Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy.pptx
- 1. TREATMENT OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY By Dr. Golam Mortuza
- 2. Management of Diabetes Drugs for DM: ŌĆó Oral hypoglycaemic drugs ŌĆó Insulin injections Other cares: ŌĆó Diet and Exercise ŌĆó Risk reduction: Rx of Hypertension and Hyperlipidemia ŌĆó R/O Anaemia and Renal failure ŌĆó Quit smoking and tobacco in any form
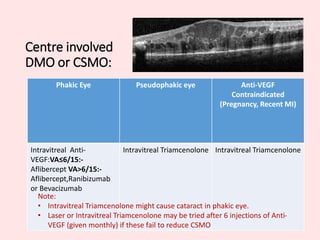
- 3. Centre involved DMO or CSMO: Phakic Eye Pseudophakic eye Anti-VEGF Contraindicated (Pregnancy, Recent MI) Intravitreal Anti- VEGF:VAŌēż6/15:- Aflibercept VA>6/15:- Aflibercept,Ranibizumab or Bevacizumab Intravitreal Triamcenolone Intravitreal Triamcenolone Note: ŌĆó Intravitreal Triamcenolone might cause cataract in phakic eye. ŌĆó Laser or Intravitreal Triamcenolone may be tried after 6 injections of Anti- VEGF (given monthly) if these fail to reduce CSMO
- 4. Off Centre DMO (outside 500╬╝ from foveola): Focal or Grid laser Note: ŌĆó Intravitreal Anti-VEGF or Triamcinolone may be tried if it fails to reduce oedema
- 5. DMO with PDR: Inj Ranibizumab or Aflibercept followed by PRP. Note: PRP is done in 2-3 sittings to get rid of exerbation of macular oedema.
- 6. PDR without DMO: PRP in 2-3 sittings Note: Alternatively Inj Ranibizumab or Aflibercept may be given. Inj Bevacizumab is not that effective.
- 7. Indications of Surgery in Diabetic Retinopaty: ŌĆó Resistant cases, particularly if VMT or ERM is present ŌĆóADED