Types of Network Architecture
- 1. COMPUTER NETWORKS Prepared by S.Sabari Giri Murugan Faculty G2-Grade KL University SESSION II Types of Network Architecture- Peer-to-Peer & Client/Server, Workgroup Vs. Domain. Network Topologies, Types of Topologies, Logical and physical topologies, selecting the Right Topology
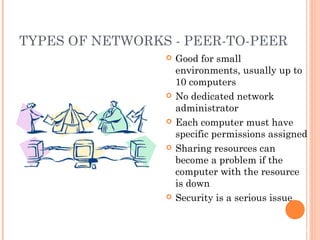
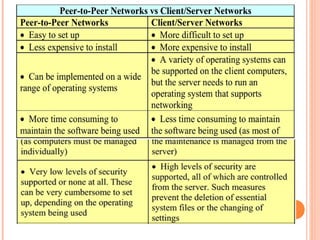
- 3. TYPES OF NETWORKS - PEER-TO-PEER ’éó Good for small environments, usually up to 10 computers ’éó No dedicated network administrator ’éó Each computer must have specific permissions assigned ’éó Sharing resources can become a problem if the computer with the resource is down ’éó Security is a serious issue 3
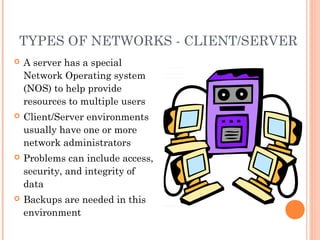
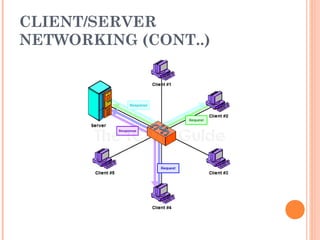
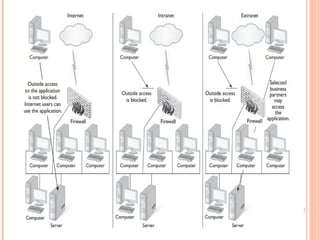
- 4. TYPES OF NETWORKS - CLIENT/SERVER ’éó A server has a special Network Operating system (NOS) to help provide resources to multiple users ’éó Client/Server environments usually have one or more network administrators ’éó Problems can include access, security, and integrity of data ’éó Backups are needed in this environment 4
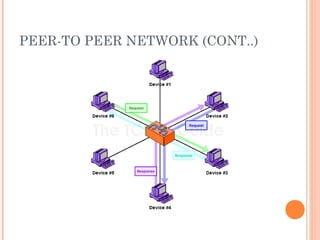
- 5. PEER-TO PEER NETWORK (CONT..)
- 9. NETWORK TOPOLOGY ’éó A topology is a way of ŌĆ£laying outŌĆØ the network. Topologies can be either physical or logical. ’éó Physical topologies describe how the cables are run. ’éó Logical topologies describe how the network messages travel
- 10. TOPOLOGY ’éó Topology: physical or logical arrangement of devices 10
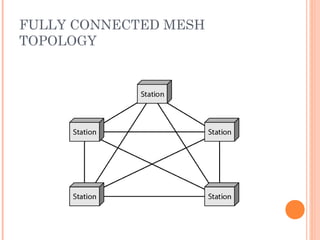
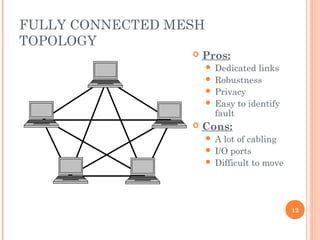
- 12. FULLY CONNECTED MESH TOPOLOGY 12 ’éó Pros: ’éŚ Dedicated links ’éŚ Robustness ’éŚ Privacy ’éŚ Easy to identify fault ’éó Cons: ’éŚ A lot of cabling ’éŚ I/O ports ’éŚ Difficult to move
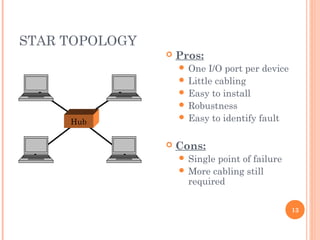
- 13. STAR TOPOLOGY 13 ’éó Pros: ’éŚ One I/O port per device ’éŚ Little cabling ’éŚ Easy to install ’éŚ Robustness ’éŚ Easy to identify fault ’éó Cons: ’éŚ Single point of failure ’éŚ More cabling still required Hub
