Tutorial iii dna extraction
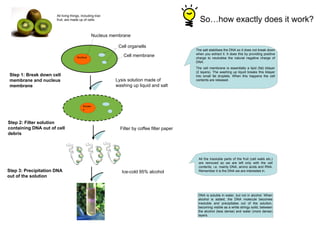
- 1. DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is packed in nucleus of cells It looks like a double-helix found by Watson and Crick in 1953 DNA is the blueprint of life Interesting facts! One DNA molecule in a human cell is 1 meter long while diameter of the cell’s nucleus is 1/10^5 meter A-T; G-C in a double-helix DNA, so if the sequence of one strand is known, we can find the sequence of the other Extraction DNA from kiwi fruits All living things, including kiwi fruit, are made up of cells. Step 1: Break down cell membrane and nucleus membrane Step 2: Filter solution containing DNA out of cell debris Step 3: Precipitation DNA out of the solution Nucleus membrane Cell organells Nucleus Cell membrane Nucleu s Lysis solution made of washing up liquid and salt Filter by coffee filter paper Ice-cold 95% alcohol
- 2. So…how exactly does it work? All living things, including kiwi The salt stabilises the DNA so it does not break down when you extract it. It does this by providing positive charge to neutralise the natural negative charge of DNA. The cell membrane is essentially a lipid (fat) bilayer (2 layers). The washing up liquid breaks this bilayer into small fat droplets. When this happens the cell contents are released. All the insoluble parts of the fruit (cell walls etc.) are removed so we are left only with the cell contents, i.e. mainly DNA, amino acids and RNA. Remember it is the DNA we are interested in. DNA is soluble in water, but not in alcohol. When alcohol is added, the DNA molecule becomes insoluble and precipitates out of the solution, becoming visible as a white stringy solid, between the alcohol (less dense) and water (more dense) layers. fruit, are made up of cells. Step 1: Break down cell membrane and nucleus membrane Step 2: Filter solution containing DNA out of cell debris Step 3: Precipitation DNA out of the solution Nucleus membrane Cell organells Nucleus Cell membrane Nucleu s Lysis solution made of washing up liquid and salt Filter by coffee filter paper Ice-cold 95% alcohol