Types of insulator
- 2. âĒ An electrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely, and which therefore does not conduct an electric current, under the influence of an electric field. âĒ A perfect insulator does not exist, but some materials such as glass, paper and Teflon, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. âĒ Insulators are used in electrical equipment to support and separate electrical conductors without allowing current through themselves.
- 3. There are several types of insulators but the most commonly used are : 1) Pin Insulator 2) Suspension Insulator 3) Strain Insulator and 4) Shackle insulator.
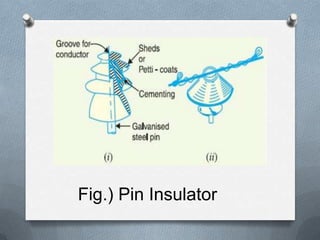
- 5. ï A pin insulator consists of a nonconducting material such as porcelain, glass, plastic, polymer, or wood. ïAs the name suggests, the pin type insulator is secured to the cross-arm on the pole. ïThere is a groove on the upper end of the insulator for housing the conductor. ïThe conductor passes through this groove and is bound by the annealed wire of the same material as the conductor. ï Pin type insulators are used for transmission and distribution of electric power at voltages upto 33 kV. ïBeyond operating voltage of 33 kV, the pin type insulators become too bulky and hence uneconomical
- 7. Fig.) Glass suspension insulator
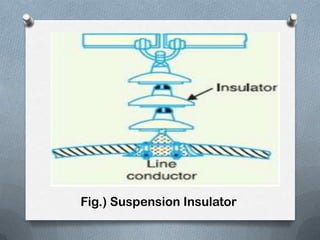
- 8. ï For high voltages (>33 kV), it is a usual practice to use suspension type insulators consist of a number of porcelain discs connected in series by metal links in the form of a string. ï The conductor is suspended at the bottom end of this string while the other end of the string is secured to the cross-arm of the tower. ï Each unit or disc is designed for low voltage, say 11 kV. ï The number of discs in series would obviously depend upon the working voltage. ï For instance, if the working voltage is 66 kV, then six discs in series will be provided on the string.
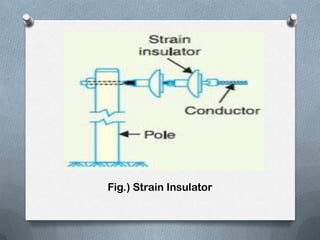
- 11. ï When there is a dead end of the line or there is corner or sharp curve, the line is subjected to greater tension. ï In order to relieve the line of excessive tension, strain insulators are used. ï For low voltage lines (< 11 kV), shackle insulators are used as strain insulators. ï However, for high voltage transmission lines, strain insulator consists of an assembly of suspension insulators as shown in Figure. ï The discs of strain insulators are used in the vertical plane. ï When the tension in lines is exceedingly high, at long river spans, two or more strings are used in parallel.
- 14. ï In early days, the shackle insulators were used as strain insulators. ï But now a days, they are frequently used for low voltage distribution lines. ï Such insulators can be used either in a horizontal position or in a vertical position. ï They can be directly fixed to the pole with a bolt or to the cross arm.