Unbalanced assignment problem
0 likes636 views
an unbalanced assignment model problem (operations research), solved
1 of 4
Download to read offline

Ad
Recommended
Dividend Decisions By Reliance Industries
Dividend Decisions By Reliance IndustriesAkshay69Bhatia
╠²
The document discusses the dividend decisions of Reliance Industries Ltd over 4 years from 2005-2009. Some key points:
- RIL's dividend payout ratio increased from 100% to 130% from 2005-2008 tracking the increase in EPS, but remained at 130% in 2009 even as EPS declined.
- RIL's high retention rate of over 85% each year has allowed it to undertake major expansion projects, contributing to rising share prices even with low dividends.
- Models like Walter and Gordon show how high returns on reinvested earnings can increase share prices despite low payouts, in line with RIL's performance.RFID at the Metro
RFID at the MetroVivor Kuotsu
╠²
The document discusses Metro Group's implementation of RFID technology. Metro Group is Germany's largest retailer with over 2,300 locations across 30 countries. In early 2004, Metro announced plans to rollout RFID at the pallet and case level across 250 stores and 10 warehouses in collaboration with 100 suppliers. The initial rollout faced problems with tag quality and reader accuracy. Later, Metro expanded RFID tagging to case level which provided more benefits but also required more investment. Financial analysis showed Metro's total cash flow and sales increased after implementing RFID. For next steps, the document recommends expanding pallet tagging while gradually introducing case tagging with key suppliers.Differentiation strategy
Differentiation strategyProf.(Dr.) Nitin Zaware
╠²
The document discusses differentiation strategy as a means for firms to gain competitive advantage by adding unique value to products or services. It outlines the advantages of differentiation, such as reduced rivalry and increased customer loyalty, while also noting limitations like the difficulty of sustaining differentiation and the risk of imitation by competitors. The content emphasizes the importance of effectively communicating the differentiation benefits to maintain consumer perception of value.CSR activity of International Business Machine (IBM). Information about how c...
CSR activity of International Business Machine (IBM). Information about how c...Hitarth Patel
╠²
IBM's Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) strategy emphasizes sustainability and stakeholder engagement in areas such as environmental conservation, community support, supplier standards, and employee welfare. The company implements numerous programs focused on minimizing environmental impacts, enhancing supplier relationships, and fostering community development through education and entrepreneurship initiatives. Through these efforts, IBM aims to achieve corporate citizenship while ensuring profitability and addressing the interests of its diverse stakeholders.Strategic control
Strategic controlVidhu Arora
╠²
Strategic control involves tracking a strategy as it is implemented, detecting problems or changes, and making adjustments. It has several purposes, including helping achieve goals by monitoring and evaluating the strategic management process. There are different types of strategic control, including premise control to test assumptions, implementation control to monitor plans, strategic surveillance for broad monitoring, and special alert control for rapid response to unexpected events. Strategic control is meant to continually assess changes and their impact on an organization's strategy.Questionnaire
QuestionnaireMeghraj Choudhary
╠²
This document contains a questionnaire about customer brand loyalty and purchasing decisions. It asks respondents questions about which brand attributes are most important to them, what influences their decisions to purchase certain brands over others, and how much brand name, quality, price, features, family/peer opinions, and advertisements impact their choices. It also collects demographic information about respondents like their name, address, education, occupation, age, and monthly income.Business policy & strategic management
Business policy & strategic managementShashankdiv
╠²
This document discusses business policy and strategic management. It begins by defining business policy as guidelines that govern an organization's actions and define decision-making boundaries. It then discusses strategic management, including defining corporate and business unit strategies. It also covers Mintzberg's five perspectives of strategy - plan, ploy, pattern, position, and perspective. Finally, it discusses the importance of vision, mission, and objective statements in guiding an organization's strategic direction.Ikea - A case study in stimulating innovation and change
Ikea - A case study in stimulating innovation and changeAnkit Uttam
╠²
IKEA is used as a case study of a company that successfully stimulates innovation and change. IKEA communicates its innovation strategy widely and partners everyone in developing the strategy. Some innovations IKEA has implemented include popup advertising, moving showrooms, and storage balconies. In contrast, Kodak failed to inject innovations into its products and lost market share as a result. The document outlines six ways companies can stimulate innovation, such as being open to new ideas, uncovering change champions, and allowing occasional failures by taking risks. Barriers to innovation include inadequate funding, closed-mindedness, and inflexible processes.Operations Research - Application and Scope in Business Areas
Operations Research - Application and Scope in Business AreasSundar B N
╠²
Operation research is an analytical method used to solve problems and make decisions in organizations. It involves breaking problems down into basic components and solving them through mathematical analysis. The main objective is to find the optimal solution given limited resources. Operation research can be applied to many business areas, including accounting, finance, production, marketing, personnel planning, and more. It has also been used successfully in industries like airlines, telecommunications, manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation.merger & aquisitions ppt.
merger & aquisitions ppt.Vijaykumar Nishad
╠²
This document summarizes key topics related to mergers and acquisitions including:
- Definitions of mergers, acquisitions, and takeovers.
