Understanding the Genetic Material, discovery and composition of DNA and how it replicates l.pptx
- 2. ÔÇ° Gregor Mendel ÔÇ° Proposed the 2 fundamental principles of heredity. ÔÇ° Hugo de Vries ÔÇ°Carl Erich Correns ÔÇ°Erich Seysenegg ÔÇ°William Jasper Spillman DISCOVERY OF DNA AS GENETIC MATERIAL
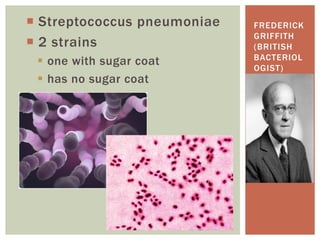
- 3. ÔÇ° Streptococcus pneumoniae ÔÇ° 2 strains ÔÇß one with sugar coat ÔÇß has no sugar coat FREDERICK GRIFFITH (BRITISH BACTERIOL OGIST)
- 5. ÔÇ° Identified the molecule that transformed R-strain bacteria into S-strain ÔÇ° Isolated diff. molecules ÔÇ° Concluded R strained picked up DNA & turned into S strained. OSWALD AVERY (CANADIAN-AMERICAN PHYSICIAN)
- 7. Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase ÔÇ° Worked to prove that DNA not proteins was indeed the genetic material. ÔÇ° used bacteriophage ÔÇß composed of DNA core and a protein coat ÔÇ° Used radioactive labelling
- 9.  Phoebus Levene (biochemist)  Identified the basic structure of nucleotides, and DNA  Nucleotides have sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous bases  DNA Nucleotides contain 5 carbon sugar  Phosphate  Adenine (A)  Guanine (G)  Cytosine (C)  Thymine (T)  Erwin Chargaff analysed the amount of each nitrogenous bases  1:1 ratio of pyramidines and purines  Chargaff’s rule (A paired to T) (G paired to C) THE COMPOSITION OF DNA
- 10. ÔÇ°Determined the components of a double helix ÔÇ°Hypothesized a method for DNA replication ÔÇ°Won a Nobel prize with Maurice Wilkins ÔÇ°The DNA molecule resembles a winding staircase. WATSON AND CRICK
- 12. ÔÇ°DNA Replication- copying of genetic information ÔÇ°AATCCGTAG ÔÇ°If the 2 strands of DNA molecules separates, each strand will expose all the information necessary to construct 2 identical strands. ÔÇ°Semiconservative replication- old strands are conserved in each daughter molecule HOW THE DNA REPLICATES
- 13. 1. Unwinding and Unzipping- the old strands that make up the parent DNA molecule are unwound. 2. Complementary base pairing- free nucleotides in the surrounding medium are positioned through the process of complementary base pairing. 3. Joining- the complementary nucleotides join to form new strands. STEPS IN DNA REPLICATION
- 14. EVALUATION!!!
- 15. 1.ATATCGGAGTACGTGCTA (Old strand) 2.TTAACAGTACGTGGCGCT (Old strand) SUPPLY THE CORRECT BASE PAIRS