Umbilical artery doppler [1]
- 1. Umbilical artery doppler [1] Dr. Kamal Sayed MBBS MSc US UAA
- 2. INTRODUCTION • Non-invasive assessment of circulation • • Fetal circulatory system • • Umbilical artery • • Umbilical vein • • Aorta • • Heart • • Middle cerebral artery
- 3. Dopp Equation : fd = 2 ft v/c fd {dopp freq} / ft [transmitted freq] / v [sound speed]/ c [blood velocity] • Physics of doppler ultrasound • • Refers to the change in frequency wave transmission [ft] • when motion occurs b/w source of wave transmission & observer [rf]. • Dopp sfift frequency [fd] = [ft-fr] • • 1] US beam into 2] circulating blood 3] million red cell • 4] speed red cell movement [velocity of blood flow{c}]. • Speed of sound [v] • Dopp Equation : fd = 2 ft v/c • şÝşÝߣ [4] •
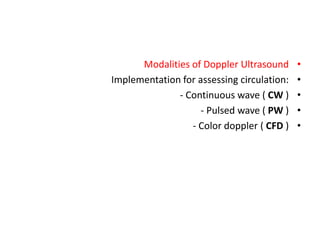
- 5. • Modalities of Doppler Ultrasound • Implementation for assessing circulation: • - Continuous wave ( CW ) • - Pulsed wave ( PW ) • - Color doppler ( CFD )
- 6. • Pulse wave : @ Vascular location. @ Interrogation deep vessel. şÝşÝߣ [7] • Continuous wave : @ Determining and monitoring fetal heart rate. @ Cannot identify exact location. şÝşÝߣ [8] • Color flow : @ estimation of mean doppler shifted frequency. • @ real time of 2 dimensional of anatomic structures. • @ Provide qualitative hemodynamic information • @ Presence and direction of blood flow. • şÝşÝߣ [9] • •
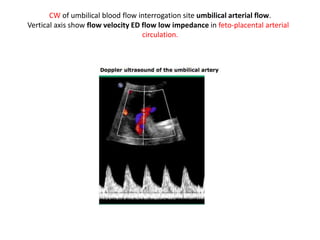
- 8. CW of umbilical blood flow interrogation site umbilical arterial flow. Vertical axis show flow velocity ED flow low impedance in feto-placental arterial circulation.
- 10. • Doppler waveform Analysis • • Reflect blood velocity in circulation. • • Presence and direction of flow • • Volume of flow • • Impedance • • Peak systolic frequency ( S ) • • End- diastolic frequency ( D ) • • Average frequency shift value over the cardiac cycle ( A ) • şÝşÝߣ [11] • •
- 12. • The commonly used obstetrical applications : • 1* (S/D) ratio = Peak systolic frequency shift TO end-diastolic frequency shift : [PSV/EDV]. • 2*(RI) Resistance index : Is the difference between peak systolic and end diastolic shift, divided by peak systolic shift [PSV – EDV / PSV]. • 3* (PI) Pulsatility index : is the difference between PSV & EDV divided by the time- average flow velocity • PI = (vmax - vmin) / (vmean) • # higher PI is associated with higher downstream vascular resistance.
- 13. • # UA doppler reflects resistance in the fetal side of the placenta. • # Uterine artery doppler reflects resistance in the maternal side of the placenta. • # MCA doppler reflects redistribution of blood flow. • # a simple Rule to remember : • UA S/D ratio should be under 3.0 [mean 2.5] after 30 wks gestation. • şÝşÝߣ [14/15]
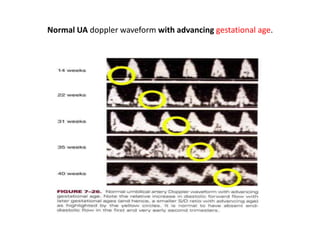
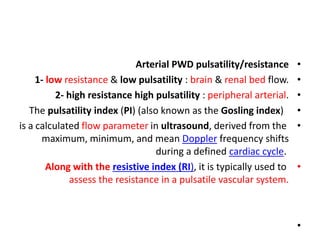
- 16. • Factor affecting the waveform • Gestational age • 1- EDV increase with gestation. • 2- Decline in feto-placental blood flow impedance • 3- Decline S/D Ratio and RI. • # there is relative increase in diastolic forward flow with later gestational ages [a smaller S/D ratio with advancing age] • # it normal to have absent ED flow in the 1ST & very early 2ND trimester. • slide [17] • •
- 17. Normal UA doppler waveform with advancing gestational age.