- Advantages like legal simplicity and increased net worth for shareholders, and disadvantages like requiring shareholder approval.
- Types of mergers like horizontal, vertical, and conglomerate mergers.
- Types of acquisitions like friendly and hostile acquisitions.
- Reasons for acquisitions like increased market power and speed to market, and problems with acquisitions like integration difficulties and inability to achieve synergies.
- Case examples are provided to illustrate various concepts.Public Relations in IMC
Public Relations in IMCAditya Sheth
╠²
This document discusses the role and importance of public relations (PR) in integrated marketing communication, highlighting its functions such as promoting goodwill, managing corporate communications, and addressing negative publicity. It emphasizes the advantages of PR, including credibility and cost-effectiveness, while also noting challenges like the difficulty in quantifying benefits. The Als Ice Bucket Challenge is cited as a successful PR case study, illustrating the effectiveness of engaging communities and harnessing organic content for awareness and fundraising.Organisation ethics development system
Organisation ethics development systemHamza Ali
╠²
This document outlines the important elements of an Organization Ethics Development System (OEDS), including moral leadership, regular assessment, an ethics steering committee, written codes of conduct, preventative steps, ethics training, nominating an ethics officer, and establishing ethics reporting and conflict resolution processes. It also emphasizes the need for ongoing ethics audits and evaluations.Sickness in small scale industries
Sickness in small scale industries Lakshmi Mohan
╠²
The document defines industrial sickness as an industrial company that has accumulated losses exceeding its net worth for two consecutive years and has suffered cash losses. It lists several signs of industrial sickness including declining capacity utilization, liquidity shortages, and failure to maintain proper financial records or pay statutory dues. Internal causes include lack of financing, poor production policies, ineffective marketing and personnel management, and weak corporate management. External causes include constraints related to labor, marketing, production, and access to financing. Industrial sickness can result in huge financial losses, job losses, reduced investment and tax revenue. Early identification and interventions such as infrastructure improvements, technology upgrades, marketing assistance and government review can help address industrial sickness.GreinerŌĆÖs Growth Curve
GreinerŌĆÖs Growth CurveStephen Dann
╠²
Greiner's Growth Curve model identifies five phases of growth that a company passes through: 1) Creativity, 2) Direction, 3) Delegation, 4) Coordination, and 5) Collaboration. Each phase has a period of stability and evolution that ends with a period of crisis or turmoil that must be resolved for the company to progress to the next phase. The model helps understand organizational problems companies may face during rapid growth periods.Estrategia de sostenibilidad 2020, GRUPO IKEA
Estrategia de sostenibilidad 2020, GRUPO IKEAIKEA Espa├▒a
╠²
The IKEA Group's sustainability strategy for 2020, titled 'People & Planet Positive,' aims to drive innovation and transform the business to promote a sustainable future. The strategy emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices such as resource and energy independence, community engagement, and creating products that enable customers to live sustainably at home. By collaborating with various stakeholders and implementing responsible practices, IKEA intends to strengthen its competitiveness while maintaining a positive impact on people and the planet.HPL_Group I Case Analysis_Nutrifix Ghana_26.03.15.v1.0
HPL_Group I Case Analysis_Nutrifix Ghana_26.03.15.v1.0Alexander Martinus Christian, S.H., MBA
╠²
The document discusses an investment opportunity in Ghana offered by the Ghanaian government to the fertilizer company Nitrofix to establish a fertilizer plant. It provides background information on Ghana's economy, politics, investment policies, and fertilizer market in the early 1980s. It also outlines three potential investment structures - a private enterprise fully owned by Nitrofix, a joint state enterprise owned by both Nitrofix and Ghana, and Nitrofix operating the plant as contractors while Ghana owns the physical assets - for Nitrofix advisor Craig Michael Lee to consider in making an investment recommendation.The Dilemmas of Innovation Management
The Dilemmas of Innovation ManagementIBM Research
╠²
IBM faces three main dilemmas in managing innovation: balancing bottom-up and top-down approaches; focusing on long-term research versus short-term success; and determining how open to be with innovation versus developing proprietary intellectual property. Successfully navigating these tensions is key to innovation success. The document discusses IBM's efforts to balance these dilemmas through collaborative open innovation with partners while still generating patents and intellectual property.Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibilityshrinivas kulkarni
╠²
This document outlines a lecture on corporate social responsibility (CSR). It discusses the types and nature of social responsibilities, CSR principles and strategies, models of CSR, best practices, the need for CSR, and arguments for and against CSR. The key models discussed are the Friedman model, Ackerman model, Carroll model, environmental integrity and community model, and the stockholders and stakeholders model. The document also provides examples of CSR practices by companies like IBM UK and Avon, and issues faced by companies like Coca-Cola and Nike regarding their social responsibilities.Dell Case Study
Dell Case StudyRaminder Pal Singh
╠²
