Two way slab
- 1. Two way slab
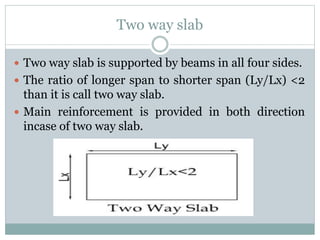
- 2. Two way slab ï Two way slab is supported by beams in all four sides. ï The ratio of longer span to shorter span (Ly/Lx) <2 than it is call two way slab. ï Main reinforcement is provided in both direction incase of two way slab.
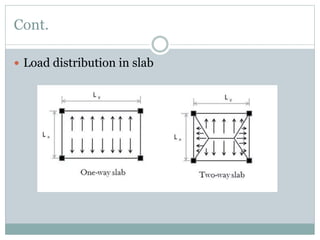
- 3. Cont. ï Load distribution in slab
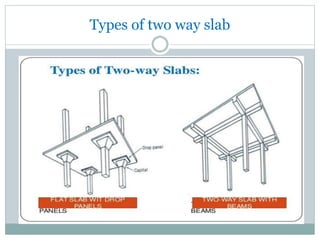
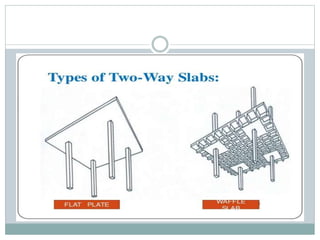
- 4. Types of two way slab
- 6. Design steps for two way slab ï Step 1: Preliminary Design. ï Find depth of slab using deflection control criteria. ï Take span/d = 28 for simply supported slab and 32 for continuous slab. ï D âĨ Dmin = 100mm for normal design and 125mm for earthquake resistant design. ï Step 2: Analysis of Slab. ï Slab is analyzed by IS code method. (Ref. Annex D-1 and Annex D-2).
- 7. ï Step 3: Design of Slab. ï Verify depth of slab âDâ. ï Determine âAstâ and âÎĶâ and number of bars in shorter direction of slab. ï Slab section is normally designed as Singly Reinforced Under Reinforced Rectangular Section. ï Ast = Mu/(0.87fy(d-0.416xu)) which should not be less than Astmin. ï Check slab for shear in shorter direction.
- 8. ï Step 4: Check slab at limit state of serviceability in deflection in shorter direction. ï l/d âĪ ÎąÎēÎģÎīÎģ ï Step 5: Detailing of reinforcement: ï Curtail/bend the surplus bars as per detailing rules of code. (Ref. Annex) ï Check development length at support. ï Ld âĪ 1.3Ml / Vu + ld ï Provide torsion reinforcement at the discontinuous edge of slab as per codal provision.