TYPHOID FEVER
- 2. Introduction ï Typhoid fever is a life threatening infection of the intestinal tract and bloodstream caused by Salmonella Typhi bacteria of the family enterobacteriaceae or salmonella paratyphi (A,B or C) ï Clinically characterized by typical continuous fever for 3 to 4 weeks with relative bradycardia with involvement of intestinal lymphoid tissue, reticuloendothelial system & gallbladder ï S. Typhi is a gram negative, non-spore forming, motile bacteria. ï The bacteria grows best at 37°C.
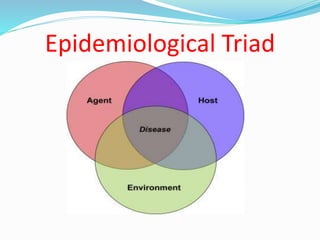
- 7. Agent ï Typhoid fever is caused by S.Typhi. ï Persons with typhoid fever carry the bacteria in their bloodstream & intestinal tract. ï Both cases & carriers carry Salmonella Typhi in their feces. ï S typhi is a gram negative, spore forming, motile bacteria. ï The bacteria grows best at 37°C.
- 8. Host factors ï AGE:- It affects all ages but higher rate is found in childrens of 5-19 years. ï SEX:- Cases are greater in males, than females. Carriers are greater in females. ï Immunity:- All ages are susceptible. Antibody may b stimulated by infection or by immunization.
- 9. Environment ï Incidence is reported through0ut the year but peak incidence is reported during July-September. I,e the increased rainy season & fly population. ï The bacilli are also found in water, soil, ice & food. water: 2 to 7 days, but not multiply soil: 35 to 70 days. Food: Multiply and survive for sometime. In milk it grows rapidly without altering its taste.
- 10. Others ï Pollution of drinking water supplies. ï Open field defecation & urination. ï Low personal hygiene. ï Poor food hygiene. ï Health ignorance.
- 11. Pathophysiology Ingestion of contaminated food or water Salmonella bacteria Invade small intestine and enter the bloodstream Carried by white blood cells in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow Multiply and reenter the bloodstream
- 12. Bacteria invade the gallbladder, biliary system, and the lymphatic tissue of the bowel and multiply in high numbers Then pass into the intestinal tract and can be identified for diagnosis in cultures from the stool tested in the laboratory
- 13. Incubation Period ï Incubation period is usually 10-14 days. It may be as short as 3 days or as long as 21 days.
- 14. Modes of transmission ï Typhoid fever occurs through fecal oral route or urine-oral route. ïDirect Transmission:- Through hands contaminated with faeces or urine of cases or carriers. ïIndirect transmission:- Through ingestion of contaminated food, H2O, milk, Soil. ïFlies play a role in transmission.
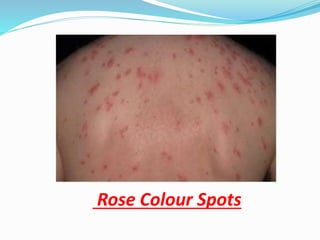
- 15. Clinical symptoms ï High fever ranges from 103-104°F (39° to 40°C) ï Weakness, headache, abdominal pain, loss of appetite. ï The patient looks: constipation, diarrhea. ï Rose colour spots appears in some cases.
- 16. Headache
- 17. High Fever
- 18. Weakness
- 19. Dry Cough
- 20. Abdominal Pain
- 21. Chest Congestion
- 23. Constipation
- 24. Complications ï Hallucination ï Endocarditis ï Myocarditis ï Pancreatitis ï Pneumonia ï Meningitis ï Bleeding in intestine ï Holes in intestine
- 25. Diagnosis ï Blood culture ï Stool culture ï Urine culture ï Bone marrow culture ï ELISA from blood (igM & igG) ï WIDAL test.
- 26. Treatement ï Activity- Rest is helpful. ï Medical Care- Antibiotics, Corticosteroids, Antipyretics. ï Diet- Fluid & electrolytes should be monitered. soft digestable food is preferred. * ï Surgical care- in case of intestinal perforation.
- 27. ï First line antibiotics- Choloramphenicol-oral, IV 500mg qid (50mg/kg in 4 doses) for 14 days. ï Trimethoprim-Sulphamethoxazole-Oral, IV 160-800mg bid(4-20mg/kg in 2 doses) 14 days. ï Ampicillin/Amoxycillin-Oral,IM,IV 1000-2000mg qid(50-100mg/kg in 4 doses for 14 days. ï 2nd line antibiotics- Ciprofloxacin Oral/IV 500mg bid or 200mg bid 10-14 days. ï Norfloxacin Oral 400mg bid 10 days.
- 28. Preventive measures ï Carriers should be prevented from handling food, milk, or water for others ï Isolation ï Disinfection ï Water sanitation ï Food sanitation ï Excretic disposal ï Fly control
- 29. Vaccines ï Two vaccines are given:
- 31. Summary and Conclusion ïžIntroduction ïžEpidemiological triad ïžPathophysiology ïžIncubation period ïžModes of transmission ïžClinical symptoms ïžDiagnosis ïžTreatement & prevention