TRX Suspension Trainer
- 1. TRX Force Tactical Kit www.prosuspensiontrainer. com
- 2. Thioredoxin ïĒ protein essential for life in mammals ïĒ acts as an antioxidant to prevent oxidative stress ïĒ acts as an electron donor in a variety of cellular reactions ïĒ restores oxidatively inactivated enzymes to their reduced & active state ïĒ www.prosuspensiontrainer.com
- 3. Thioredoxin exists in either the reduced or oxidized form Trx H S H S Reduced Thioredoxin Oxidized Thioredoxin LEGEND SH = thiol S-S = disulfide Trx S S
- 4. Thioredoxin participates in dithiol- disulfide exchange reactions H S S S S S H S H S RNR oxidized RNR reduced reduced Trx oxidized Trx H S
- 5. Trx thioredoxin S H S H Trx S S ribonucleotide reductase S H S H RNR S S thioredoxin reductase RNRNADPH NADP+ Thioredoxin reductase & thioredoxin www.prosuspensiontrainer.com
- 6. Hypothesis ïĒ Thioredoxin reductase is a major determinant of thioredoxin redox state ïĒ If true, then deletion of thioredoxin reductase should shift the redox state of thioredoxin from primarily reduced to primarily oxidized ïĒ www.prosuspensiontrainer.com
- 7. SH IAA DTT IAM Protein electrophoretic mobility shift assay (PEMSA) Iodoacetic acid Dithiothreitol Iodoacetamide LEGEND SH = thiol = Thioredoxin A- = negative charge M = neutral state = Disulfide S S acetone wash SH SH SH S S SH SH SH SH SH SH SA- SA- SA- SA- S S SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SH SH SA- SA- SA- SA- SM SM SA- TRX ox TRX ox TRX ox TRX ox TRX red TRX red TRX red TRX red
- 8. Trx red SH SH SH SH SH SH Trx ox SH SH SH SH S S SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SA- SH SH SH SH SH SH SM SM SM SM SM SM SM or SA- SM or SA- SM or SA- SM or SA- SM or SA- SM or SA- DTT IAA IAM IAA/IAM Protein electrophoretic mobility shift assay 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 1 2 3 4 TrxSS TrxSH ureaPAGE - +
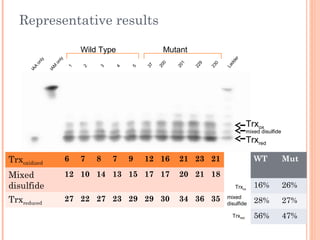
- 9. Representative results IAA only 1 2 3 4 5 37 200 201 229 230 Ladder Wild Type Mutant Trxoxidized 6 7 8 7 9 12 16 21 23 21 Mixed disulfide 12 10 14 13 15 17 17 20 21 18 Trxreduced 27 22 27 23 29 29 30 34 36 35 Mut 26% 27% 47% mixed disulfide Trxred Trxox Trxox mixed disulfide Trxred IAM only WT 16% 28% 56%
- 10. Conclusion ïĒ Thioredoxin reductase is not the major determinant of thioredoxin redox state ïĒ Another pathway must be able to reduce thioredoxin
- 11. Acknowledgement ïĒ Dr. Gary Merrill ï Biochemistry & Biophysics Lab ïĒ Dr. Kevin Ahern ïĒ Howard Hughes Medical Institute ïĒ Undergraduate, Research, Innovation, Scholarship & Creativity ïĒ www.prosuspensiontrainer.com
Editor's Notes
- #3: To start off, Thioredoxins are proteins found in nearly all known organisms (from plants and bacteria to mammals) and are essential for life in mammals. They are an antioxidant that prevents oxidative stress, since an accumulation of oxidative stress can lead to certain diseases and certain cancer. Reduced trx participates in many cellular functions by donating its electrons and restoring oxidative inactive enzymes back to its reduced and active state (through the cysteine thiols-disulfide exchange). What is Oxidative stress? Oxidative stress is caused by an imbalance in the production of reactive oxygen and accumulation of them can lead to diseases such as As an antioxidant, Thioredoxin helps with preventing oxidative stress, which can lead to diseases such as cancer. We study thioredoxin because
- #4: It does this through the cysteine thiols-disulfide exchange. Thioredoxin has 102 amino acids, but the one we focus mainly on is cysteine because it contains sulfur thiols that have high level of activity. (In this case, the thiols are represented by the SH). Mice has 6 thiols, but only two of them are the active sites that participate in the reaction. The other four are structural thiols and functions to hold the shape and structure of the protein. As you can see, there are two subunits of trx, reduced trx and oxidized trx. Reduced trx is the important one because it participates in the cysteine thiols-disulfide exchange my donating its electron. In this example, reduced trx supplyies the oxidized form of RNR to reduce its disulfide. As a result, trx becomes oxidized. Like oxidized trx, oxidized RNR is limited in its functions. Reduced RNR is important because it regulates levels of dNTP which corresponds with DNA synthesis. RNR is one of many enzymes that are reduced by trx, so what happens if trx becomes oxidized?