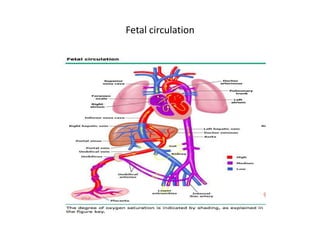
- 18. • Fetal circulation • *Umbilical cord Connects placenta to fetus. *oxygenated blood moves to the fetal circulation. • *Umbilical vein Carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus. • * Fetal circulation pathway : • *placenta * umbilical vein * ductus venosus ( shunt 1, : shunts blood away from the fetus' liver) * inferior vena cava (oxygenated blood mixes with venous) * right atrium thru foramen ovale ( shunt 2)
- 19. • * some blood flows to the right ventricle to the lungs * ductus arteriosus ( shunt 3) shunts blood away from fetus lung to the aorta * left atrium (blood from pulmonary veins and foramen ovale) to left ventricle to aorta • Name the 3 shunts in the fetal circulation pathway ? • 1) ductus venosus 2) foramen ovale 3) ductus arteriosus
- 20. • *Ductus venosus shunts (#1) blood Away from the fetus' liver. • *Foramen ovale shunts (#2) opens to the Right and left atrium Moves blood to right and left atrium • *Ductus arteriosus shunts (3) Blood away from the fetus lung to the aorta. • Why do fetus have shunts ? • Because that organ is not in use [Liver and lung]
- 21. • *Tearing of the uterine wall [Placenta abruptia]. • *Placenta previa [Is when the placenta is delivered before the fetus]. • Outcome of placenta problems : • * Fetal asphyxia * increased risk of brain damage * respiratory distress in immediate post natal period •
- 23. • Arterial PWD pulsatility/resistance • 1- low resistance & low pulsatility : brain & renal bed flow. • 2- high resistance high pulsatility : peripheral arterial. • The pulsatility index (PI) (also known as the Gosling index) • is a calculated flow parameter in ultrasound, derived from the maximum, minimum, and mean Doppler frequency shifts during a defined cardiac cycle. • Along with the resistive index (RI), it is typically used to assess the resistance in a pulsatile vascular system. •
- 24. • The pulsatility index is the difference between systolic flow • velocity and diastolic flow velocity, divided by the time- averaged flow velocity, and is related to downstream vascular resistance (higher pulsatility index is associated with higher downstream vascular resistance). • PULSATILITY INDEX : PI = (vmax - vmin) / (vmean)
- 25. • Umbilical artery (UA) Doppler indices, i.e., pulsatility index (PI), resistance index (RI), and systolic/diastolic ratio (S/D) calculated from blood flow velocities, are used as an important clinical tool for evaluating fetal wellbeing in high- risk pregnancies and to predict outcome of growth restricted fetuses. • The purpose of this study was to determine the range, mean and standard deviations of pulsatility index (PI), resistance index (RI) and systolic/diastolic (S/D) ratio of the uterine artery at 22nd & 23rd weeks of pregnancy with normal as well as those with abnormal outcome.
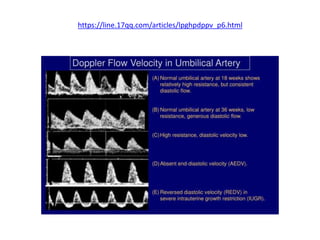
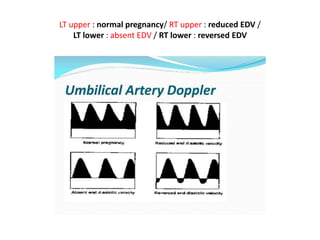
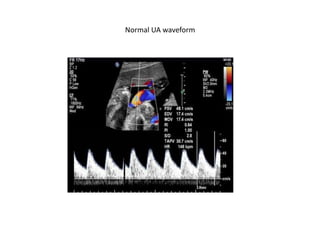
- 26. • What is normal umbilical artery Doppler? • @ The umbilical arterial waveform usually has : • 1- a "sawtooth" pattern • 2- with flow always in the forward direction, that is towards the placenta. • @ An abnormal UA waveform shows : • Absent OR reversed diastolic flow. • [Before the 15th week, the absence of diastolic flow may be a normal finding.] • şÝşÝߣ [18]
- 27. Normal Umbilical Artery Doppler
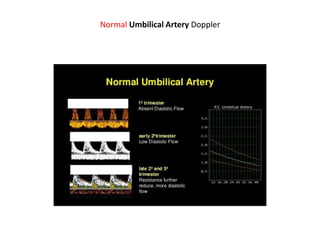
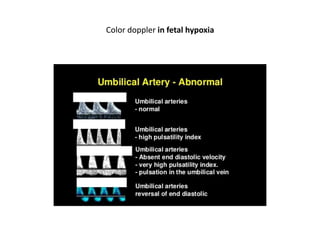
- 28. Color doppler in fetal hypoxia
- 30. LT upper : normal pregnancy/ RT upper : reduced EDV / LT lower : absent EDV / RT lower : reversed EDV
- 31. • Uterine artery PI provides a measure of uteroplacental perfusion and high PI implies impaired placentation with consequent increased risk of developing @ preeclampsia, @fetal growth restriction, @ abruption @ and stillbirth. • The uterine artery PI is considered to be increased if it is above the 90th centile. • Low-dose aspirin [LDA] and omega-3 fatty acids improve uterine artery blood flow velocity in women with recurrent miscarriage due to impaired uterine perfusion .