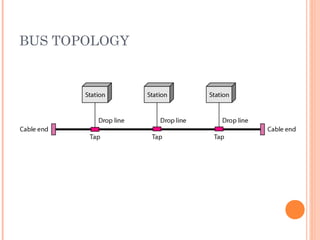
- 15. BUS TOPOLOGY 15
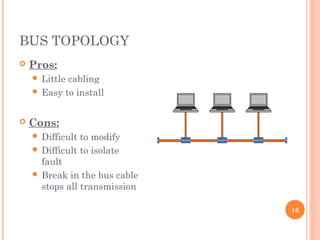
- 16. BUS TOPOLOGY 16 ’éó Pros: ’éŚ Little cabling ’éŚ Easy to install ’éó Cons: ’éŚ Difficult to modify ’éŚ Difficult to isolate fault ’éŚ Break in the bus cable stops all transmission
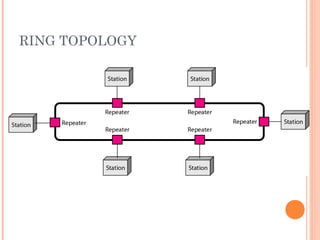
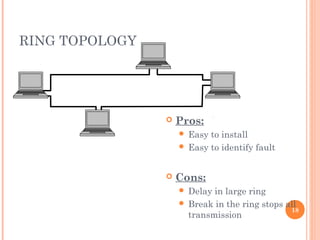
- 17. RING TOPOLOGY 17
- 18. RING TOPOLOGY 18 ’éó Pros: ’éŚ Easy to install ’éŚ Easy to identify fault ’éó Cons: ’éŚ Delay in large ring ’éŚ Break in the ring stops all transmission
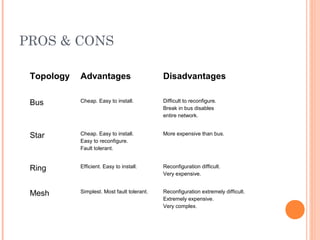
- 19. PROS & CONS Topology Advantages Disadvantages Bus Cheap. Easy to install. Difficult to reconfigure. Break in bus disables entire network. Star Cheap. Easy to install. Easy to reconfigure. Fault tolerant. More expensive than bus. Ring Efficient. Easy to install. Reconfiguration difficult. Very expensive. Mesh Simplest. Most fault tolerant. Reconfiguration extremely difficult. Extremely expensive. Very complex.
- 20. NETWORKING MODELS ’éó Two networking models: ’éŚ Workgroup ’éŚ Domain 20
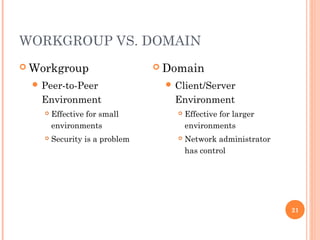
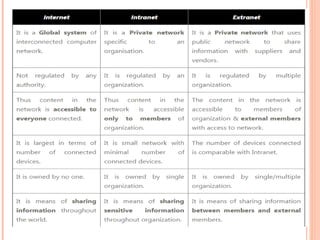
- 21. WORKGROUP VS. DOMAIN 21 ’éó Workgroup ’éŚ Peer-to-Peer Environment ’éó Effective for small environments ’éó Security is a problem ’éó Domain ’éŚ Client/Server Environment ’éó Effective for larger environments ’éó Network administrator has control
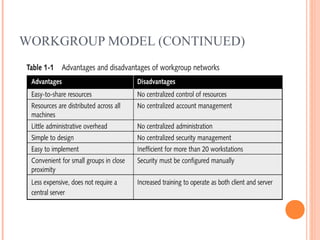
- 22. WORKGROUP MODEL ’éó All computers are equal ’éó Also known as peer-to-peer ’éó Each computer maintains own set of ’éŚ Resources ’éŚ Accounts ’éŚ Security information 22
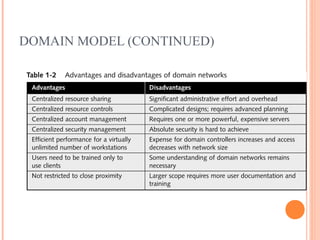
- 24. DOMAIN MODEL ’éó Centralizes all shared resources ’éó Single point of administrative and security control ’éó Simpler to manage from administrative and security standpoint ’éó Requires at least one domain controller (DC) 24