Unit 1 Introduction to Machine Learning Concept
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes11 views
Unit 1 Introduction to Machine Learning
1 of 10
Download to read offline





Recommended
Unit1_Introduction to ML_Defination_application.pdf



Unit1_Introduction to ML_Defination_application.pdfRAMESHWAR CHINTAMANI
Ěý
Introduction: Definition, Real life applications, Introduction to Data in Machine
Learningmachine learning.pptx



machine learning.pptxAkshiGupta18
Ěý
Machine learning is a technique where computers learn from data to improve their abilities without being explicitly programmed. It works by building models from historical data to make predictions on new data. The accuracy of predictions depends on the amount of data used to build the model. There are three main types of machine learning: supervised learning which uses labeled training data, unsupervised learning which learns without labels, and reinforcement learning where an agent learns from rewards and penalties.Machine Learning Presentation



Machine Learning PresentationSk Samiul Islam
Ěý
"Unveiling the Magic of Machine Learning: Join me for a concise yet insightful presentation on the captivating world of Machine Learning (ML). Discover how ML algorithms transform data into predictive models, driving smarter decisions. From regression to classification and beyond, we'll delve into the basics, demystify key concepts, and showcase real-world applications. Let's explore the algorithms shaping our digital landscape and understand how they're revolutionizing industries. Don't miss this opportunity to grasp the essence of ML in a nutshell!"Introduction to Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning



Introduction to Artificial Intelligence And Machine LearningSharathsvSharathsv
Ěý
Introduction to Machine LearningLecture 1: What is Machine Learning?



Lecture 1: What is Machine Learning?Marina Santini
Ěý
Opening lecture to the Machine Learning for Language Technology course at Uppsala University, Sweden. Autumn 2015Machine learning



Machine learningeonx_32
Ěý
Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. It uses algorithms to recognize patterns in data and make predictions. The document discusses common machine learning algorithms like linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, and k-means clustering. It also provides examples of machine learning applications such as face detection, speech recognition, fraud detection, and smart cars. Machine learning is expected to have an increasingly important role in the future.Introduction to ML (Machine Learning)



Introduction to ML (Machine Learning)SwatiTripathi44
Ěý
This ppt is for beginners in ML to get them familiar with common terms and keywords they will come across while studying this field.Introduction to Machine Learning



Introduction to Machine LearningKmPooja4
Ěý
This document summarizes Pooja's seminar presentation on machine learning. It introduces machine learning and compares it to traditional programming. It describes the main types of machine learning: supervised learning which uses labeled data to make predictions, unsupervised learning which finds patterns in unlabeled data, and reinforcement learning where an agent learns from feedback. The document discusses concepts like classification, regression, and feedback in machine learning systems. It also outlines some applications and concludes that machine learning can improve lives by advancing technology.Introduction to Machine Learning Learning Types ML Life Cycle Dataset for ML ...



Introduction to Machine Learning Learning Types ML Life Cycle Dataset for ML ...RahulNavale5
Ěý
Machine learningIntroduction to machine learning



Introduction to machine learningSalman Khan
Ěý
This document is a seminar presentation on machine learning that was submitted by Salman Saifi. It introduces machine learning and discusses the types of machine learning including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. It explains the importance of machine learning and its applications in areas like fraud detection, customer support, image and speech recognition, recommendations, and more. The presentation concludes by noting that machine learning is an important form of artificial intelligence that is already being used in many industries to improve lives.Introduction to machine learning



Introduction to machine learningSalman Khan
Ěý
Machine learning is the study of computer algorithms that allow computer program to automatically improves through experienceIntro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation -2



Intro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation -2Ankit Gupta
Ěý
Intro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation -2,
project on Machine Learning ,Intro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation Introduction to Machine Learning.pptx



