Turner syndrome presentation last
- 1. Turner syndrome Salem, Katja, Ida, Helene og Karoline
- 2. Background • Henry Turner in 1938 7 patients, who were referred to him for dwarfism. (short stature, infertility) • Otto Ullrich in 1930 in the German literature described "congenital atonic-sclerotic muscular dystrophy,“ • Loss of part or all of an X , whereas gains of one or more X chromosomes result in Klinefelter syndrome in males. • Genes related to reproduction & cognition. • Gonadal development and to neurocognitive alterations. • Frequency of mosaicism range from 67% - 90%. 2
- 3. Genotype • Monosomy • Principles behind Turner Syndrome – Nondisjunction – Haploinsufficiency 3
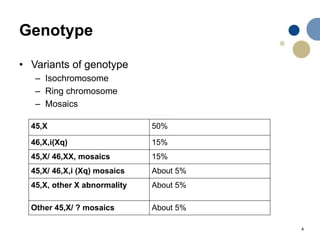
- 4. Genotype • Variants of genotype – Isochromosome – Ring chromosome – Mosaics 45,X 50% 46,X,i(Xq) 15% 45,X/ 46,XX, mosaics 15% 45,X/ 46,X,i (Xq) mosaics About 5% 45,X, other X abnormality About 5% Other 45,X/ ? mosaics About 5% 4
- 5. Phenotype • Individuals can be more or less affected phenotypically • Diagnosed in utero performing: amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, and abnormal ultrasound findings (heart defect, kidney abnormality, cystic hygroma, ascites, increased nuchal translucency). • In newborns (some have it): webbing of neck, short neck and edema of hands and feet • Often diagnosed during puberty because of short stature: rarely become taller than 1.43-1.47 m (without treatment) – SHOX gene • Sometimes diagnosed when lack of /late onset of puberty • Some diagnosed in relation to infertility 5
- 6. Phenotype • 5-10 % have severe constriction of aorta, about 30 % have fusion of two of the valves – operated as soon as diagnosed • High blood pressure • About 30 % have malfunctioning kidneys • Twice the risk of developing diabetes type II • About 30% ahve a thyroid problem (hypothyroidism) – can be treated • Problems with learning maths and problems with spatial perception. Sometimes language skills above average. Normal general intelligence 6
- 7. 7
- 8. In utero diagnoses • shows early-onset signs that could be detected in the first trimester. (cystic hygroma, fetal hydrops, cardiac defects and increased nuchal translucency. Among heart defects, coarctation of the aorta is the most common (44.4% of all cardial defects) • • • http://sonoworld.com/fetus/page.aspx?id=2831 Primigravida came to our department at 15 weeks of gestation. She had non-contributive family or personal history. We have seen cystic hygroma and fetal hydrops. The amniocentesis result showed monosomy X, 45 X0. The pregnancy was terminated afterwards. Image 1 shows a transverse view of the fetal neck showing cystic hygroma. Image 2 shows a 3D image of the cystic hygroma 8
- 9. Risk and treatment • Present in 1-2% of all conceptuses ïƒ 99% of such foetuses abort spontaneously • Incidence between 1 in 1000 and 1 in 5000 female live births • Not associated with advanced maternal or paternal age ïƒ usually sporadic • Treatment: – – – – growth hormone supplements estrogen therapy progesterone therapy Additional: echocardiography, renal ultrasonography, glucose tolerance test 9
- 11. Sources: • http://www.turnersyndrom.no/ts.html • http://turners.nichd.nih.gov/clinical.html • Genetics in medicine, chapter 6 and 10, 7th ed. 11