Tu1
- 1. Introduction to C Tom Chao Zhou CSC2100B Data Structures Tutorial 1
- 2. Outline ? Information ? Introduction to C ? Basics ? If Statement ? Loops ? Functions ? Switch case ? Pointers ? Structures ? File I/O
- 3. Information ? Your TA Team: ? Jianye Hao ? jyhao AT cse.cuhk.edu.hk ? Tom Chao Zhou ? czhou AT cse.cuhk.edu.hk ? Xin Xin ? xxin AT cse.cuhk.edu.hk ? Haifeng Wan ? hfwan AT cse.cuhk.edu.hk
- 4. Information ? Course Information: ? Web Page: ? http://wiki.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/irwin.king/teaching/csc2100b/2010 ? Tutorial Page: ? http://wiki.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/irwin.king/teaching/csc2100b/tutorials ? Anti-plagiarism Policy: ? http://www.cuhk.edu.hk/policy/academichonesty/
- 5. Information ? Assignment ? There will be both written and programming parts in assignments. ? Written part: submit to the assignment box in 10/F SHB. ? Programming part: via Online Judge systems. (Will be introduced next week) ? You will receive your login Id for CSC2100B online judge via your sxxxxxxx@mailserv.cuhk.edu.hk email account. (A few days later). ? Keep it safe and do not disclose it.
- 6. Introduction to C ? Basics ? If Statement ? Loops ? Functions ? Switch case ? Pointers ? Structures ? File I/O
- 8. Introduction to C: Basics //a simple program that has variables #include <stdio.h> int main() { int x; //(32 bits) char y; //(8 bits) float z; //(32 bits) double t; //(64 bits) printf(ˇ°hello worldˇnˇ±); int test; //wrong, The variable declaration must appear first return 0; }
- 9. Introduction to C: Basics //reading input from console #include <stdio.h> int main() { int num1; int num2; printf( "Please enter two numbers: " ); scanf( "%d %d", &num1,&num2 ); printf( "You entered %d %d", num1, num2 ); return 0; }
- 10. Introduction to C: if statement #include <stdio.h> int main() { int age; /* Need a variable... */ printf( "Please enter your age" ); /* Asks for age */ scanf( "%d", &age ); /* The input is put in age */ if ( age < 100 ) { /* If the age is less than 100 */ printf ("You are pretty young!n" ); /* Just to show you it works... */ } else if ( age == 100 ) { /* I use else just to show an example */ printf( "You are oldn" ); } else { printf( "You are really oldn" ); /* Executed if no other statement is*/ } return 0; }
- 11. Introduction to C: Loops(for) #include <stdio.h> int main() { int x; /* The loop goes while x < 10, and x increases by one every loop*/ for ( x = 0; x < 10; x++ ) { /* Keep in mind that the loop condition checks the conditional statement before it loops again. consequently, when x equals 10 the loop breaks. x is updated before the condition is checked. */ printf( "%dn", x ); } return 0; }
- 12. Introduction to C: Loops(while) #include <stdio.h> int main() { int x = 0; /* Don't forget to declare variables */ while ( x < 10 ) { /* While x is less than 10 */ printf( "%dn", x ); x++; /* Update x so the condition can be met eventually */ } return 0; }
- 13. Introduction to C: Loops(do while) #include <stdio.h> int main() { int x; x = 0; do { /* "Hello, world!" is printed at least one time even though the condition is false*/ printf( "%dn", x ); x++; } while ( x != 10 ); return 0; }
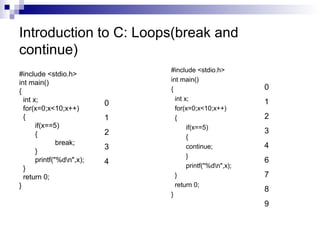
- 14. Introduction to C: Loops(break and continue) #include <stdio.h> int main() { int x; for(x=0;x<10;x++) { if(x==5) { break; } printf("%dn",x); } return 0; } #include <stdio.h> int main() { int x; for(x=0;x<10;x++) { if(x==5) { continue; } printf("%dn",x); } return 0; } 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9
- 15. Introduction to C: function #include <stdio.h> //function declaration int mult ( int x, int y ); int main() { int x; int y; printf( "Please input two numbers to be multiplied: " ); scanf( "%d", &x ); scanf( "%d", &y ); printf( "The product of your two numbers is %dn", mult( x, y ) ); return 0; } //define the function body //return value: int //utility: return the multiplication of two integer values //parameters: take two int parameters int mult (int x, int y) { return x * y; }