Dell was founded in 1984 on a direct business model that sells computer systems directly to customers. This eliminates retailers and allows Dell to build each system to order based on customer specifications. Dell also introduces new technology faster than competitors. Dell grew rapidly in the 1980s-1990s and became the largest PC seller. It introduced online sales in 1996. Dell's configure-to-order and just-in-time manufacturing approaches minimize inventory costs. Dell gains benefits like cash flow, reduced costs, strong customer relationships, and demand forecasting from its direct model. It drives innovation through customer feedback.CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY ARGUMENTS FOR AND AGAINST
CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY ARGUMENTS FOR AND AGAINSTSundar B N
╠²
This document discusses corporate social responsibility (CSR). It defines CSR as a company's commitment to operate ethically and contribute to sustainable development by improving life for its employees, their families, local communities, and society. The document outlines the meaning and definition of CSR, arguments for and against requiring CSR, and how CSR is addressed in Indian law. It concludes that standardizing CSR processes will make CSR easier to implement in the future as industry participates in economic growth globally.Business Ethics and Corporate Excellence
Business Ethics and Corporate ExcellenceRajiv Sikroria
╠²
The document discusses ethics and corporate excellence in business. It outlines ethical issues like bribery, insider trading, and discrimination. It also discusses factors for corporate excellence like leadership, customer focus, quality assurance, and social responsibility. The document provides examples of companies implementing ethics and social responsibility programs, such as Tata Group's code of ethical practices and Starbucks' sustainably sourced coffee.Emerging technology trends for the entrepreneur
Emerging technology trends for the entrepreneurBala Iyer
╠²
The document discusses major technology trends for entrepreneurial leaders to understand, including:
1. The rise of utility platforms and platform-based competition which rewards agility
2. The disintegration of organizational boundaries through digital spaces which can lower costs
3. The explosion of data enabling personalization through analytics for customer satisfaction
4. The increasingly connected world through networks which provides access to resources
5. Knowledge is being democratized through open sources rewarding learning organizationsGroup 3 salmon and tordjman as on 19th july 16
Group 3 salmon and tordjman as on 19th july 16Lalitha Sri Pulipati
╠²
The document discusses Salmon and Tordjman's 1989 classification of retail internationalization theories. It identifies two main strategies: global and multinational. The global strategy replicates a retailer's formula worldwide with standardized marketing and centralized management to achieve economies of scale. Multinational retailers maintain some common elements but also adapt to local conditions, giving more autonomy to foreign subsidiaries. Examples of global retailers include Benetton, Ikea, and McDonald's, while multinational retailers include C&A, Carrefour, and Auchan. The classification provides a framework but has limitations like discouraging localization.Wipro ethics
Wipro ethicsKIIT University
╠²
Wipro is an Indian multinational corporation that provides IT, consulting and business process services. It was founded in 1945 as Western India Vegetable Products Limited and later changed its name to Wipro Limited in 1982. The company initially manufactured vegetable oils but shifted focus to IT services in the 1970s and 1980s. Some key points:
- Wipro has a workforce of over 140,000 employees serving clients in 61 countries. It provides a wide range of products and services including IT services, business process outsourcing, consulting, and more.
- The company emphasizes business ethics and corporate social responsibility. It was the first Indian company to establish a code of business conduct and introduces programs like its ombudsman processReason of merger
Reason of mergerDharmik
╠²
Mergers allow companies to increase in value by combining resources, achieve better financial planning through diversification of operations, and realize economies of scale by utilizing combined production and distribution networks. Mergers also enable growth through external expansion and expertise in new areas, as well as stabilization through diversifying business scopes and consistently earning profits despite economic fluctuations. However, mergers can negatively impact the national economy, eliminate healthy competition from smaller competitors, and lead to monopolies through excessive concentration of economic power which is undesirable for customers.What is CSR and Why is it Important
What is CSR and Why is it ImportantFrontStream
╠²
The document discusses Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as a corporation's commitment to the community and sustainable practices, highlighting its importance for brand trust and shareholder engagement. It details frameworks for CSR action, core facets including sustainability, legal compliance, and employee well-being, as well as implementation strategies for both small and large businesses. The content emphasizes the significance of aligning business operations with socially responsible practices to enhance community relations and long-term success.Technological environment
Technological environmentanmolverma24
╠²
The document discusses the technological environment and the impact of technology. It defines technology and classifies it into different categories. It then describes the five stages of the technology cycle - awareness, acquisition, adaptation, advancement, and abandonment. Next, it discusses the impact of technology in three areas: social implications, economic implications, and plant-level changes. Some key impacts mentioned are increased productivity, need for R&D spending, jobs becoming more intellectual, and changes to organization structure.Corporate sickness
Corporate sicknessMaica Batiancela
╠²
