Trickling filters ppt.
- 1. -MUTTU M S RAMAIAH INSTITUTE OF TECHONLOGY
- 2. ’üĮ There are 3 major biological treatment techniques: 1. Attached growth process(Fixed film process). 2. Suspended growth process. 3. Combined process.
- 3. ’üĮ In this process micro organisms are responsible for conversion of organic matter present in waste water to gases and cell tissues are attached to some inert medium such as rock, slag, ceramic or plastic material. ’üĮ This process include: 1.Intermittent sand filters 2.Trickling filters 3.Rotating biological contactors 4.Packed bed reactors 5.Anaerobic lagoons. 6.Fixed film denitrification.
- 4. ’üĮ In this process micro organisms are responsible for conversion of organic matter present in waste water to gases and cell tissues are maintained in suspension within the liquid in the reactor by employing either natural or mechanical mixing. ’üĮ This process include: 1.Activated sludge process. 2.Aerated lagoons. 3.Sludge digestion system. 4.Suspended growth nitrification & denitrification
- 5. ’üĮ This process includes both attached growth and suspended growth process. ’üĮ This process include : 1.Trickling filter, activated sludge. 2.Activated sludge, trickling filter. 3.Faculative lagoons.
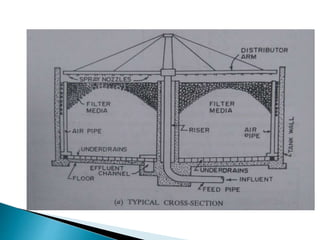
- 6. CONSTRUCTION: It consist of mainly four parts: 1.water tight holding tank. 2.Distribution system. 3.Filter media. 4.Underdrainage system.
- 8. ’āś The tank is either rectangular or square if fixed nozzles are used and circular in shape if rotary distributors are used. ’āś As rotary distributors are more reliable & easy to maintain and operate. So circular shape is most commonly used. ’āś The walls are either masonry or concrete walls ’āś The walls are constructed such that they should withstand the pressure exerted by sewage from inside. ’āś The walls are made water tight.
- 9. ’āś The under drain system is supported by a floor which slopes to a collection channel. ’āś It also consists a filter media which should have high specific surface area, high percent void space, resistance to abrasion & insoluble in sewage water.
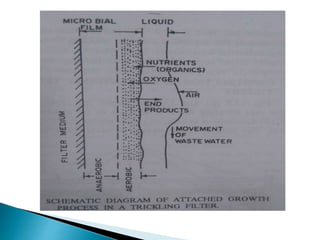
- 10. ’üĮ The sewage is allowed to sprinkle over filter media through nozzles or rotary distributors. ’üĮ The biological purification is mainly done by aerobic bacteria which form a bacterial film known as biofilm or slime layer around filter media. ’üĮ This biofilm layer is aerobic only upto a depth of 0.1 to 0.2mm and remaining part is anaerobic. ’üĮ The organic matter is degraded by aerobic micro organisms on the outer portion of biofilm.
- 11. ’üĮ The food concentration is high at the outer surface of biofilm hence the growth of micro organisms is more at the outer surface of the biofilm. ’üĮ The most diffused oxygen is consumed by micro organism at the outer surface before it reaches to the depth. Hence the anaerobic environment is developed near the inner surface of the biofilm.
- 13. ’üĮ Eventually there is scouring of slime layer due to flowing liquid and fresh slime layer begins to grow on the media. ’üĮ This phenomenon of scouring of slime is called sloughing or unloading of the filter. ’üĮ The trickling filter is always preceded by primary sedimentation with skimming devices to remove the scum. ’üĮ The effluent from the filter is then taken to secondary sedimentation tanks for settling out organic solids oxidised while passing through filter.