Tutorial ABaqus
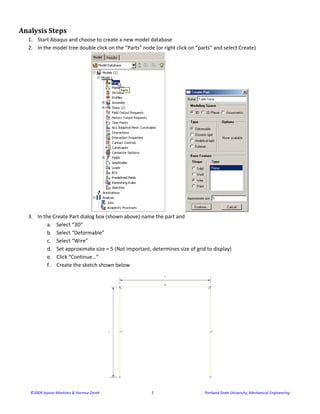
- 2. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       2                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  Analysis Steps  1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database  2. In the model tree double click on the “Parts” node (or right click on “parts” and select Create)       3. In the Create Part dialog box (shown above) name the part and  a. Select “3D”  b. Select “Deformable”  c. Select “Wire”  d. Set approximate size = 5 (Not important, determines size of grid to display)  e. Click “Continue…”  f. Create the sketch shown below   
- 3. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       3                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  4. In the toolbox area click on the “Create Datum Plane:   Offset From Principle Plane” icon  a. Select the “XY Plane” and enter a value of 1 for the offset                    5. In the toolbox area click on the “Create Wire: Planar” icon  a. Click on the outline of the datum plane created in the previous step  b. Select any one of the lines to appear vertical and on the right  c. In the toolbox area click on the “Project Edges” icon  d. Select all of the lines in the viewport and click “Done”      6. In the toolbox area click on the “Create Datum Plane: 3 points” icon (click on the small black triangle in the  bottom‐right corner of the icon to get all of the datum plane options)  a. Select 3 points on the top of the geometry   
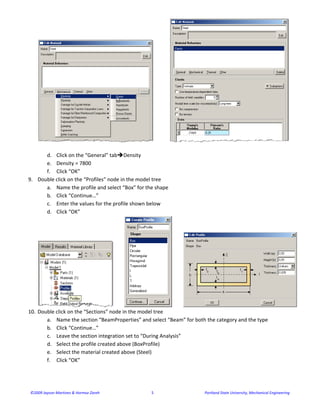
- 4. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       4                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  7. In the toolbox area click on the “Create Wire: Planar” icon  a. Click on the outline of the datum plane created in the previous step  b. Select any one of the lines to appear vertical and on the right  c. Sketch two lines to connect finish the wireframe of the table  d. Click on “Done”    8. Double click on the “Materials” node in the model tree    a. Name the new material and give it a description  b. Click on the “Mechanical” tab Elasticity Elastic  c. Define Young’s Modulus (210e9)  and Poisson’s Ratio  (0.25) 
- 5. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       5                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering        d. Click on the “General” tab Density  e. Density = 7800  f. Click “OK”  9. Double click on the “Profiles” node in the model tree  a. Name the profile and select “Box” for the shape  b. Click “Continue…”  c. Enter the values for the profile shown below  d. Click “OK”                      10. Double click on the “Sections” node in the model tree  a. Name the section “BeamProperties” and select “Beam” for both the category and the type  b. Click “Continue…”  c. Leave the section integration set to “During Analysis”  d. Select the profile created above (BoxProfile)  e. Select the material created above (Steel)  f. Click “OK” 
- 6. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       6                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering            11. Expand the “Parts” node in the model tree, expand the node of the part just created, and double click on  “Section Assignments”  a. Select the entire geometry in the viewport  b. Select the section created above (BeamProperties)  c. Click “OK”      12. Expand the “Assembly” node in the model tree and then double click on “Instances”  a. Select “Dependent” for the instance type  b. Click “OK”     
- 7. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       7                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  13. Double click on the “Steps” node in the model tree  a. Name the step, set the procedure to “Linear perturbation”, and select “Frequency”  b. Click “Continue…”  c. Give the step a description  d. Select “Lanczos” for the Eigensolver  e. Select the radio button “Value” under “Number of eigenvalues requested “ and enter  10  f. Click “OK”            14. Double click on the “BCs” node in the model tree  a. Name the boundary conditioned “Fixed” and select “Symmetry/Antisymmetry/Encastre” for the type  b. Click “Continue…”  c. Select the end of each leg and press “Done” in the prompt area  d. Select “ENCASTRE” for the boundary condition (“ENCASTRE” means completely fixed/clamped)  e. Click “OK”     
