Unidad i act5_vasallo ricardo
Download as DOCX, PDF0 likes184 views
CIRCUITOS ELECTRICOS II UFT SAIA B
1 of 5
Download to read offline
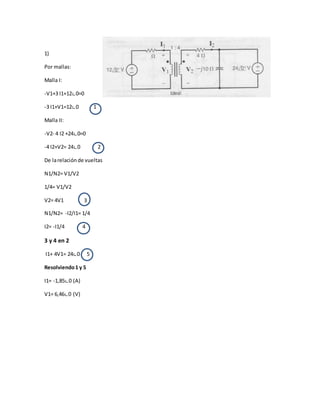
![De 4:
I2= 1,85∟0A=0,46∟0 (A)
4
De 3:
V2= 4(6,46∟0)(V)= 25,84∟0 (V)
2)
Por mallas
Malla I
(2-J4+ 2J+ 3) I1-J I2-3 I2= 32∟0
(5-J2) I1 –(3+J) I2=32∟0 1
-(3+J) I1 +(3+J2+J2+3) I2=0
-(3+J) I1+(6 I2)=0 2
I1= 6 I1/3+J 3
Sustituimos3en1
((5-J) 6 I2/3)+J – (3+J) I2= 32∟0 4
[((5-J) 6/3)+J– (3+J)] I2= 32∟0
[5,4-5,8J] I2= 32∟0
I2= 32∟0 (V)
(5,4-5,8J) Ω
I2= 4.04 ∟47,05 (A)
Del circuitovemosque
Io= I2
Io= 4,04∟75,05 (A)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unidadiact5vasalloricardo-150207221109-conversion-gate02/85/Unidad-i-act5_vasallo-ricardo-2-320.jpg)
![3)
Por mallas
Malla I
(1-J) I1 – (-JI2)= 24∟0
(1-J) I1+ J I2= 24∟0 1
-(-JI1) + (3-J+ J2-J2+J2) I2 – J I2-JI2=0
J I1 + (3+J-2 J) I2=0
J I1 + (3-J) I2=0
I1= (-(-3-J)/J) I2 2
Sustituimos2en1
(1-j) [(-(3-j)/j)] I2+ J I2= 24∟0
[(1-J)(3-J) J+J] I2=24∟0
[4+3 J] I2= 24∟0
I2= ((24∟0)/(4+3 J)) (A)
= (( 24∟0)/(5∟+36,87)) (A)
I2= 4,8∟ -36,87 (A)
De laLey de Ohm
Vo= 3 I2
= 3(4,8∟ -36,87 (V)
Vo= 14,4∟ -36,87 (V)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unidadiact5vasalloricardo-150207221109-conversion-gate02/85/Unidad-i-act5_vasallo-ricardo-3-320.jpg)


Recommended
If it’s friday, it must be kakooma mk



If it’s friday, it must be kakooma mkmarykienstra
Ìý
This document discusses using math games to engage students in learning basic math facts and skills. It describes the Kakooma math game app that students can play individually or in teams to practice operations at different levels of difficulty. The document advocates using Kakooma and other games like Estimation Station on Fridays for friendly team competitions and to spark rich mathematical discussions. It provides several other game resources and emphasizes how games can promote collaboration, number sense, and engagement for students of various levels.The solution for building a smarter workforce 



The solution for building a smarter workforce Gautam Munshi
Ìý
At Redwood we have conceptualized and built lookbeyondresumes.com which is a very sharp analytics engine to predict which candidates will succeed in specified roles . For further details feel free to reach out to me . Would be delighted to hear from anyone is is determined of significantly improving their organizations hiring decisions Enhancing your reading class with technology1



Enhancing your reading class with technology1marykienstra
Ìý
This document discusses ways to enhance reading class with technology by having students do activities like researching topics, responding to readings, collaborating, creating scripts and book trailers using apps, writing journal entries or responses that can be shared on discussion boards or blogs, conducting author studies where they learn about an author and create related multimedia projects, connecting with authors through video chats or social media, and allowing creative responses beyond traditional writing. The goal is to make reading come alive for students and engage them through technology.Using technology to increase student engagement in math1



Using technology to increase student engagement in math1marykienstra
Ìý
This document discusses how teachers can use technology to transform math class by increasing student engagement and promoting collaboration. It provides examples of apps and websites that teachers can use to present information, differentiate instruction, and allow students to practice skills or create videos, pictures, and podcasts. Specific apps and websites highlighted include Explain Everything, Tellagami, IXL, and gregtangmath.com. The goal is to focus on collaboration and discussion to improve student engagement in math class through the use of educational technology tools.I pads for student creation mk



I pads for student creation mkmarykienstra
Ìý
This document discusses how students can use iPads and apps to demonstrate their knowledge and engage with content in new ways beyond traditional worksheets and assignments. It provides examples of several apps - Explain Everything, Creative Book Builder, Tellagami, and iMovie - that allow students to create video screencasts, digital books, animated stories, and movies. The document suggests how these apps can be used across subjects for students to explain math problems, write and publish digital books, create character narratives, and produce video projects. It emphasizes that these tools allow for more authentic writing in different formats, facilitate discussion and sharing of work, and provide an electronic portfolio system through uploading projects to the Canvas platform.Explanation of paygo



