Trigonometry
- 1. A mathematics PowerPoint by Eric Zhao
- 2. Trigonometry is the study and solution of Triangles. Solving a triangle means finding the value of each of its sides and angles. The following terminology and tactics will be important in the solving of triangles. Pythagorean Theorem (a2 +b2 =c2 ). Only for right angle triangles Sine (sin), Cosecant (csc or sin-1 ) Cosine (cos), Secant (sec or cos-1 ) Tangent (tan), Cotangent (cot or tan-1 ) Right/Oblique triangle
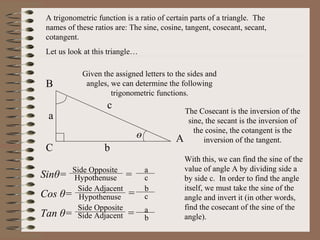
- 4. A trigonometric function is a ratio of certain parts of a triangle. The names of these ratios are: The sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, cotangent. Let us look at this triangleŌĆ” a c b ė® A B C Given the assigned letters to the sides and angles, we can determine the following trigonometric functions. The Cosecant is the inversion of the sine, the secant is the inversion of the cosine, the cotangent is the inversion of the tangent. With this, we can find the sine of the value of angle A by dividing side a by side c. In order to find the angle itself, we must take the sine of the angle and invert it (in other words, find the cosecant of the sine of the angle). Sin╬Ė= Cos ╬Ė= Tan ╬Ė= Side Opposite Side Adjacent Side Adjacent Side Opposite Hypothenuse Hypothenuse = = = a b c a b c
- 5. Try finding the angles of the following triangle from the side lengths using the trigonometric ratios from the previous slide. 6 10 8 ╬Ė A B C ╬▒ ╬▓ Click for the AnswerŌĆ” The first step is to use the trigonometric functions on angle A. Sin ╬Ė =6/10 Sin ╬Ė =0.6 Csc0.6~36.9 Angle A~36.9 Because all angles add up to 180, B=90-11.537=53.1 C 2 34┬║ A B ╬▒ ╬▓ The measurements have changed. Find side BA and side AC Sin34=2/BA 0.559=2/BA 0.559BA=2 BA=2/0.559 BA~3.578 The Pythagorean theorem when used in this triangle states thatŌĆ” BC2 +AC2 =AB2 AC2 =AB2 -BC2 AC2 =12.802-4=8.802 AC=8.8020.5 ~3
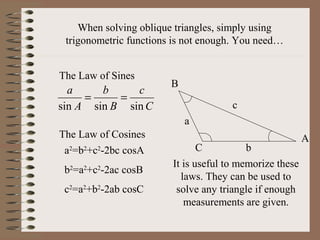
- 7. When solving oblique triangles, simply using trigonometric functions is not enough. You needŌĆ” The Law of Sines C c B b A a sinsinsin == The Law of Cosines a2 =b2 +c2 -2bc cosA b2 =a2 +c2 -2ac cosB c2 =a2 +b2 -2ab cosC It is useful to memorize these laws. They can be used to solve any triangle if enough measurements are given. a c b A B C
- 8. When solving a triangle, you must remember to choose the correct law to solve it with. Whenever possible, the law of sines should be used. Remember that at least one angle measurement must be given in order to use the law of sines. The law of cosines in much more difficult and time consuming method than the law of sines and is harder to memorize. This law, however, is the only way to solve a triangle in which all sides but no angles are given. Only triangles with all sides, an angle and two sides, or a side and two angles given can be solved.