Introduction to Machine Learning.pptxDr. Amanpreet Kaur
Ěý
- Machine learning is a field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed by using example data. It is a form of artificial intelligence.
- There are three main types of machine learning: supervised learning where examples are labeled, unsupervised learning where unlabeled examples reveal inherent groupings of data, and reinforcement learning where an agent learns from trial and error using rewards.
- Machine learning has many applications including web search, computational biology, finance, robotics, and social networks. It involves collecting and preparing data, developing models, and evaluating models to make predictions on new data.Machine Learning Basics - By Animesh Sinha 



Machine Learning Basics - By Animesh Sinha Animesh Sinha
Ěý
Machine Learning Basics
- What is Machine Learning
- Types of Machine Learning
- Some Machine Learning Algorithms
- Use Cases of Machine Learning detailed Presentation on supervised learning



detailed Presentation on supervised learningZAMANCHBWN
Ěý
A brief introduction to supervised learning, its types, advantages & disadvantages which case we should use it and which case is not used.MachineLearning_Unit-I.pptxScrum.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Mo...



MachineLearning_Unit-I.pptxScrum.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Mo...22eg105n11
Ěý
Scrum.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxIntroduction to machine learning



Introduction to machine learningDeepeshYadav38
Ěý
In this presentation on machine learning I have talked about different types of machine learning algorithms like supervised learning , unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning. also I have talked about the difference between AI, ML, Data science, Deep learning.Machine Learning SPPU Unit 1



Machine Learning SPPU Unit 1Amruta Aphale
Ěý
The document discusses different types of machine learning including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. It provides examples of each type, such as using labeled data to classify emails as spam or not spam for supervised learning, grouping fruits by color without labels for unsupervised learning, and using rewards to guide an agent through a maze for reinforcement learning. The document also covers applications of machine learning across different domains like banking, biomedical, computer, and environment.Machine Learning by Rj



Machine Learning by RjShree M.L.Kakadiya MCA mahila college, Amreli
Ěý
This document provides an overview of machine learning presented by Mr. Raviraj Solanki. It discusses topics like introduction to machine learning, model preparation, modelling and evaluation. It defines key concepts like algorithms, models, predictor variables, response variables, training data and testing data. It also explains the differences between human learning and machine learning, types of machine learning including supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning is further divided into classification and regression problems. Popular algorithms for supervised learning like random forest, decision trees, logistic regression, support vector machines, linear regression, regression trees and more are also mentioned.Module1 of Introduction to Machine Learning



Module1 of Introduction to Machine LearningMayuraD1
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the "Introduction to Machine Learning" course, including:
- The course is worth 3 credits and takes place in the 2022-23 academic year.
- Module 1 covers what machine learning is, its history and applications, different categories of machine learning like supervised and unsupervised learning, and key terminology.
- Machine learning enables machines to learn from data, improve performance, and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. It is a subset of artificial intelligence focused on algorithm development.Machine Learning Chapter one introduction



Machine Learning Chapter one introductionARVIND SARDAR
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, covering various topics. It defines machine learning as a branch of artificial intelligence that uses data and algorithms to enable computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. Various types of machine learning are discussed, including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Key concepts like hypothesis space, overfitting, evaluation metrics, and linear regression are introduced. Examples of well-posed learning problems are also provided.Lecture 3: Basic Concepts of Machine Learning - Induction & Evaluation



Lecture 3: Basic Concepts of Machine Learning - Induction & EvaluationMarina Santini
Ěý
Induction, Induction pipeline, Training set, test set, development set, Parameters, Hyperparameters, Accuracy, precision, recall, f-measure, Confusion matrix, Crossvalidation, Leave one out, Stratification
Machine Learning Ch 1.ppt



Machine Learning Ch 1.pptARVIND SARDAR
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, covering various topics. It defines machine learning as a branch of artificial intelligence that uses algorithms and data to enable machines to learn. It discusses different types of machine learning, including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. It also covers important machine learning concepts like overfitting, evaluation metrics, and well-posed learning problems. The history of machine learning is reviewed, from early work in the 1950s to recent advances in deep learning.unit 1.2 supervised learning.pptx



unit 1.2 supervised learning.pptxDr.Shweta
Ěý
Supervised learning is a fundamental concept in machine learning, where a computer algorithm learns from labeled data to make predictions or decisions. It is a type of machine learning paradigm that involves training a model on a dataset where both the input data and the corresponding desired output (or target) are provided. The goal of supervised learning is to learn a mapping or relationship between inputs and outputs so that the model can make accurate predictions on new, unseen data.vStructural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...



Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...slayshadow705
Ěý
This presentation provides an in-depth analysis of structural quality control in the KRP 401600 section of the Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3) in Uzbekistan. As a Structural QA/QC Inspector, I have identified critical welding defects, alignment issues, bolting problems, and joint fit-up concerns.
Key topics covered:
✔ Common Structural Defects – Welding porosity, misalignment, bolting errors, and more.
✔ Root Cause Analysis – Understanding why these defects occur.
✔ Corrective & Preventive Actions – Effective solutions to improve quality.
✔ Team Responsibilities – Roles of supervisors, welders, fitters, and QC inspectors.
✔ Inspection & Quality Control Enhancements – Advanced techniques for defect detection.
📌 Applicable Standards: GOST, KMK, SNK – Ensuring compliance with international quality benchmarks.
🚀 This presentation is a must-watch for:
âś… QA/QC Inspectors, Structural Engineers, Welding Inspectors, and Project Managers in the construction & oil & gas industries.
âś… Professionals looking to improve quality control processes in large-scale industrial projects.
📢 Download & share your thoughts! Let's discuss best practices for enhancing structural integrity in industrial projects.
Categories:
Engineering
Construction
Quality Control
Welding Inspection
Project Management
Tags:
#QAQC #StructuralInspection #WeldingDefects #BoltingIssues #ConstructionQuality #Engineering #GOSTStandards #WeldingInspection #QualityControl #ProjectManagement #MOF3 #CopperProcessing #StructuralEngineering #NDT #OilAndGasMore Related Content
Similar to Unit 1 Introduction to Machine Learning Concept (20)
Introduction to Machine Learning



Introduction to Machine LearningKmPooja4
Ěý
This document summarizes Pooja's seminar presentation on machine learning. It introduces machine learning and compares it to traditional programming. It describes the main types of machine learning: supervised learning which uses labeled data to make predictions, unsupervised learning which finds patterns in unlabeled data, and reinforcement learning where an agent learns from feedback. The document discusses concepts like classification, regression, and feedback in machine learning systems. It also outlines some applications and concludes that machine learning can improve lives by advancing technology.Introduction to Machine Learning Learning Types ML Life Cycle Dataset for ML ...



Introduction to Machine Learning Learning Types ML Life Cycle Dataset for ML ...RahulNavale5
Ěý
Machine learningIntroduction to machine learning



Introduction to machine learningSalman Khan
Ěý
This document is a seminar presentation on machine learning that was submitted by Salman Saifi. It introduces machine learning and discusses the types of machine learning including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. It explains the importance of machine learning and its applications in areas like fraud detection, customer support, image and speech recognition, recommendations, and more. The presentation concludes by noting that machine learning is an important form of artificial intelligence that is already being used in many industries to improve lives.Introduction to machine learning



Introduction to machine learningSalman Khan
Ěý
Machine learning is the study of computer algorithms that allow computer program to automatically improves through experienceIntro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation -2



Intro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation -2Ankit Gupta
Ěý
Intro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation -2,
project on Machine Learning ,Intro/Overview on Machine Learning Presentation Introduction to Machine Learning.pptx



Introduction to Machine Learning.pptxDr. Amanpreet Kaur
Ěý
- Machine learning is a field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed by using example data. It is a form of artificial intelligence.
- There are three main types of machine learning: supervised learning where examples are labeled, unsupervised learning where unlabeled examples reveal inherent groupings of data, and reinforcement learning where an agent learns from trial and error using rewards.
- Machine learning has many applications including web search, computational biology, finance, robotics, and social networks. It involves collecting and preparing data, developing models, and evaluating models to make predictions on new data.Machine Learning Basics - By Animesh Sinha 



Machine Learning Basics - By Animesh Sinha Animesh Sinha
Ěý
Machine Learning Basics
- What is Machine Learning
- Types of Machine Learning
- Some Machine Learning Algorithms
- Use Cases of Machine Learning detailed Presentation on supervised learning



detailed Presentation on supervised learningZAMANCHBWN
Ěý
A brief introduction to supervised learning, its types, advantages & disadvantages which case we should use it and which case is not used.MachineLearning_Unit-I.pptxScrum.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Mo...