Corporate sickness is a significant problem, with many large and medium sized companies in India considered sick. Sickness can be caused by both internal factors like poor management and external factors like increased competition. While some sick organizations have been successfully turned around, others have not recovered their past success. Early indicators of potential sickness include declining earnings ratios and worsening debt and liability ratios. Strategic management practices aim to put organizations on a path of sustainable growth.Vam
VamAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document discusses determining initial basic feasible solutions for a transportation problem using VogelŌĆÖs Approximation Method and the North-West Corner Rule. It provides a structured table with costs, availability, and requirements for different origins and destinations. The total transportation cost is calculated to be 190.Simplex method maximisation
Simplex method maximisationAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document summarizes the simplex method for solving linear programming problems involving maximization. It involves 12 steps: 1) Formulating the LPP, 2) Introducing slack, surplus and artificial variables, 3) Formulating the initial basic solution, 4) Constructing the initial simplex table, 5) Checking for positive elements in the Cj-Zj row, 6) Identifying the incoming basic variable, 7) Choosing the incoming basic variable if multiple positives exist, 8) Identifying the outgoing basic variable, 9) Constructing the next simplex table using row operations, 10) Completing the new simplex table, 11) Repeating steps 5-10, and 12) Terminating when theMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Operations Research - Application and Scope in Business Areas
Operations Research - Application and Scope in Business AreasSundar B N
╠²
Operation research is an analytical method used to solve problems and make decisions in organizations. It involves breaking problems down into basic components and solving them through mathematical analysis. The main objective is to find the optimal solution given limited resources. Operation research can be applied to many business areas, including accounting, finance, production, marketing, personnel planning, and more. It has also been used successfully in industries like airlines, telecommunications, manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation.merger & aquisitions ppt.
merger & aquisitions ppt.Vijaykumar Nishad
╠²
This document summarizes key topics related to mergers and acquisitions including:
- Definitions of mergers, acquisitions, and takeovers.
- Advantages like legal simplicity and increased net worth for shareholders, and disadvantages like requiring shareholder approval.
- Types of mergers like horizontal, vertical, and conglomerate mergers.
- Types of acquisitions like friendly and hostile acquisitions.
- Reasons for acquisitions like increased market power and speed to market, and problems with acquisitions like integration difficulties and inability to achieve synergies.
- Case examples are provided to illustrate various concepts.Public Relations in IMC
Public Relations in IMCAditya Sheth
╠²
This document discusses the role and importance of public relations (PR) in integrated marketing communication, highlighting its functions such as promoting goodwill, managing corporate communications, and addressing negative publicity. It emphasizes the advantages of PR, including credibility and cost-effectiveness, while also noting challenges like the difficulty in quantifying benefits. The Als Ice Bucket Challenge is cited as a successful PR case study, illustrating the effectiveness of engaging communities and harnessing organic content for awareness and fundraising.Organisation ethics development system
Organisation ethics development systemHamza Ali
╠²
This document outlines the important elements of an Organization Ethics Development System (OEDS), including moral leadership, regular assessment, an ethics steering committee, written codes of conduct, preventative steps, ethics training, nominating an ethics officer, and establishing ethics reporting and conflict resolution processes. It also emphasizes the need for ongoing ethics audits and evaluations.Sickness in small scale industries
Sickness in small scale industries Lakshmi Mohan
╠²
The document defines industrial sickness as an industrial company that has accumulated losses exceeding its net worth for two consecutive years and has suffered cash losses. It lists several signs of industrial sickness including declining capacity utilization, liquidity shortages, and failure to maintain proper financial records or pay statutory dues. Internal causes include lack of financing, poor production policies, ineffective marketing and personnel management, and weak corporate management. External causes include constraints related to labor, marketing, production, and access to financing. Industrial sickness can result in huge financial losses, job losses, reduced investment and tax revenue. Early identification and interventions such as infrastructure improvements, technology upgrades, marketing assistance and government review can help address industrial sickness.GreinerŌĆÖs Growth Curve
GreinerŌĆÖs Growth CurveStephen Dann
╠²
Greiner's Growth Curve model identifies five phases of growth that a company passes through: 1) Creativity, 2) Direction, 3) Delegation, 4) Coordination, and 5) Collaboration. Each phase has a period of stability and evolution that ends with a period of crisis or turmoil that must be resolved for the company to progress to the next phase. The model helps understand organizational problems companies may face during rapid growth periods.Estrategia de sostenibilidad 2020, GRUPO IKEA
Estrategia de sostenibilidad 2020, GRUPO IKEAIKEA Espa├▒a
╠²
The IKEA Group's sustainability strategy for 2020, titled 'People & Planet Positive,' aims to drive innovation and transform the business to promote a sustainable future. The strategy emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices such as resource and energy independence, community engagement, and creating products that enable customers to live sustainably at home. By collaborating with various stakeholders and implementing responsible practices, IKEA intends to strengthen its competitiveness while maintaining a positive impact on people and the planet.HPL_Group I Case Analysis_Nutrifix Ghana_26.03.15.v1.0