Explanation of paygoRichard Hoffman
Ìý
PAYGO (Pay-As-You-Go) is a budget rule that requires new spending increases or tax cuts be offset by spending cuts or tax increases so as not to add to the deficit. It was first established by the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 and extended several times before being reinstated in 2010. When in effect during the Clinton administration, it helped reduce budget deficits and achieve a surplus, but allowing it to expire during George W. Bush's term contributed to growing deficits.Let’s talk about grading



Let’s talk about gradingmarykienstra
Ìý
This document discusses grading students and proposes alternative approaches. It presents sample student jumping jack scores over time. It then introduces a rubric to grade jumping jack performance on a scale from beginning to exemplary. The document suggests shifting from grades to focusing on learning, standards, and specific feedback. It advocates changing grading to provide more detailed information on what students know and still need to learn in order to improve.Math engagement party ictm 2014



Math engagement party ictm 2014marykienstra
Ìý
The document discusses ways to improve student engagement in math by making it more social, fun, and creative. It recommends having students collaborate on lessons and discussions, using apps and games for practice, and allowing students to create videos or other projects to show their understanding. Specific techniques mentioned include using websites like Kakooma for challenges, the Math Doodles app, turning problems into games using Kahoot, having students be "experts" on problems and discuss them, and using dice or cards for skill practice. The goal is to engage students through social interaction, fun activities, and opportunities for creative work.Analytics 101 - Getting Started 



Analytics 101 - Getting Started Gautam Munshi
Ìý
This document discusses analytics and data mining techniques. It begins by outlining common measures used in analytics like time, proportions, size, and financials. It then discusses the universal language of cause and effect in analytics and how analytics finds relationships between causes and effects. The document outlines various sources of data, fundamental concepts in analytics like increased computing power and data volume, and common tools. It provides examples of universal applications of analytics across marketing, customer service, and other functions. The document charts the evolution of analytics from basic surveys to more advanced techniques leveraging social media, text, and sensors. It outlines the CRISP-DM process for analytics projects and career paths in analytics. Finally, it discusses various data mining techniques categorized asBring Your Math Class To Life ICTM 2015



Bring Your Math Class To Life ICTM 2015marykienstra
Ìý
The document provides suggestions for engaging math students and bringing math concepts to life. It recommends making math social through discussion and collaboration in lessons. It also suggests leaving worksheets behind and using alternative methods like online games, dice, cards and real-world projects. The document further advocates creating rituals like weekly challenges that students love. It concludes by encouraging teachers to let students create items like foldables, videos and puzzles to demonstrate their understanding of math concepts.The habits of mind pdf



The habits of mind pdfmarykienstra
Ìý
The document describes 16 types of intelligent behaviors called "Habits of Mind" that can be used in school, activities, and life. These habits include persisting through tasks, managing impulsivity, listening with empathy, thinking flexibly, self-reflection or metacognition, striving for accuracy, questioning and problem-posing, applying past knowledge to new situations, clear communication, open-minded data gathering, creativity and innovation, appreciation of beauty, responsible risk-taking, humor, cooperative thinking, and continuous learning. The habits involve behaviors like sticking with problems, thinking before acting, considering others' perspectives, adapting perspectives, self-awareness, ensuring correctness, curiosity, making connections, precise expression, using all senses, novelMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (6)
Explanation of paygo



Explanation of paygoRichard Hoffman
Ìý
PAYGO (Pay-As-You-Go) is a budget rule that requires new spending increases or tax cuts be offset by spending cuts or tax increases so as not to add to the deficit. It was first established by the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 and extended several times before being reinstated in 2010. When in effect during the Clinton administration, it helped reduce budget deficits and achieve a surplus, but allowing it to expire during George W. Bush's term contributed to growing deficits.Let’s talk about grading



Let’s talk about gradingmarykienstra
Ìý
This document discusses grading students and proposes alternative approaches. It presents sample student jumping jack scores over time. It then introduces a rubric to grade jumping jack performance on a scale from beginning to exemplary. The document suggests shifting from grades to focusing on learning, standards, and specific feedback. It advocates changing grading to provide more detailed information on what students know and still need to learn in order to improve.Math engagement party ictm 2014



Math engagement party ictm 2014marykienstra
Ìý
The document discusses ways to improve student engagement in math by making it more social, fun, and creative. It recommends having students collaborate on lessons and discussions, using apps and games for practice, and allowing students to create videos or other projects to show their understanding. Specific techniques mentioned include using websites like Kakooma for challenges, the Math Doodles app, turning problems into games using Kahoot, having students be "experts" on problems and discuss them, and using dice or cards for skill practice. The goal is to engage students through social interaction, fun activities, and opportunities for creative work.Analytics 101 - Getting Started 