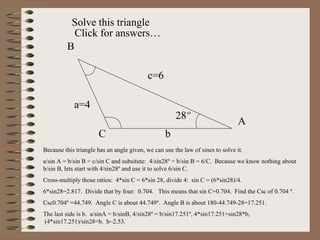
- 9. a=4 c=6 b A B C 28┬║ Solve this triangle Click for answersŌĆ” Because this triangle has an angle given, we can use the law of sines to solve it. a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C and subsitute: 4/sin28┬║ = b/sin B = 6/C. Because we know nothing about b/sin B, lets start with 4/sin28┬║ and use it to solve 6/sin C. Cross-multiply those ratios: 4*sin C = 6*sin 28, divide 4: sin C = (6*sin28)/4. 6*sin28=2.817. Divide that by four: 0.704. This means that sin C=0.704. Find the Csc of 0.704 ┬║. Csc0.704┬║ =44.749. Angle C is about 44.749┬║. Angle B is about 180-44.749-28=17.251. The last side is b. a/sinA = b/sinB, 4/sin28┬║ = b/sin17.251┬║, 4*sin17.251=sin28*b, (4*sin17.251)/sin28=b. b~2.53.
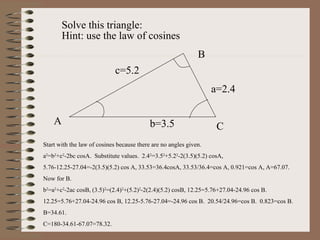
- 10. a=2.4 c=5.2 b=3.5A B C Solve this triangle: Hint: use the law of cosines Start with the law of cosines because there are no angles given. a2 =b2 +c2 -2bc cosA. Substitute values. 2.42 =3.52 +5.22 -2(3.5)(5.2) cosA, 5.76-12.25-27.04=-2(3.5)(5.2) cos A, 33.53=36.4cosA, 33.53/36.4=cos A, 0.921=cos A, A=67.07. Now for B. b2 =a2 +c2 -2ac cosB, (3.5)2 =(2.4)2 +(5.2)2 -2(2.4)(5.2) cosB, 12.25=5.76+27.04-24.96 cos B. 12.25=5.76+27.04-24.96 cos B, 12.25-5.76-27.04=-24.96 cos B. 20.54/24.96=cos B. 0.823=cos B. B=34.61. C=180-34.61-67.07=78.32.
- 12. Trigonometric identities are ratios and relationships between certain trigonometric functions. In the following few slides, you will learn about different trigonometric identities that take place in each trigonometric function.
- 13. What is the sine of 60┬║? 0.866. What is the cosine of 30┬║? 0.866. If you look at the name of cosine, you can actually see that it is the cofunction of the sine (co-sine). The cotangent is the cofunction of the tangent (co-tangent), and the cosecant is the cofunction of the secant (co-secant). Sine60┬║=Cosine30┬║ Secant60┬║=Cosecant30┬║ tangent30┬║=cotangent60┬║
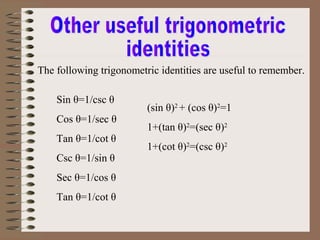
- 14. Sin ╬Ė=1/csc ╬Ė Cos ╬Ė=1/sec ╬Ė Tan ╬Ė=1/cot ╬Ė Csc ╬Ė=1/sin ╬Ė Sec ╬Ė=1/cos ╬Ė Tan ╬Ė=1/cot ╬Ė The following trigonometric identities are useful to remember. (sin ╬Ė)2 + (cos ╬Ė)2 =1 1+(tan ╬Ė)2 =(sec ╬Ė)2 1+(cot ╬Ė)2 =(csc ╬Ė)2