- #6: Thatâs where thioredoxin reductase comes in. It is the only known enzyme to reduce oxidized trx. The picture shown display the relationship between trx and trx reductase. Trx reductase catalyzes the NADPH dependent reaction that supplies the electrons to reduced oxidized trx. As you can see, itâs all connected back to trx reductase, so what happens if we take away trx reductase? Would levels of oxidized trx accumulates?
- #7: My hypothesis states that thioredoxin reductase is a major determinant in thioredoxin redox state. For my project, I worked with mutant and WT mice, where the mutant mice is missing the trx reductase gene. Dr. Gary Merrill in collaborating with other professors were able to develop a line of mutant mice that was only missing the gene in liver. They had tried to get rid of trx reductase completely, however the embryos died very early in development. But they were able to survive to old age if it was only deleted in the liver. So far we know that thioredoxin reductase reduces thioredoxin, so for the mutant mice we take away the thioredoxin reductase gene and kept the gene in the wild type mice. For these two groups, I will look at the thioredoxin protein bands and compare the two groups. If my hypothesis is true, then there should be a big difference in the reduced thioredoxin band between the wild type and the mutant group. In other words, we should see a big signal in the wild type than the mutant.
- #8: This is basically a detailed run through about the 3 reagents that are use to separate the reduced and the oxidized form of thioredoxin. As I mentioned before, mice have six thiols. The picture shown before only showed the 2 thiols because those two were the one that are actively participating in chemical reactions. But as you can see, reduced trx has six free thiols while oxidized trx only has four free thiols. The extra 2 thiols represent represent the reduced form of trx while the disulfide represent trx in its oxidized form. First off, they are treated with iodoacetic acid which introduces a carbomethyl group (?) to the thiols, giving it a -1 charge. Since reduced trx has 6 free thiols, it is represented by a -6 charge. Then comes the acetone wash to get rid of any extra negative residue from the acetic acid and is treated with Dithiothreitol to reduced the disulfide bond to free up new thiols. (This step only affects the oxidized trx) Then itâs treated with Iodoacetamide to add a neutral charge to the free thiols. Then we run the protein through a urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to separate the protein depending on its charge. As you can see, reduced trx have a -6 charge and oxidized trx should have a -4 charge. Check out empire today
- #9: As the picture shown on the right, there are 7 rungs, starting with no charge (or a neutral charge) represented by the 0 to -6 charge (the reduced trx). Trx is treated to Dithiothreitol, to reduced the disulfide bond of any oxidized trx and the reduced trx shouldnât be affect. Now that all trx is in its reduced form, we were able to create a standard for reference. The first pathway was treated trx only with Iodoacetic acid, which adds all neutral charge making it a -6 charge (as shown on band in lane 1). Or we can treat it with Iodoacetamide, which introduce all neutral charge (meaning 0 charge), which is shown in lane 2. Lastly, a mixture of Iodoacetic acid and iodoacetamide gives a ladder from the neutral charge to the -6 charge. Lane 4 shows the two bands where the oxidized trx (-4 charge) and the reduced trx (-6 charge) bands should be in comparison with the standards.
- #12: Dr. Gary Merrill Dr. Kevin Ahern Howard Hughes Medical Institute Undergraduate, Research, Innovation, Scholarship & Creativity