- 8. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       8                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  15. In the model tree double click on “Mesh” for the Table frame part, and in the toolbox area click on the “Assign  Element Type” icon  a. Select “Standard” for element type  b. Select “Linear” for geometric order  c. Select “Beam” for family  d. Click “OK”            16. In the toolbox area click on the “Seed Part” icon  a. Set the approximate global size to 0.1        17. In the toolbox area click on the “Mesh Part” icon  a. Click “Yes” in the prompt area     
- 9. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       9                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  18. In the menu bar select View Part Display Options  a. Check the Render beam profiles option  b. Click “OK”          19. Change the Module to “Property”  a. Click on the “Assign Beam Orientation” icon  b. Select the portions of the geometry that are perpendicular to the Z axis  c. Click “Done” in the prompt area   d. Accept the default value of the approximate n1 direction (0,0,‐1)  e. Click “OK” in the prompt area            f. Select the portions of the geometry that are parallel to the Z axis 
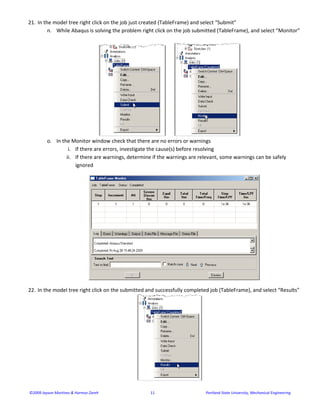
- 10. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       10                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  g. Click “Done” in the prompt area  h. Enter a vector that is perpendicular to the Z axis for the approximate n1 direction (i.e. 0,1,0)    i. Click “OK” followed by “Done” in the prompt area  20. In the model tree double click on the “Job” node  j. Name the job “TableFrame”  k. Click “Continue…”  l. Give the job a description  m. Click “OK”        
- 11. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       11                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  21. In the model tree right click on the job just created (TableFrame) and select “Submit”  n. While Abaqus is solving the problem right click on the job submitted (TableFrame), and select “Monitor”        o. In the Monitor window check that there are no errors or warnings  i. If there are errors, investigate the cause(s) before resolving  ii. If there are warnings, determine if the warnings are relevant, some warnings can be safely  ignored    22. In the model tree right click on the submitted and successfully completed job (TableFrame), and select “Results”   
- 12. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       12                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering  23. In the menu bar click on Viewport Viewport Annotations Options  p. The locations of viewport items can be specified on the corresponding tab in the Viewport Annotations  Options  q. Click “OK”        24. Display the deformed contour overlaid with the undeformed geometry  r. In the toolbox area click on the following icons  iii. “Plot Contours on Deformed Shape”  iv. “Allow Multiple Plot States”  v. “Plot Undeformed Shape”              25. In the menu bar click on Results  Step/Frame  s. Change the mode by double clicking in the “Frame” portion of the window  t. Observe the eigenvalues and frequencies  u. Leave the dialogue box open to be able to switch the mode shapes while animating 
- 13. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       13                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering                        26. In the toolbox area click on “Animation Options”  v. Change the Mode to “Swing”  w. Click “OK”  x. Animate by clicking on “Animate:  Scale Factor” icon in the toolbox area            27. Click on a different Frame in the “Step/Frame” dialogue box to change the mode  28. Expand the “TableFrame.odb” node in the result tree, expand the “History Output” node, and right‐click on  “Eigenfrequency:  …”  y. Select “Save As…”  z. Name = Frequencies 
- 14. ©2009 Jayson Martinez & Hormoz Zareh                                                       14                                                      Portland State University, Mechanical Engineering        aa. Repeat for “Eigenvalue”  bb. Observe the XYData nodes in the result tree    29. In the menu bar click on Report XY…    cc. Select from = All XY data  dd. Highlight “Eigenvalues”  ee. Click on the “Setup” tab  ff. Click “Select…” and specify the desired name and location of the report  gg. Click “Apply”  hh. Click on the “XY Data” tab  ii. Highlight “Frequencies”  jj. Click “OK”