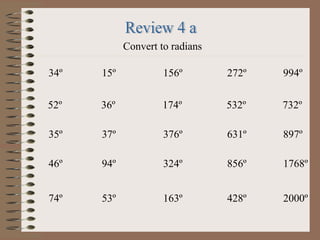
- 16. Degrees and pi radians are two methods of showing trigonometric info. To convert between them, use the following equation. 2ŽĆ radians = 360 degrees 1ŽĆ radians= 180 degrees Convert 500 degrees into radians. 2ŽĆ radians = 360 degrees, 1 degree = 1ŽĆ radians/180, 500 degrees = ŽĆ radians/180 * 500 500 degrees = 25ŽĆ radians/9
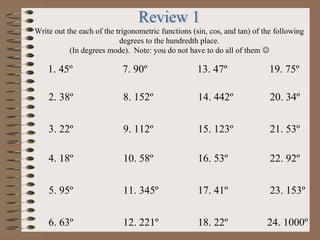
- 18. Write out the each of the trigonometric functions (sin, cos, and tan) of the following degrees to the hundredth place. (In degrees mode). Note: you do not have to do all of them ’üŖ 1. 45┬║ 2. 38┬║ 3. 22┬║ 4. 18┬║ 5. 95┬║ 6. 63┬║ 7. 90┬║ 8. 152┬║ 9. 112┬║ 10. 58┬║ 11. 345┬║ 12. 221┬║ 13. 47┬║ 14. 442┬║ 15. 123┬║ 16. 53┬║ 17. 41┬║ 18. 22┬║ 19. 75┬║ 20. 34┬║ 21. 53┬║ 22. 92┬║ 23. 153┬║ 24. 1000┬║
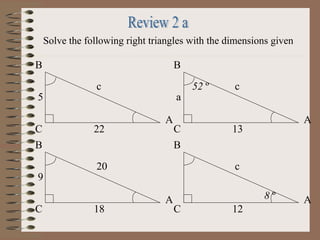
- 19. Solve the following right triangles with the dimensions given 5 c 22 A B C 9 20 18 A B C A a c 13 B C 52 ┬║ c 12 8 ┬║ A B C
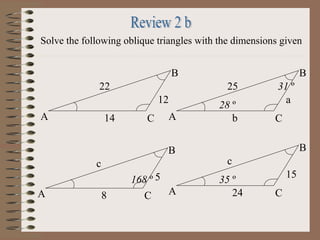
- 20. Solve the following oblique triangles with the dimensions given 12 22 14A B C a 25 b 28 ┬║ A B C 31 ┬║ 15 c 24 35 ┬║ A B C 5 c 8A B C 168 ┬║
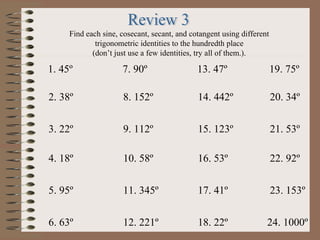
- 21. 1. 45┬║ 2. 38┬║ 3. 22┬║ 4. 18┬║ 5. 95┬║ 6. 63┬║ 7. 90┬║ 8. 152┬║ 9. 112┬║ 10. 58┬║ 11. 345┬║ 12. 221┬║ 13. 47┬║ 14. 442┬║ 15. 123┬║ 16. 53┬║ 17. 41┬║ 18. 22┬║ 19. 75┬║ 20. 34┬║ 21. 53┬║ 22. 92┬║ 23. 153┬║ 24. 1000┬║ Find each sine, cosecant, secant, and cotangent using different trigonometric identities to the hundredth place (donŌĆÖt just use a few identities, try all of them.).
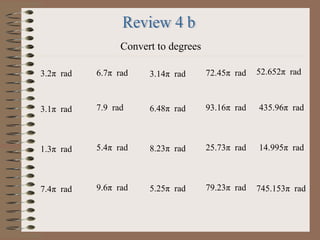
- 23. Convert to degrees 3.2ŽĆ rad 3.1ŽĆ rad 1.3ŽĆ rad 7.4ŽĆ rad 6.7ŽĆ rad 7.9 rad 5.4ŽĆ rad 9.6ŽĆ rad 3.14ŽĆ rad 6.48ŽĆ rad 8.23ŽĆ rad 5.25ŽĆ rad 72.45ŽĆ rad 93.16ŽĆ rad 25.73ŽĆ rad 79.23ŽĆ rad 52.652ŽĆ rad 435.96ŽĆ rad 14.995ŽĆ rad 745.153ŽĆ rad
- 24. Creator Eric Zhao Director Eric Zhao Producer Eric Zhao Author Eric ZhaoMathPower Nine, chapter 6Basic Mathematics Second edition By Haym Kruglak, John T. Moore, Ramon Mata-Toledo