- 32. • Umbilical arterial (UA) Doppler assessment is used in surveillance of fetal well-being in the third trimester of pregnancy. Abnormal umbilical artery Doppler is a marker of placental insufficiency and consequent intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or suspected pre-eclampsia. • Umbilical artery Doppler assessment has been shown to reduce perinatal mortality and morbidity in high-risk obstetric situations.
- 33. • The spectral Doppler indices measured at the fetal end, the free loop, and the placental end of the umbilical cord are different with the impedance highest at the fetal end. • The changes in the indices are likely to be seen at the fetal end first. • Ideally, the measurements should be made in the free cord, however, for consistency of recording in cases being followed up, a fixed site would be more appropriate, i.e. fetal end, placental end, or intra-abdominal portion. • Due to difficulty with measuring the cord at the fetal end in many IUGR fetuses, measurement in a free loop is acceptable .
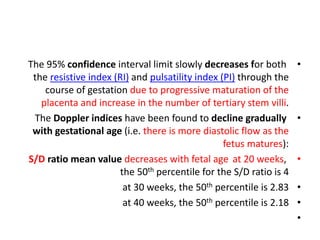
- 34. • The 95% confidence interval limit slowly decreases for both the resistive index (RI) and pulsatility index (PI) through the course of gestation due to progressive maturation of the placenta and increase in the number of tertiary stem villi. • The Doppler indices have been found to decline gradually with gestational age (i.e. there is more diastolic flow as the fetus matures): • S/D ratio mean value decreases with fetal age at 20 weeks, the 50th percentile for the S/D ratio is 4 • at 30 weeks, the 50th percentile is 2.83 • at 40 weeks, the 50th percentile is 2.18 •
- 35. • RI mean value decreases from 0.756 to 0.609 • PI mean value decreases from 1.270 to 0.967 • Classification of severity • 1- In IUGR fetuses AND fetuses developing intrauterine distress, the UA blood velocity waveform usually changes in a progressive manner as below : • @ reduction in end-diastolic flow : increasing RI values, PI values, and S/D ratio • @ absent end-diastolic flow (AEDF): RI = 1 • @ reversal of end-diastolic flow (REDF)
- 36. • 2- Abnormal UA Doppler is an indication of further sonographic workup of the degree of placental insufficiency: • @ fetal MCA Doppler assessment • @ ductus venosus flow assessment • @ umbilical venous flow assessment • 3- Change in blood flow impedance in fetal regional circulation underlie this phenomenon. • 4- Doppler shows circulatory changes associated with fetal compromise and perinatal prognostication. • • şÝşÝߣ [37]
- 39. IUGR [UA]
- 40. • Sequence changes in FHR, doppler findings, biophysical parameters • 1- reflect fetal homeostatic response to chronic hypoxia. • 2- Abnormal elevation of doppler : @ precede loss of variability and reactivity. • 3- leading to decline and loss of fetal breathing and movements.
- 41. POOR OUTCOME! • “Death occurs if there are no interventions” when : • 1- Reversed end diastolic velocity in the umbilical artery • 2- Absence or reversed atrial wave in the ductus venosus. • 3- Rapid Loss of hear rate variability.
- 46. • Doppler velocimetry of UA provide a noninvasive measure of the fetopacental hemodynamic state. • • UA Doppler reflect impedance of downstream circulation • • Abnormality of doppler correlated to fetoplacental vascular • maldevelopment (Fetal hypoxia, fetal acidosis and adverse perinatal outcome). • • In Pregnancy complicated by fetal growth restriction or preeclampsia at >34 wga result in AEDV or REDV which will recommend prompt delivery rather than expectant management. • •
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]
Dr. Kamal Sayed MBBS MSc US UAA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-1-320.jpg)

![Dopp Equation : fd = 2 ft v/c
fd {dopp freq} / ft [transmitted freq] / v [sound speed]/ c [blood velocity]
•
Physics of doppler ultrasound
•
• Refers to the change in frequency wave transmission [ft]
•
when motion occurs b/w source of wave transmission &
observer [rf].
•
Dopp sfift frequency [fd] = [ft-fr]
•
• 1] US beam into 2] circulating blood 3] million red cell
•
4] speed red cell movement [velocity of blood flow{c}].
