Types Of Cataract
- 1. -Suraj Dalal (2nd Year Student of Hari Jyot College of Optometry, Navsari)
- 2. Objectives • Why This Talk? • Growth Of The Lens • Basic Anatomy Of lens • Prevalence Of Cataract in India • Definition of Cataract • Classification • Quiz
- 3. Why This talk?? • To Diagnose the type of cataract correctly • For Providing the patient a proper guidelines for its treatment • For better counselling.
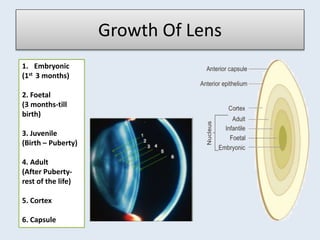
- 4. Growth Of Lens 1. Embryonic (1st 3 months) 2. Foetal (3 months-till birth) 3. Juvenile (Birth – Puberty) 4. Adult (After Puberty- rest of the life) 5. Cortex 6. Capsule
- 5. Anatomy of Lens • Lens Epithelium:-  Carry out Metabolic activities which also include DNA , RNA , Protein , And Lipid Biosynthesis.  Generates Epithelial lens which furthur elongates to form Lens Fibers cells.  This New Cells are Do not have organells & generate energy from glycolysis. • Nucleus & Cortex:-  No cells are lost from The Lens.  Nucleus is Central part containing Oldest Fibers  Cortex is Peripheral Part Containing Youngest Fibers. Lens Fibers are Hexagonal in shape.
- 6. Anatomy of Lens • Capsule:-  Elastic Transparent Basement Membrane made of Epithelial Cells  Provides Source of attachment For the Zonular Fibres.  Contains Lens Substance & Help in Accomodation. • Zonules:-  Originates from the basal lamina of the non pigmented epithelium of pars plana and pars plicata of ciliary body.  Are distributed as:- o the Anterior fibers. o Equatorial Fibers. o Posterior fibers.
- 7. Prevalance of Cataract in India
- 8. Prevalence In Rural Areas
- 9. Prevalence In Urban Areas
- 10. One Question?? • Cornea Do Aerobic Respiration & Lens Do Anaerobic Respiration.
- 11. Definition • A cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye which leads to a decrease in vision. • Or in simple words it is “ development of any opacity in Lens or its Capsule. • Cataract is like “ Looking through a waterfall”
- 12. Reason Behind The Cataract • Hydration Of Lens. • Denaturation Of Lens Fibres. • Slow Sclerorsis.
- 13. Cataract Etiological Morphological Congenital & Developmental Aquired 1. Senile 2. Traumatic 3. Complicated 4. Metabolic 5. Electric 6. Radiational 7. Toxic 8. Other diseases 1. Capsule 2. Sub-capsular 3. Cortical 4. Nuclear 5. Polar Classification
- 15. Congenital Cataract • Congenital Cataracts Occur in a variety of morphologic configurations like :-
- 16. CONGENITAL CATARACT Polar Anterior Polar cataract • Pyramidal Cataract • Re-Duplicated Cataract
- 17. CONGENITAL CATARACT Polar Posterior polar Cataract • Mitendorf’s Dot • PHPV
- 18. Congenital Cataract Coronary Cataract • Club Shaped opacities
- 19. CONGENITAL CATARACT Lamellar cataracts. (a) Lamellar opacities around the fetal nucleus with cortical riders (see arrows) on the periphery; (b) optical section under slit-lamp biomicroscopy; (c) lamellar opacities around the fetal nucleus without cortical riders on the periphery; (d) optical section under slit-lamp biomicroscopy Lamellar Cataract
- 20. Congenital Cataract Central pulverulent cataract • Opacification in Embryonic nucleus
- 21. Congenital Cataract Sutural cataract Sutural cataracts. (a) Y-suture with perinuclear opacities; (b) anterior Y-suture with cortiacal cerulean opacities; (c) anterior and posterior Y-sutures with cortical punctate opacities (d) Dendritic sutural cataract
- 22. Congenital Cataract Membranous Cataract • Occurs Due to resorbed of lens proteins
- 23. Congenital Cataract Focal dot opacities • Also know As Cataracta-punctata Caerulea
- 24. Congenital Cataract Complete Cataract • Opacification of all the lens fibres. • No red relfex is observed.
- 25. Aquired Cataract
- 26. Aquired Cataract Cortical (Soft Cataract)
- 27. Aquired Cataract Cortical (Soft Cataract) Cuneiform Cataract • Wedge-Shaped spokes At periphery
- 28. Aquired Cataract Cortical (Soft Cataract) Cupuliform Cataract • Opacity At Axial region of posterior Cortex. • It Causes Harmalopia.
- 29. Stages Of Maturation Stage of lamellar separation Immature cataract Mature cataract Hypermature cataract—morgagnianHypermature sclerotic cataract
- 30. Aquired Cataract Nuclear Cataract • Colours of this cataract tinted dark brown, dusky red or even black. • Lenticular Myopia. • Second Sight.
- 31. Stages Cataracta Brunescens Cataracta Nigra
- 32. Grading Grade NS II Grade NS III: Amber color; Grade NS IV: Brown cataract Grade NS IV+: Black cataract
- 33. Aquired Cataract Sub-Capsular Cataract • Fibrous Metaplasia • Bladder Cells • Iridiscent Sheen ( first Sign) • Granular or plaque-like Opacities
- 34. LOCS
- 35. Secondary Cataract Chronic Anterior uveitis Acute congestive angle closure Glaukomflecken Hereditary fundus dystrophies
- 36. Systemic Disorder Cataract Diabetic snowflake Christmas Tree Cataract in Myotonic Dystrophy shield-like anterior subcapsular cataract in Atopic dermatitis
- 37. Physical Factors leading to Cataract Trauma Electric Shock Radiation
- 38. Toxic Agents leading to Cataract Cortico-steroids chlorpromazine cataract Sunflower
- 39. After Cataract • PCO- Posterior capsular opacification. Elschnig pearl formation (arrow)
- 40. No Slit-Lamp….. No Problem!! • We Can Also see the cataract with torch light or Retinoscope just we need to observe the following things:- • Color Of the lens • Iris Shadow • Vision of the person
- 41. One More Question?? • Lens is Named “ Crystalline Lens” just because it transmit light like a Crystal !! Really??
- 42. QUIZ!! This cataract is so dense that the cortex has liquefied, allowing the nucleus to sink to the bottom of the lens capsule. This special type of very dense cataract is known as a Morgagnian cataract. posterior sclerosing cataractcortical spoking cataract
- 43. Summary
- 44. References
- 45. Any Doubt??
- 46. Insta Name :- @mr.cool_buddyEmail- surajdalal2000@gmail.com Mobile :- +91 9714222217