trends.pptx
- 1. FRAMEWORK, SCOPE AND TRENDS IN NURSING PRACTICE
- 2. Trends in nursing practice
- 3. Trends in nursing practice âĒ Trends in nursing are closely tied to what is happening to healthcare in general. âĒ Trends are fascinating phenomena, but they do not exist in vacuums. âĒ Most are interrelated; one trend often spawns another.
- 4. Broadening Focus: âĒ The focus of nursing has broadened from the care of the ill person to the care of the people in illness and from care of only the patient to care of the client, the family, and in some instance the community. âĒ In the past, nursing, like medicine was oriented towards disease and illness.
- 5. Scientific basis: âĒ In the past nursing largely was either intuitive or relied on experience or observation rather than on research. âĒ Through trail and error the individual nurses discovered with measures would assist the client and many nurses became highly skilled in providing care through experience.
- 6. Technology: âĒ Technology or mechanization is being applied in the health field extensively. âĒ Certain areas of a hospital are more technologic than others. âĒ Nurses find themselves in the midst of this rapidly changing, increasingly technologic environment in hospital and in clientâs homes.
- 7. Expansion of employment opportunities: âĒ Nursing practice trends include a growing variety of employment setting in which nurses have greater independence, autonomy, and respect as member of the health care team. âĒ Nursing roles continue to expand and develop, broadening the focus of nursing care and providing a more holistic and all- encompassing domain
- 8. Nursingâs public perception: âĒ Any member of society who has been ill, hospitalized or visited an emergency department has experienced nursing campaign noted âeverybody needs a nurse.
- 9. Nursingâs impact on politics and health policy: âĒ The ability to influence or persuade an individual holding a government office to exert the power of that office to affect a decide outcome is known as political power or influence.
- 10. Globalization of Health âĒ Healthcare has become a global issue âĒ People are mobile, diseases can travel âĒ Nurses need to have an understanding of the issues pertaining to global health
- 11. Nursing Roles âĒ Caregiver âĒ Clinical Decision Maker âĒ Client Advocate âĒ Rehabilitator âĒ Comforter âĒ Communicator âĒ Collaborator âĒ Teacher
- 12. Modern nursing trends 1. Case method: This is the oldest models of nursing care delivery where one nurse provided all the care needed by a particular client.
- 13. Functional Nursing: âĒ It is a task oriented model where distinct duties are assigned to specific personnel for e.g. one takes all the vital signs and other does all the dressing and so on. âĒ Tasks are divided and client sees several people during the shift.
- 14. Team nursing: âĒ It emerged to accommodate the staff with varying level of education and skill.
- 15. Total care: âĒ It refers to assignments in which a nurse assumes all the care for small group of clients. This method focuses more on the client as whole
- 16. Primary nursing: âĒ Here an RN assumes 24 hrs accountability for the client care and for the nursing care of assigned client during his or her shift.
- 17. Patient focused care: âĒ An updated version of team nursing and primary care is called patient focused care where an RN is partnered with one or more assistive personnel to take care of a group of clients. âĒ The RN may work with an assistant, respiratory therapist.
- 18. Ambulatory care centres: âĒ Some office settings have broadened to include diagnostic and treatment facilities such as laboratory, radiology service, sometimes surgery. âĒ They are often operated by large health care systems such as corporation who has hospital and other facilities.
- 19. Nursing informatics: âĒ It is a nursing speciality integrating nursing science, computer science, information science in identifying, collecting, processing and managing data and information to support nursing administration, research and expansion of knowledge.
- 20. Standardized nursing terminologies: âĒ The demand of current health care systems is challenging the nursing profession to define its practice and the impact it has on the health and the health care of an individualâs families and communities. âĒ Nursing has moved towards standardizing nursing terminology. It is used to clearly define and evaluate nursing care.
- 21. Evidence based practice : âĒ Nurses are faced with the challenge of providing safe, effective care. One way to achieve this goal is to provide evidence based practise.
- 22. Hospice services: âĒ Hospice means shelter for those on a difficult journey. âĒ These services occur in clients home or in special facilities to the terminally ill.
- 23. Summary âĒ Trends in Nursing practice
- 24. Article âĒ Stevens, K., (May 31, 2013) "The Impact of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing and the Next Big Ideas" OJIN: The Online Journal of Issues in Nursing Vol. 18, No. 2, Manuscript 4. DOI: 10.3912/OJIN.Vol18No02Man04
- 25. Introduction âĒ The impact of evidence-based practice (EBP) has echoed across nursing practice, education, and science. âĒ EBP is aimed at hardwiring current knowledge into common care decisions to improve care processes and patient outcomes. âĒ This article briefly describes the EBP movement and considers some of the impact of EBP on nursing practice, models and frameworks, education, and research.
- 26. Impact on Nursing Practice âĒ EBP to be successfully adopted and sustained, nurses and other healthcare professionals recognized that it must be adopted. âĒ Federal, state, local, and other regulatory and recognition actions are necessary for EBP adoption. âĒ Sophisticated implementation plan is required before the evidence-based intervention is adopted across an institution.
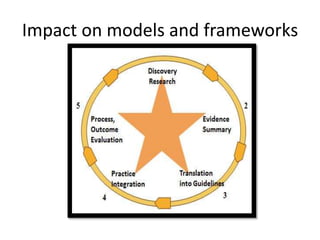
- 27. Impact on models and frameworks
- 28. Impact on Nursing Education âĒ Education for all health professions were in need of âa major overhaulâ to prepare health professions with new skills to assume new roles âĒ Current educational programs do not adequately prepare nurses, physicians, pharmacists or other health professionals. âĒ All health professionals should be educated to deliver patient-centered care as members of an interdisciplinary team emphasizing evidence- based practice, quality improvement approaches, and informatics
- 29. âĒ Impact on Nursing Research âĒ The Next Big Ideas- Dissemination & Implementation (D&I) Grants, Improvement Science Research Network
- 30. CONCLUSION: âĒ Transition generally occurs or takes place in each and every individual of this world. âĒ Nurses as an individual, involved in caring profession, also faces this transition âĒ Some ways to Prepare for transition process are: â Positing thinking, flexible to adjust in various situations, organized personal life, practice healthy life style, find an ideal mentor, have some fun and able to know what is expected to learn to rules of road early.