•
Speed of sound [v]
•
Dopp Equation : fd = 2 ft v/c
•
şÝşÝߣ [4]
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-3-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-4-320.jpg)
![•
Pulse wave : @ Vascular location. @ Interrogation deep
vessel. şÝşÝߣ [7]
•
Continuous wave : @ Determining and monitoring fetal
heart rate. @ Cannot identify exact location. şÝşÝߣ [8]
•
Color flow : @ estimation of mean doppler shifted
frequency.
•
@ real time of 2 dimensional of anatomic structures.
•
@ Provide qualitative hemodynamic information
•
@ Presence and direction of blood flow.
•
şÝşÝߣ [9]
•
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-6-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-7-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-9-320.jpg)
![•
Doppler waveform Analysis
•
• Reflect blood velocity in circulation.
•
• Presence and direction of flow
•
• Volume of flow
•
• Impedance
•
• Peak systolic frequency ( S )
•
• End- diastolic frequency ( D )
•
• Average frequency shift value over the cardiac cycle ( A )
•
şÝşÝߣ [11]
•
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-10-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-11-320.jpg)
![•
The commonly used obstetrical applications :
•
1* (S/D) ratio = Peak systolic frequency shift TO end-diastolic
frequency shift : [PSV/EDV].
•
2*(RI) Resistance index : Is the difference between peak
systolic and end diastolic shift, divided by peak systolic shift
[PSV – EDV / PSV].
•
3* (PI) Pulsatility index : is the difference between PSV & EDV
divided by the time- average flow velocity
•
PI = (vmax - vmin) / (vmean)
•
# higher PI is associated with higher downstream vascular
resistance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-12-320.jpg)
![•
# UA doppler reflects resistance in the fetal side of the
placenta.
•
# Uterine artery doppler reflects resistance in the maternal
side of the placenta.
•
# MCA doppler reflects redistribution of blood flow.
•
# a simple Rule to remember :
•
UA S/D ratio should be under 3.0 [mean 2.5] after 30 wks
gestation.
•
şÝşÝߣ [14/15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-13-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-14-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-15-320.jpg)
![•
Factor affecting the waveform
•
Gestational age
•
1- EDV increase with gestation.
•
2- Decline in feto-placental blood flow impedance
•
3- Decline S/D Ratio and RI.
•
# there is relative increase in diastolic forward flow with later
gestational ages [a smaller S/D ratio with advancing age]
•
# it normal to have absent ED flow in the 1ST & very early 2ND
trimester.
•
slide [17]
•
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-16-320.jpg)


![•
*Ductus venosus shunts (#1) blood Away from the fetus' liver.
•
*Foramen ovale shunts (#2) opens to the Right and left atrium
Moves blood to right and left atrium
•
*Ductus arteriosus shunts (3) Blood away from the fetus lung
to the aorta.
•
Why do fetus have shunts ?
•
Because that organ is not in use
[Liver and lung]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-20-320.jpg)
![•
*Tearing of the uterine wall [Placenta abruptia].
•
*Placenta previa [Is when the placenta is delivered before the
fetus].
•
Outcome of placenta problems :
•
* Fetal asphyxia
* increased risk of brain damage
* respiratory distress in immediate post natal period
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-21-320.jpg)


![•
What is normal umbilical artery Doppler?
•
@ The umbilical arterial waveform usually has :
•
1- a "sawtooth" pattern
•
2- with flow always in the forward direction, that is towards
the placenta.
•
@ An abnormal UA waveform shows :
•
Absent OR reversed diastolic flow.
•
[Before the 15th week, the absence of diastolic flow may be
a normal finding.]
•
şÝşÝߣ [18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-26-320.jpg)
![•
Uterine artery PI provides a measure of uteroplacental
perfusion and high PI implies impaired placentation with
consequent increased risk of developing @ preeclampsia,
@fetal growth restriction, @ abruption @ and stillbirth.
•
The uterine artery PI is considered to be increased if it is
above the 90th centile.
•
Low-dose aspirin [LDA] and omega-3 fatty acids improve
uterine artery blood flow velocity in women with recurrent
miscarriage due to impaired uterine perfusion .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-31-320.jpg)



![•
2- Abnormal UA Doppler is an indication of further
sonographic workup of the degree of placental insufficiency:
•
@ fetal MCA Doppler assessment
•
@ ductus venosus flow assessment
•
@ umbilical venous flow assessment
•
3- Change in blood flow impedance in fetal regional
circulation underlie this phenomenon.
•
4- Doppler shows circulatory changes associated with fetal
compromise and perinatal prognostication.
•
•
şÝşÝߣ [37]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-36-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-37-320.jpg)
![IUGR [UA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-39-320.jpg)


![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-42-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-43-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-44-320.jpg)
![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-45-320.jpg)

![Umbilical artery doppler [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbilicalarterydoppler1-210517112207/85/Umbilical-artery-doppler-1-47-320.jpg)