabetes Post-hoc analysis based on the achievement of >10% WL irrespec%ve of the study group The Look Ahead Research Group. Lancet 2016 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 <2% loss 2-5% loss 5-10% loss >10% loss p=0.034 Adjusted Hazard ra%o (95% CI) Incidence of CVD at 10 y Weight Loss Category at 1 y follow up 1.00 1.08 1.16 0.79 0 10 20 30 40 50 <2% WL 2-5% WL 5-10% WL > 10% WL Distribu%on of WL categories % ILI 18% 47% 75% 92% % cont 82% 53% 25% 8% ŌĆóŌĆ» Posi0ve impact of WL on CVD, if >10% WL is achieved ŌĆóŌĆ» Importance of iden0fying responders and factors associated with Ōåæ likelihood of >10% WL
- 17. Sjostrom L, J Int Med 2013 Swedish Obese Subjects Study Control, n=2037; Bariatric Surgery, n= 2010 (>10 years follow up) 1.ŌĆ» Major and sustained weight loss compared to conven0onal treatment 2.ŌĆ» Reduc0on of all cause mortality 3.ŌĆ» Reduc0on of cardiovascular mortality and incidence of 1st CV event (fatal or no fatal) 4.ŌĆ» Preven0on and remission of diabetes 5.ŌĆ» Reduc0on of the incidence of myocardial infarc%on in subjects with T2D 6.ŌĆ» Reduc0on of obesity-related cancer incidence and mortality (in women) 7.ŌĆ» Improved quality of life 8.ŌĆ» Reduc0on of health costs (up to 20 years follow up) Health Bene’¼üts Associated with Bariatric Surgery
- 19. Summary ŌĆóŌĆ» Tackling the obesity epidemics requires ac0on beyond preven0on ŌĆóŌĆ» Trea0ng obesity is an e’¼Ćec0ve means to improve obesity-related comorbidi0es ŌĆóŌĆ» E’¼Ćorts should be made to make e’¼Ćec0ve therapies available to obese subjects with obesity-related comorbidi0es ŌĆōŌĆ» Although high-intensity lifestyle interven0ons are e’¼Ćec0ve, research is needed to beler uon how make these interven0ons feasible ŌĆōŌĆ» More research is needed to substan0ate the bene’¼üts of drug-assissted weight loss ŌĆōŌĆ» E’¼Ćorts should be made to make bariatric surgery to eligible pa0ents