ubaid afzal
- 1. Traumatic acid and plants ŌĆó Traumatic acid is a monounsaturated dicarboxylic acid naturally occurring in plants. ŌĆó The compound was first isolated from wounded bean plants by American chemists James English Jr. and James Frederick Bonner and Dutch scientist in 1939.
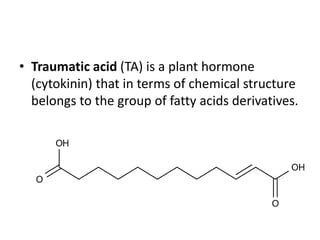
- 2. ŌĆó Traumatic acid (TA) is a plant hormone (cytokinin) that in terms of chemical structure belongs to the group of fatty acids derivatives.
- 3. CONTIŌĆ”.. ŌĆó Traumatic acid is biosynthesized in plants by non-enzymatic oxidation of traumatin. ŌĆó At normal conditions traumatic acid is a solid crystaline water insoluble substances. ŌĆó The salts and esters of traumatic acid are called traumatates.
- 4. CONTIŌĆ”. ŌĆó Traumatic acid is a potent wound healing agent in plants ("wound hormone") that stimulates cell division near a trauma site to form a protective callus and to heal the damaged tissue. It may also act as a growth hormone especially in inferior plants. ŌĆó For example; Algae
- 5. CONTIŌĆ” The first effect of TA in plants was found to be an intense stimulation of cell division within a wounded area. The formation of callus tissue Precursors of traumatic acid are 18-carbon non-saturated fatty acids: linolic and linolenic acids, which are released from membrane lipid fractions as a result of phospholipases A2 and D.
- 6. ŌĆó It is also known that these phospholipases are mainly activated as a reaction to an injury of the plant However, research carried out over the past several years has shown that the synthesis of traumatic acid is induced not only through injury, but also by other environmental stress factors such as high and low temperature or UV radiation or osmotic shock.