- 16. #include <stdio.h> //function declaration, need to define the function body in other places void playgame(); void loadgame(); void playmultiplayer(); int main() { int input; printf( "1. Play gamen" ); printf( "2. Load gamen" ); printf( "3. Play multiplayern" ); printf( "4. Exitn" ); printf( "Selection: " ); scanf( "%d", &input ); switch ( input ) { case 1: /* Note the colon, not a semicolon */ playgame(); break; //don't forget the break in each case case 2: loadgame(); break; case 3: playmultiplayer(); break; case 4: printf( "Thanks for playing!n" ); break; default: printf( "Bad input, quitting!n" ); break; } return 0; } switch case
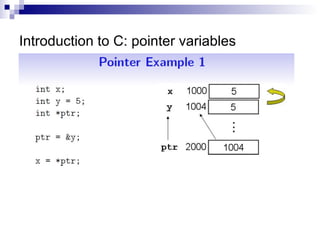
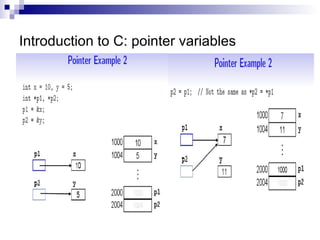
- 17. Introduction to C: pointer variables ? Pointer variables are variables that store memory addresses. ? Pointer Declaration: ? int x, y = 5; ? int *ptr; ? /*ptr is a POINTER to an integer variable*/ ? Reference operator &: ? ptr = &y; ? /*assign ptr to the MEMORY ADDRESS of y.*/ ? Dereference operator *: ? x = *ptr; ? /*assign x to the int that is pointed to by ptr */
- 18. Introduction to C: pointer variables
- 19. Introduction to C: pointer variables
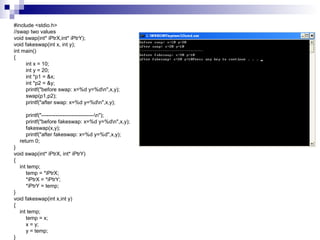
- 20. #include <stdio.h> //swap two values void swap(int* iPtrX,int* iPtrY); void fakeswap(int x, int y); int main() { int x = 10; int y = 20; int *p1 = &x; int *p2 = &y; printf("before swap: x=%d y=%dn",x,y); swap(p1,p2); printf("after swap: x=%d y=%dn",x,y); printf("------------------------------n"); printf("before fakeswap: x=%d y=%dn",x,y); fakeswap(x,y); printf("after fakeswap: x=%d y=%d",x,y); return 0; } void swap(int* iPtrX, int* iPtrY) { int temp; temp = *iPtrX; *iPtrX = *iPtrY; *iPtrY = temp; } void fakeswap(int x,int y) { int temp; temp = x; x = y; y = temp; }
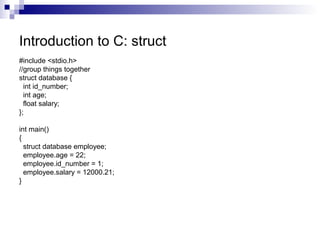
- 21. Introduction to C: struct #include <stdio.h> //group things together struct database { int id_number; int age; float salary; }; int main() { struct database employee; employee.age = 22; employee.id_number = 1; employee.salary = 12000.21; }
- 22. //content in in.list //foo 70 //bar 98 //biz 100 #include <stdio.h> int main() { FILE *ifp, *ofp; char *mode = "r"; char outputFilename[] = "out.list"; char username[9]; int score; ifp = fopen("in.list", mode); if (ifp == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't open input file in.list!n"); exit(1); } ofp = fopen(outputFilename, "w"); if (ofp == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't open output file %s!n", outputFilename); exit(1); } while (fscanf(ifp, "%s %d", username, &score) == 2) { fprintf(ofp, "%s %dn", username, score+10); } fclose(ifp); fclose(ofp); return 0; } mode: r - open for reading w - open for writing (file need not exist) a - open for appending (file need not exist) r+ - open for reading and writing, start at beginning w+ - open for reading and writing (overwrite file) a+ - open for reading and writing (append if file exists) File I/O
- 23. ?Q & A















![//content in in.list
//foo 70
//bar 98
//biz 100
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *ifp, *ofp;
char *mode = "r";
char outputFilename[] = "out.list";
char username[9];
int score;
ifp = fopen("in.list", mode);
if (ifp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open input file in.list!n");
exit(1);
}
ofp = fopen(outputFilename, "w");
if (ofp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open output file %s!n", outputFilename);
exit(1);
}
while (fscanf(ifp, "%s %d", username, &score) == 2) {
fprintf(ofp, "%s %dn", username, score+10);
}
fclose(ifp);
fclose(ofp);
return 0;
}
mode:
r - open for reading
w - open for writing (file need not exist)
a - open for appending (file need not exist)
r+ - open for reading and writing, start at beginning
w+ - open for reading and writing (overwrite file)
a+ - open for reading and writing (append if file
exists)
File I/O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tu1-141023230334-conversion-gate01/85/Tu1-22-320.jpg)