HPL_Group I Case Analysis_Nutrifix Ghana_26.03.15.v1.0Alexander Martinus Christian, S.H., MBA
╠²
The document discusses an investment opportunity in Ghana offered by the Ghanaian government to the fertilizer company Nitrofix to establish a fertilizer plant. It provides background information on Ghana's economy, politics, investment policies, and fertilizer market in the early 1980s. It also outlines three potential investment structures - a private enterprise fully owned by Nitrofix, a joint state enterprise owned by both Nitrofix and Ghana, and Nitrofix operating the plant as contractors while Ghana owns the physical assets - for Nitrofix advisor Craig Michael Lee to consider in making an investment recommendation.The Dilemmas of Innovation Management
The Dilemmas of Innovation ManagementIBM Research
╠²
IBM faces three main dilemmas in managing innovation: balancing bottom-up and top-down approaches; focusing on long-term research versus short-term success; and determining how open to be with innovation versus developing proprietary intellectual property. Successfully navigating these tensions is key to innovation success. The document discusses IBM's efforts to balance these dilemmas through collaborative open innovation with partners while still generating patents and intellectual property.Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibilityshrinivas kulkarni
╠²
This document outlines a lecture on corporate social responsibility (CSR). It discusses the types and nature of social responsibilities, CSR principles and strategies, models of CSR, best practices, the need for CSR, and arguments for and against CSR. The key models discussed are the Friedman model, Ackerman model, Carroll model, environmental integrity and community model, and the stockholders and stakeholders model. The document also provides examples of CSR practices by companies like IBM UK and Avon, and issues faced by companies like Coca-Cola and Nike regarding their social responsibilities.Dell Case Study
Dell Case StudyRaminder Pal Singh
╠²
Dell was founded in 1984 on a direct business model that sells computer systems directly to customers. This eliminates retailers and allows Dell to build each system to order based on customer specifications. Dell also introduces new technology faster than competitors. Dell grew rapidly in the 1980s-1990s and became the largest PC seller. It introduced online sales in 1996. Dell's configure-to-order and just-in-time manufacturing approaches minimize inventory costs. Dell gains benefits like cash flow, reduced costs, strong customer relationships, and demand forecasting from its direct model. It drives innovation through customer feedback.CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY ARGUMENTS FOR AND AGAINST
CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY ARGUMENTS FOR AND AGAINSTSundar B N
╠²
This document discusses corporate social responsibility (CSR). It defines CSR as a company's commitment to operate ethically and contribute to sustainable development by improving life for its employees, their families, local communities, and society. The document outlines the meaning and definition of CSR, arguments for and against requiring CSR, and how CSR is addressed in Indian law. It concludes that standardizing CSR processes will make CSR easier to implement in the future as industry participates in economic growth globally.Business Ethics and Corporate Excellence
Business Ethics and Corporate ExcellenceRajiv Sikroria
╠²
The document discusses ethics and corporate excellence in business. It outlines ethical issues like bribery, insider trading, and discrimination. It also discusses factors for corporate excellence like leadership, customer focus, quality assurance, and social responsibility. The document provides examples of companies implementing ethics and social responsibility programs, such as Tata Group's code of ethical practices and Starbucks' sustainably sourced coffee.Emerging technology trends for the entrepreneur
Emerging technology trends for the entrepreneurBala Iyer
╠²
The document discusses major technology trends for entrepreneurial leaders to understand, including:
1. The rise of utility platforms and platform-based competition which rewards agility
2. The disintegration of organizational boundaries through digital spaces which can lower costs
3. The explosion of data enabling personalization through analytics for customer satisfaction
4. The increasingly connected world through networks which provides access to resources
5. Knowledge is being democratized through open sources rewarding learning organizationsGroup 3 salmon and tordjman as on 19th july 16
Group 3 salmon and tordjman as on 19th july 16Lalitha Sri Pulipati
╠²
The document discusses Salmon and Tordjman's 1989 classification of retail internationalization theories. It identifies two main strategies: global and multinational. The global strategy replicates a retailer's formula worldwide with standardized marketing and centralized management to achieve economies of scale. Multinational retailers maintain some common elements but also adapt to local conditions, giving more autonomy to foreign subsidiaries. Examples of global retailers include Benetton, Ikea, and McDonald's, while multinational retailers include C&A, Carrefour, and Auchan. The classification provides a framework but has limitations like discouraging localization.Wipro ethics
Wipro ethicsKIIT University
╠²
Wipro is an Indian multinational corporation that provides IT, consulting and business process services. It was founded in 1945 as Western India Vegetable Products Limited and later changed its name to Wipro Limited in 1982. The company initially manufactured vegetable oils but shifted focus to IT services in the 1970s and 1980s. Some key points:
- Wipro has a workforce of over 140,000 employees serving clients in 61 countries. It provides a wide range of products and services including IT services, business process outsourcing, consulting, and more.
