Tuning presentation v1
- 1. Tony Arman Technical Department â GBB Plant 3/15/2013 1
- 2. ï― Importance of PID control ï― Review the basics of PID control ï― Learn how to tune âĶ.. 2
- 3. ï― Today, most manufacturing plants use DCS (Distributed Control System) for process control. ï― DCS manufacturers use PID algorithm for control. 3
- 4. ï― PID algorithm goes back more than a 100 years and is considered to be the âBestâ controller. ï― PID algorithm has one major draw back; ï― It is linear. Life is NOT 4
- 5. ï― The following abbreviations are used in the PID controller. ï― P â Proportional ( = 100/Gain) ï― I â Integral ( = 1/Reset) ï― D â Derivative ( = Rate = Preact) ï― Error = SP - PV 5
- 6. 6
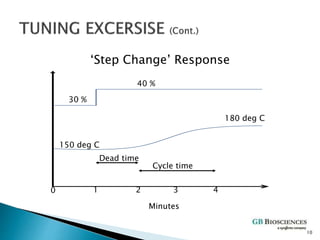
- 7. ï― Scenario : âStep Change Methodâ ï― You are asked to look at a tuning for a Temp. Controller that is not stable. 7
- 8. ï― Step 1: ï― You ask the operator to place the loop in Manual (Output = 30%). ï― Temperature lines out at ~ 150 deg C (range = 0-300 deg C). 8
- 9. ï― Step 2: ï― After a while you ask the operator to raise the output to 40 %. ï― You wait until Temp. lines out at 180 deg C. ï― Based on the controller response, estimate the tuning parameters. 9
- 10. âStep Changeâ Response 30 % 40 % 150 deg C 180 deg C Minutes 0 1 2 3 4 Dead time Cycle time 10
- 11. ï― Calculate System Parameters: ï― Gain = % Manipulated / % Measured =(40-30) % / ((180 â 150) / 300) % = 10 / 10 = 1.0 P ï― Response time = 2 minutes I ï― Dead time = 1 minute D 11
- 12. ï― Enter Controller Parameters (For Honeywell DCS): ï― Set the PID parameters to 50 % of the estimate; ï― Overall Gain, K = 0.5 ï― Integral Time, T1 = 1.0 minute ï― Derivative Time, T2 = 0.5 minute 12
- 13. ï― Tips: ï― Most loops do NOT require derivative action. ï― Be conservative, plan for some upsets. ï― Listen to the operators. ï― Are you tuning the âRightâ loop? 13
- 14. ï― Misc: ï― Feed Back (typical) ï― Feed Forward (anticipate) ï― Inverse Response (challenging) ï― Types of Algorithm (Honeywell â B) ï― PID Action (Output â§, PVâĐ, Direct) ï― Self Regulating (Flow, Temp., Press [yes], Level [Not]) 14
- 15. 15













![ï― Misc:
ï― Feed Back (typical)
ï― Feed Forward (anticipate)
ï― Inverse Response (challenging)
ï― Types of Algorithm (Honeywell â B)
ï― PID Action (Output â§, PVâĐ, Direct)
ï― Self Regulating (Flow, Temp., Press [yes],
Level [Not])
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuningpresentationv1-151119195157-lva1-app6891/85/Tuning-presentation-v1-14-320.jpg)