Analytics 101 - Getting Started Gautam Munshi
Ìý
This document discusses analytics and data mining techniques. It begins by outlining common measures used in analytics like time, proportions, size, and financials. It then discusses the universal language of cause and effect in analytics and how analytics finds relationships between causes and effects. The document outlines various sources of data, fundamental concepts in analytics like increased computing power and data volume, and common tools. It provides examples of universal applications of analytics across marketing, customer service, and other functions. The document charts the evolution of analytics from basic surveys to more advanced techniques leveraging social media, text, and sensors. It outlines the CRISP-DM process for analytics projects and career paths in analytics. Finally, it discusses various data mining techniques categorized asBring Your Math Class To Life ICTM 2015



Bring Your Math Class To Life ICTM 2015marykienstra
Ìý
The document provides suggestions for engaging math students and bringing math concepts to life. It recommends making math social through discussion and collaboration in lessons. It also suggests leaving worksheets behind and using alternative methods like online games, dice, cards and real-world projects. The document further advocates creating rituals like weekly challenges that students love. It concludes by encouraging teachers to let students create items like foldables, videos and puzzles to demonstrate their understanding of math concepts.The habits of mind pdf



The habits of mind pdfmarykienstra
Ìý
The document describes 16 types of intelligent behaviors called "Habits of Mind" that can be used in school, activities, and life. These habits include persisting through tasks, managing impulsivity, listening with empathy, thinking flexibly, self-reflection or metacognition, striving for accuracy, questioning and problem-posing, applying past knowledge to new situations, clear communication, open-minded data gathering, creativity and innovation, appreciation of beauty, responsible risk-taking, humor, cooperative thinking, and continuous learning. The habits involve behaviors like sticking with problems, thinking before acting, considering others' perspectives, adapting perspectives, self-awareness, ensuring correctness, curiosity, making connections, precise expression, using all senses, novelUnidad i act5_vasallo ricardo
- 1. 1) Por mallas: Malla I: -V1+3 I1+12∟0=0 -3 I1+V1=12∟0 1 Malla II: -V2- 4 I2 +24∟0=0 -4 I2+V2= 24∟0 2 De larelación de vueltas N1/N2= V1/V2 1/4= V1/V2 V2= 4V1 3 N1/N2= -I2/I1= 1/4 I2= -I1/4 4 3 y 4 en 2 I1+ 4V1= 24∟0 5 Resolviendo1 y 5 I1= -1,85∟0 (A) V1= 6,46∟0 (V)
- 2. De 4: I2= 1,85∟0A=0,46∟0 (A) 4 De 3: V2= 4(6,46∟0)(V)= 25,84∟0 (V) 2) Por mallas Malla I (2-J4+ 2J+ 3) I1-J I2-3 I2= 32∟0 (5-J2) I1 –(3+J) I2=32∟0 1 -(3+J) I1 +(3+J2+J2+3) I2=0 -(3+J) I1+(6 I2)=0 2 I1= 6 I1/3+J 3 Sustituimos3en1 ((5-J) 6 I2/3)+J – (3+J) I2= 32∟0 4 [((5-J) 6/3)+J– (3+J)] I2= 32∟0 [5,4-5,8J] I2= 32∟0 I2= 32∟0 (V) (5,4-5,8J) Ω I2= 4.04 ∟47,05 (A) Del circuitovemosque Io= I2 Io= 4,04∟75,05 (A)
- 3. 3) Por mallas Malla I (1-J) I1 – (-JI2)= 24∟0 (1-J) I1+ J I2= 24∟0 1 -(-JI1) + (3-J+ J2-J2+J2) I2 – J I2-JI2=0 J I1 + (3+J-2 J) I2=0 J I1 + (3-J) I2=0 I1= (-(-3-J)/J) I2 2 Sustituimos2en1 (1-j) [(-(3-j)/j)] I2+ J I2= 24∟0 [(1-J)(3-J) J+J] I2=24∟0 [4+3 J] I2= 24∟0 I2= ((24∟0)/(4+3 J)) (A) = (( 24∟0)/(5∟+36,87)) (A) I2= 4,8∟ -36,87 (A) De laLey de Ohm Vo= 3 I2 = 3(4,8∟ -36,87 (V) Vo= 14,4∟ -36,87 (V)
- 4. 4) De larelaciónde vueltas:a= 1/2=Z La impedancia reflejadaes: Zr=A2 Z2= (1/2)2 (4+4J)= (1+J) Ω El circuitoequivalentees: Zp= (-J(1+J)/(-J+1+J)=(1-J)Ω V1= ((10∟30)/(3+Zp))*Zp(Divisorde tensión) V1=((10∟30)/(3+1-J)) (1-J) V1= 3,43∟-0,96 (V) I1= V1/Zr + - -
- 5. I1= ((3,43∟0,96)/(1+J))=2,43∟ -45,96 (A) I1= 2,43∟ -45,96 (A) V1/V2=a V2=V1/a= ((3,43∟ -0,96)/(1/2)) V2= 6,86∟ -45,96 (V) I2= a I1= 1/2(2,43∟ -45,96) A I2= 1,22∟ -45,96 (A)