- The company emphasizes business ethics and corporate social responsibility. It was the first Indian company to establish a code of business conduct and introduces programs like its ombudsman processReason of merger
Reason of mergerDharmik
╠²
Mergers allow companies to increase in value by combining resources, achieve better financial planning through diversification of operations, and realize economies of scale by utilizing combined production and distribution networks. Mergers also enable growth through external expansion and expertise in new areas, as well as stabilization through diversifying business scopes and consistently earning profits despite economic fluctuations. However, mergers can negatively impact the national economy, eliminate healthy competition from smaller competitors, and lead to monopolies through excessive concentration of economic power which is undesirable for customers.What is CSR and Why is it Important
What is CSR and Why is it ImportantFrontStream
╠²
The document discusses Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as a corporation's commitment to the community and sustainable practices, highlighting its importance for brand trust and shareholder engagement. It details frameworks for CSR action, core facets including sustainability, legal compliance, and employee well-being, as well as implementation strategies for both small and large businesses. The content emphasizes the significance of aligning business operations with socially responsible practices to enhance community relations and long-term success.Technological environment
Technological environmentanmolverma24
╠²
The document discusses the technological environment and the impact of technology. It defines technology and classifies it into different categories. It then describes the five stages of the technology cycle - awareness, acquisition, adaptation, advancement, and abandonment. Next, it discusses the impact of technology in three areas: social implications, economic implications, and plant-level changes. Some key impacts mentioned are increased productivity, need for R&D spending, jobs becoming more intellectual, and changes to organization structure.Corporate sickness
Corporate sicknessMaica Batiancela
╠²
Corporate sickness is a significant problem, with many large and medium sized companies in India considered sick. Sickness can be caused by both internal factors like poor management and external factors like increased competition. While some sick organizations have been successfully turned around, others have not recovered their past success. Early indicators of potential sickness include declining earnings ratios and worsening debt and liability ratios. Strategic management practices aim to put organizations on a path of sustainable growth.More from Anurag Srivastava (20)
Vam
VamAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document discusses determining initial basic feasible solutions for a transportation problem using VogelŌĆÖs Approximation Method and the North-West Corner Rule. It provides a structured table with costs, availability, and requirements for different origins and destinations. The total transportation cost is calculated to be 190.Simplex method maximisation
Simplex method maximisationAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document summarizes the simplex method for solving linear programming problems involving maximization. It involves 12 steps: 1) Formulating the LPP, 2) Introducing slack, surplus and artificial variables, 3) Formulating the initial basic solution, 4) Constructing the initial simplex table, 5) Checking for positive elements in the Cj-Zj row, 6) Identifying the incoming basic variable, 7) Choosing the incoming basic variable if multiple positives exist, 8) Identifying the outgoing basic variable, 9) Constructing the next simplex table using row operations, 10) Completing the new simplex table, 11) Repeating steps 5-10, and 12) Terminating when theProject networks
Project networksAnurag Srivastava
╠²
A publisher has contracted an author to produce a textbook. The production process involves the author submitting a manuscript and files, editing, sample page and cover design, artwork, formatting, and printing. The critical path through the network is the author submitting the manuscript, editing, formatting, artwork approval, plate production, and binding, taking 17 weeks total to complete the project.Or flowchart
Or flowchartAnurag Srivastava
╠²
This flowchart outlines an optimization process to find an optimal solution. It starts with finding an initial basic solution, then checks if that solution is optimal. If it is optimal, that solution is the final answer. If not, the process seeks a better solution to try and find the optimal one.Strategic management model
Strategic management modelAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document outlines a strategic management model that includes four main stages: strategic intent, formulation, implementation, and evaluation. It involves analyzing internal and external environments to determine a vision, mission, goals and objectives. Strategies are then formulated, implemented through resource allocation and structure, and evaluated for effectiveness with feedback into reformulation.Maximisation problem
