TYPES OF MECHANICAL SEALS
- 1. A technical seminar on TYPES OF MECHANICAL SEALS Presented by N.SUDHEER M.TECH(MACHINE DESIGN) 16481D1509 GUDLAVALLERU ENGINEERING COLLEGE Sheshadri Rao Knowledge Village, Gudlavalleru, PIN:521356 1
- 2. INTRODUCTION Mechanical devices known as seals, packings, and gaskets are used to prevent the leakage of fluids, gases from cylinders and cylinder heads in engines; pumps; and mixers etc. These devices also prevent the penetration of foreign matter into the concealed system. 2
- 3. SELECTION OF SEALS Seals are available in various forms and design configurations and the selection of a seal depends on: ïžPressure, ïžTemperature, ïžMedium(i.e., liquid, gases), ïžCorrosive atmosphere, and ïžShaft speed etc. 3
- 4. CLASSIFICATION OF SEALS Seals are broadly classified as static and dynamic seals. 1. Static seals a. Gaskets b. Direct contact seals c. Sealants 4
- 5. 2. Dynamic seals a. Seals used on rotating shafts i. Interfacial ii. Interstitial b. Seals used on reciprocating shafts i. Packings ii. Diaphragm iii. Rings 5
- 6. STATIC SEALS A static seal functions against mating surfaces that have no relative motion between each other. Gasket: A gasket is a thin layer of soft material such as paper, cork, copper, synthetic material, or a combination of these which is used in between two surfaces to be sealed, such as a cylinder head and cylinder in engine block. A gasket can be performed or precut to the desired shape. Clamping the gasket between the two flat surfaces makes a tight seal. 6
- 8. 8 Fig: Gasket on engine cylinder block
- 9. Direct contact seals: Direct contact seals are used where two surfaces are directly making metal to metal contact under high squeezing pressure, where very high pressures are involved. 9
- 10. 10 Fig: Direct contact seals
- 11. Sealants: Instead of being performed, some gaskets are formed in place. Squeezing a bead of plastic gasket material or sealant from a tube into one of the mating surfaces, such as valve covers, water pumps, and differential covers. 11
- 12. 12 Fig: Sealant
- 13. 13 Fig: Application of sealant to gear box
- 14. DYNAMIC SEALS Dynamic seals exist when there is motion between surfaces. Typical motions include reciprocating, oscillating, and rotation. Operational factors can greatly affect how dynamic seals perform. Factors such as swelling of seals in fluids, surface roughness of mating surfaces, lubrication, internal pressure, compression, elasticity, and friction from surfaces. 14
- 15. Dynamic seals used on rotating shafts: i. Interfacial seals: These are the seals in which seal touches the shaft. 15
- 16. ii. Interstitial seals: These are the seals where clearance between shaft and seal exists in radial and/or axial direction. 16
- 17. Dynamic seals used on reciprocating parts: ïžPackings ïžDiaphragms ïžRings 17
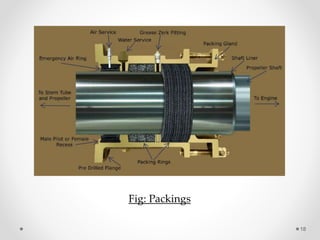
- 18. 18 Fig: Packings
- 19. The leakage rate of a mechanical shaft seal depends on a number of factors such as: ïžSurface roughness of seal faces ïžFlatness of seal faces ïžVibration and stability of shaft ïžSpeed of rotation ïžShaft diameter ïžTemperature, viscosity, and type of pumped medium ïžPump pressure ïžSeal and pump assembly. 19
- 20. THE END 20