Maximisation problemAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document presents a linear programming problem to determine the optimal production mix for two products (P1 and P2) that maximizes profit. The products have different processing times and resource requirements on milling and drilling machines, which have limited weekly hours. The problem is formulated as a linear program to maximize total profit subject to the machine hour constraints. Slack variables are introduced and the problem is solved using the simplex method to find the optimal production levels of 50 units of P1 and 20 units of P2, yielding maximum profit of Rs. 20,500.Lpp numerical
Lpp numericalAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The ABC Company has expanded its production to include AM-FM radios, utilizing a new plant capable of operating 48 hours weekly. A linear programming model is proposed to optimize the production mix of AM and AM-FM radios to maximize profits, considering specific constraints on production time and sales limits. The mathematical formulation includes profit contributions and limits on production, which must be solved to determine the optimal production strategy.Lpp numerical solved
Lpp numerical solvedAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document discusses the ABC Company's expansion into the production of AM-FM radios alongside AM radios, detailing its production capabilities and profit contributions. It formulates a linear programming model aimed at maximizing profits, given constraints on production time and sales limits. The optimal solution indicates producing 9 AM radios and 10 AM-FM radios, resulting in a maximum profit of Rs. 1160.Lpp formulation
Lpp formulationAnurag Srivastava
╠²
This document presents a linear programming problem involving assigning quality inspectors to minimize total inspection costs. There are two types of inspectors (Grade I and Grade II) with different inspection rates and accuracy. The objective is to minimize total costs based on wages, inspection pieces, and error costs with constraints on minimum inspection pieces and available inspectors.Lp formulation
Lp formulationAnurag Srivastava
╠²
This document formulates a linear programming problem to determine the optimal production quantities of Products P1 and P2 given machine time and contribution margin constraints. Product P1 takes 4 hours on machine M1 and 2 hours on M2, while Product P2 takes 2 hours on M1 and 4 hours on M2. The objective is to maximize total contribution by choosing the quantities x1 and x2 subject to the 60 hours available on M1, 48 hours on M2, and non-negativity constraints.Graphical method
Graphical methodAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document describes a production problem involving two products (P1 and P2) that are manufactured using two machines (M1 and M2). P1 requires 4 hours on M1 and 2 hours on M2, while P2 requires 2 hours on M1 and 4 hours on M2. The goal is to determine the optimal quantities of P1 and P2 to maximize total contribution, given 60 hours available on M1 and 48 hours on M2. This problem is modeled as a linear programming problem and graphically solved by plotting the constraint lines and finding their intersection point.Games
GamesAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document contains information about game theory including pure strategies, mixed strategies, and solving games. It provides examples of games represented as payoff matrices and discusses applying the principles of dominance, algebraic methods for 2x2 games, graphical methods for 2xn and mx2 games, and linear programming for mxn games. It also includes an example analyzing a 6x6 game modeling the Allied invasion of Normandy in WWII.Game theory
Game theoryAnurag Srivastava
╠²
Four teams will participate in a game involving selecting strategies of A or B. The aim is to score the maximum dividends. Scoring is based on the number of As and Bs selected. The document then explains the Prisoner's Dilemma game theory concept where two prisoners can either cooperate or betray each other, and discusses why rational individuals may not cooperate even if it is in their best interest to do so.Dual formulation example
Dual formulation exampleAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document discusses how to formulate the dual of a primal linear programming problem. It provides 10 steps for converting a primal maximization problem into a dual minimization problem. As an example, it formulates the dual of the primal problem: Maximize z = -5x1 + 2x2 subject to x1 - x2 Ōēź 2 and 2x1 + 3x2 Ōēż 5, with non-negativity constraints. The dual is formulated as: Minimize z = -2y1 + 5y2 subject to -y1 + 2y2 Ōēź -5 and y1 + 3y2 Ōēź 2, with non-negativity constraints on the dual variables y1 and y2.Decision tree solved
Decision tree solvedAnurag Srivastava
╠²
A finance manager is considering drilling a well on their property. Based on past data, there is a 70% chance of finding water at 20 meters depth, and a 20% chance of finding water between 20-25 meters if no water is found at 20 meters. The costs to drill are Rs.500 per meter plus Rs.15,000 to buy water externally if the well is not drilled. The optimal decision tree strategy is to first drill to 20 meters, and if no water, then drill further to 25 meters, resulting in an expected cost of Rs. 11,350.Decision theory numerical
Decision theory numericalAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The grocer must decide how many cases of milk to stock for tomorrow's demand. Each case sold yields a profit of Rs.3, but unsold cases at the end of the day lose Rs.5. Historical demand data shows the number of cases demanded and the probability of each quantity. The optimal decision can be determined by calculating the expected monetary value (EMV) of stocking different quantities of milk based on the probabilities and outcomes. The expected profit for the grocer if they stock the quantity with the highest EMV is Rs.47.7.Crashing
CrashingAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document outlines project management strategies for crashing activities to minimize project duration and associated costs. It provides detailed calculations of durations, costs, and slopes for various activities, indicating optimal strategies for achieving the minimum project length of 20 weeks with a total cost of Rs. 162,200. Additionally, it suggests an optimum duration range of 21-24 weeks with a cost of Rs. 160,800.Assignment model problems
Assignment model problemsAnurag Srivastava
╠²
A fast food chain wants to build four new stores and received bids from six construction companies. The document shows the bid amounts in a table and describes using the Hungarian method to determine the optimal assignment of companies to stores that minimizes the total cost. The method involves reducing the table through successive steps to reveal a unique solution with no remaining zeros. The result assigns each store to a single construction company to minimize the total cost for building all four stores.Minimisation problem
Minimisation problemAnurag Srivastava
╠²
The document discusses the Simplex method applied to a linear programming problem. It includes multiple iterations with values of variables (x1, x2) and constraints for each simplex tableau. Key calculations are shown for objective function coefficients (cj) and the resulting changes in potential solutions.Operations research
Operations researchAnurag Srivastava
╠²
Operations research (OR) is a tool used to increase the effectiveness of managerial decisions. It can help with profit maximization, production management like determining optimal product mix and scheduling, financial management, marketing management, and personnel management. Some common OR models include linear programming, transportation, assignment, and sequencing problems. OR uses mathematical techniques like linear programming, decision theory, game theory, queuing theory, simulation, network analysis, and inventory models.Ad
Unbalanced assignment problem
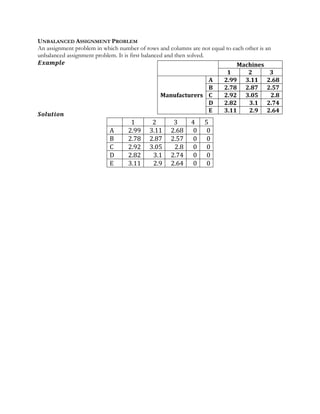
- 1. UNBALANCED ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM An assignment problem in which number of rows and columns are not equal to each other is an unbalanced assignment problem. It is first balanced and then solved. Øæ¼ØÆÖØÆéØÆÄØÆæØÆŹØÆå Øæ║ØÆÉØÆŹØÆ¢ØÆĢØÆŖØÆÉØÆÅ 1 2 3 4 5 A 2.99 3.11 2.68 0 0 B 2.78 2.87 2.57 0 0 C 2.92 3.05 2.8 0 0 D 2.82 3.1 2.74 0 0 E 3.11 2.9 2.64 0 0 Machines 1 2 3 Manufacturers A 2.99 3.11 2.68 B 2.78 2.87 2.57 C 2.92 3.05 2.8 D 2.82 3.1 2.74 E 3.11 2.9 2.64
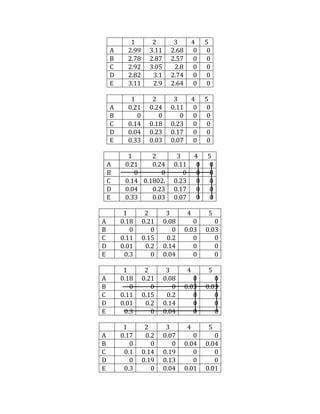
- 2. 1 2 3 4 5 A 2.99 3.11 2.68 0 0 B 2.78 2.87 2.57 0 0 C 2.92 3.05 2.8 0 0 D 2.82 3.1 2.74 0 0 E 3.11 2.9 2.64 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.21 0.24 0.11 0 0 B 0 0 0 0 0 C 0.14 0.18 0.23 0 0 D 0.04 0.23 0.17 0 0 E 0.33 0.03 0.07 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.21 0.24 0.11 0 0 B 0 0 0 0 0 C 0.14 0.1802. 0.23 0 0 D 0.04 0.23 0.17 0 0 E 0.33 0.03 0.07 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.18 0.21 0.08 0 0 B 0 0 0 0.03 0.03 C 0.11 0.15 0.2 0 0 D 0.01 0.2 0.14 0 0 E 0.3 0 0.04 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.18 0.21 0.08 0 0 B 0 0 0 0.03 0.03 C 0.11 0.15 0.2 0 0 D 0.01 0.2 0.14 0 0 E 0.3 0 0.04 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.17 0.2 0.07 0 0 B 0 0 0 0.04 0.04 C 0.1 0.14 0.19 0 0 D 0 0.19 0.13 0 0 E 0.3 0 0.04 0.01 0.01
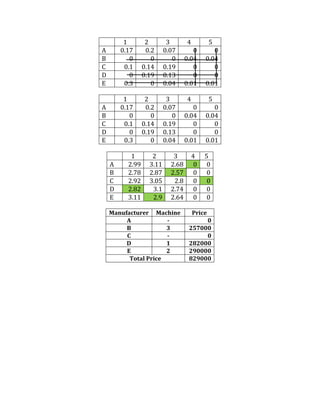
- 4. 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.17 0.2 0.07 0 0 B 0 0 0 0.04 0.04 C 0.1 0.14 0.19 0 0 D 0 0.19 0.13 0 0 E 0.3 0 0.04 0.01 0.01 1 2 3 4 5 A 0.17 0.2 0.07 0 0 B 0 0 0 0.04 0.04 C 0.1 0.14 0.19 0 0 D 0 0.19 0.13 0 0 E 0.3 0 0.04 0.01 0.01 1 2 3 4 5 A 2.99 3.11 2.68 0 0 B 2.78 2.87 2.57 0 0 C 2.92 3.05 2.8 0 0 D 2.82 3.1 2.74 0 0 E 3.11 2.9 2.64 0 0 Manufacturer Machine Price A - 0 B 3 257000 C - 0 D 1 282000 E 2 290000 Total Price 829000