MachineLearning_Unit-I.pptxScrum.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Mo...22eg105n11
Ěý
Scrum.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxAgile Model.pptxIntroduction to machine learning



Introduction to machine learningDeepeshYadav38
Ěý
In this presentation on machine learning I have talked about different types of machine learning algorithms like supervised learning , unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning. also I have talked about the difference between AI, ML, Data science, Deep learning.Machine Learning SPPU Unit 1



Machine Learning SPPU Unit 1Amruta Aphale
Ěý
The document discusses different types of machine learning including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. It provides examples of each type, such as using labeled data to classify emails as spam or not spam for supervised learning, grouping fruits by color without labels for unsupervised learning, and using rewards to guide an agent through a maze for reinforcement learning. The document also covers applications of machine learning across different domains like banking, biomedical, computer, and environment.Machine Learning by Rj



Machine Learning by RjShree M.L.Kakadiya MCA mahila college, Amreli
Ěý
This document provides an overview of machine learning presented by Mr. Raviraj Solanki. It discusses topics like introduction to machine learning, model preparation, modelling and evaluation. It defines key concepts like algorithms, models, predictor variables, response variables, training data and testing data. It also explains the differences between human learning and machine learning, types of machine learning including supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning is further divided into classification and regression problems. Popular algorithms for supervised learning like random forest, decision trees, logistic regression, support vector machines, linear regression, regression trees and more are also mentioned.Module1 of Introduction to Machine Learning



Module1 of Introduction to Machine LearningMayuraD1
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the "Introduction to Machine Learning" course, including:
- The course is worth 3 credits and takes place in the 2022-23 academic year.
- Module 1 covers what machine learning is, its history and applications, different categories of machine learning like supervised and unsupervised learning, and key terminology.
- Machine learning enables machines to learn from data, improve performance, and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. It is a subset of artificial intelligence focused on algorithm development.Machine Learning Chapter one introduction



Machine Learning Chapter one introductionARVIND SARDAR
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, covering various topics. It defines machine learning as a branch of artificial intelligence that uses data and algorithms to enable computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. Various types of machine learning are discussed, including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Key concepts like hypothesis space, overfitting, evaluation metrics, and linear regression are introduced. Examples of well-posed learning problems are also provided.Lecture 3: Basic Concepts of Machine Learning - Induction & Evaluation



Lecture 3: Basic Concepts of Machine Learning - Induction & EvaluationMarina Santini
Ěý
Induction, Induction pipeline, Training set, test set, development set, Parameters, Hyperparameters, Accuracy, precision, recall, f-measure, Confusion matrix, Crossvalidation, Leave one out, Stratification
Machine Learning Ch 1.ppt



Machine Learning Ch 1.pptARVIND SARDAR
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, covering various topics. It defines machine learning as a branch of artificial intelligence that uses algorithms and data to enable machines to learn. It discusses different types of machine learning, including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. It also covers important machine learning concepts like overfitting, evaluation metrics, and well-posed learning problems. The history of machine learning is reviewed, from early work in the 1950s to recent advances in deep learning.unit 1.2 supervised learning.pptx



unit 1.2 supervised learning.pptxDr.Shweta
Ěý
Supervised learning is a fundamental concept in machine learning, where a computer algorithm learns from labeled data to make predictions or decisions. It is a type of machine learning paradigm that involves training a model on a dataset where both the input data and the corresponding desired output (or target) are provided. The goal of supervised learning is to learn a mapping or relationship between inputs and outputs so that the model can make accurate predictions on new, unseen data.vRecently uploaded (20)
Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...



Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...slayshadow705
Ěý
This presentation provides an in-depth analysis of structural quality control in the KRP 401600 section of the Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3) in Uzbekistan. As a Structural QA/QC Inspector, I have identified critical welding defects, alignment issues, bolting problems, and joint fit-up concerns.
Key topics covered:
✔ Common Structural Defects – Welding porosity, misalignment, bolting errors, and more.
✔ Root Cause Analysis – Understanding why these defects occur.
✔ Corrective & Preventive Actions – Effective solutions to improve quality.
✔ Team Responsibilities – Roles of supervisors, welders, fitters, and QC inspectors.
✔ Inspection & Quality Control Enhancements – Advanced techniques for defect detection.
📌 Applicable Standards: GOST, KMK, SNK – Ensuring compliance with international quality benchmarks.
🚀 This presentation is a must-watch for:
âś… QA/QC Inspectors, Structural Engineers, Welding Inspectors, and Project Managers in the construction & oil & gas industries.
âś… Professionals looking to improve quality control processes in large-scale industrial projects.
📢 Download & share your thoughts! Let's discuss best practices for enhancing structural integrity in industrial projects.
Categories:
Engineering
Construction
Quality Control
Welding Inspection
Project Management
Tags:
#QAQC #StructuralInspection #WeldingDefects #BoltingIssues #ConstructionQuality #Engineering #GOSTStandards #WeldingInspection #QualityControl #ProjectManagement #MOF3 #CopperProcessing #StructuralEngineering #NDT #OilAndGasIntroduction to Safety, Health & Environment



Introduction to Safety, Health & Environmentssuserc606c7
Ěý
Introduction to
Safety, Health &EnvironmentIndustrial Valves, Instruments Products Profile



Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profilezebcoeng
Ěý
We’re excited to share our product profile, showcasing our expertise in Industrial Valves, Instrumentation, and Hydraulic & Pneumatic Solutions.
We also supply API-approved valves from globally trusted brands, ensuring top-notch quality and internationally certified solutions. Let’s explore valuable business opportunities together!
We specialize in:
• Industrial Valves (Gate, Globe, Ball, Butterfly, Check)
• Instrumentation (Pressure Gauges, Transmitters, Flow Meters)
• Pneumatic Products (Cylinders, Solenoid Valves, Fittings)
As authorized partners of trusted global brands, we deliver high-quality solutions tailored to meet your industrial needs with seamless support.IPC-9716_2024 Requirements for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Process Con...



IPC-9716_2024 Requirements for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Process Con...ssuserd9338b
Ěý
IPC-9716_2024 Requirements for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Process Control for Printed Board Assemblies.pdfWireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdf



Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdfAbhinandanMishra30
Ěý
Wireless technology used in chargerThe Golden Gate Bridge a structural marvel inspired by mother nature.pptx



The Golden Gate Bridge a structural marvel inspired by mother nature.pptxAkankshaRawat75
Ěý
The Golden Gate Bridge is a 6 lane suspension bridge spans the Golden Gate Strait, connecting the city of San Francisco to Marin County, California.
It provides a vital transportation link between the Pacific Ocean and the San Francisco Bay.
15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdf



15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdfNgocThang9
Ěý
Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New UtopiaMulti objective genetic approach with Ranking



Multi objective genetic approach with Rankingnamisha18
Ěý
Multi objective genetic approach with Ranking Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical Engineering



Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical EngineeringRajani Vyawahare
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Soil Classification System, widely used in geotechnical engineering for identifying and categorizing soils based on their properties. It covers essential aspects such as particle size distribution, sieve analysis, and Atterberg consistency limits, which play a crucial role in determining soil behavior for construction and foundation design. The presentation explains the classification of soil based on particle size, including gravel, sand, silt, and clay, and details the sieve analysis experiment used to determine grain size distribution. Additionally, it explores the Atterberg consistency limits, such as the liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit, along with a plasticity chart to assess soil plasticity and its impact on engineering applications. Furthermore, it discusses the Indian Standard Soil Classification (IS 1498:1970) and its significance in construction, along with a comparison to the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS). With detailed explanations, graphs, charts, and practical applications, this presentation serves as a valuable resource for students, civil engineers, and researchers in the field of geotechnical engineering. UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptx



UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxKesavanT10
Ěý
UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxUnit 1 Introduction to Machine Learning Concept
- 1. UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ML (MACHINE LEARNING) PREPARED BY: PROF. ARVIND MENIYA
- 2. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 2 What is Machine Learning (ML) ? • Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that is mainly concerned with the development of algorithms. • These algorithms allow a computer to learn from the data and past experiences on their own. • The term machine learning was first introduced by Arthur Samuel in 1959. • We can define it in a summarized way as: Machine learning enables a machine to automatically learn from data, improve performance from experiences, and predict things without being explicitly programmed.
- 3. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 3 What is Machine Learning (ML) ? • Machine learning constructs or uses the algorithms that learn from historical data. • The more we will provide the information, the higher will be the performance. • A machine has the ability to learn if it can improve its performance by gaining more data. • The first step in any project is defining your problem. • Even if the most powerful algorithm is used, the results will be meaningless if the wrong problem is solved.
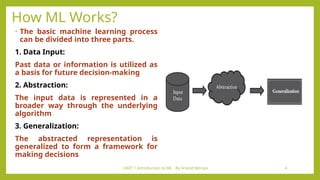
- 4. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 4 How ML Works? • The basic machine learning process can be divided into three parts. 1. Data Input: Past data or information is utilized as a basis for future decision-making 2. Abstraction: The input data is represented in a broader way through the underlying algorithm 3. Generalization: The abstracted representation is generalized to form a framework for making decisions
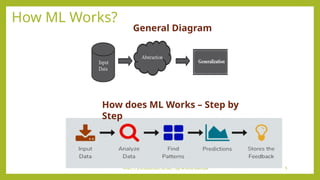
- 5. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 5 How ML Works? General Diagram How does ML Works – Step by Step
- 6. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 6
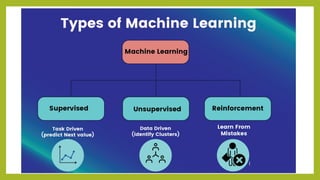
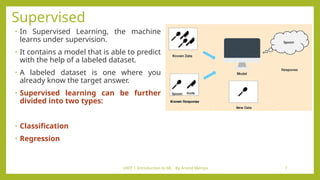
- 7. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 7 Supervised • In Supervised Learning, the machine learns under supervision. • It contains a model that is able to predict with the help of a labeled dataset. • A labeled dataset is one where you already know the target answer. • Supervised learning can be further divided into two types: • Classification • Regression
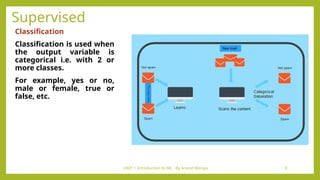
- 8. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 8 Supervised Classification Classification is used when the output variable is categorical i.e. with 2 or more classes. For example, yes or no, male or female, true or false, etc.
- 9. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 9 Supervised Regression Regression is used when the output variable is a real or continuous value. In this case, there is a relationship between two or more variables i.e., a change in one variable is associated with a change in the other variable. For example, salary based on work experience or weight based on height, etc.
- 10. UNIT 1 Introduction to ML - By Arvind Meniya 10 Real life Application of Supervised Learning Risk Assessment Supervised learning is used to assess the risk in financial services or insurance domains. Image Classification Image classification is one of the key use cases of demonstrating supervised machine learning. For example, Facebook can recognize your friend in a picture from an album of tagged photos. Fraud Detection To identify whether the transactions made by the user are authentic or not. Visual Recognition The ability of a machine learning model to identify objects, places, people, actions, and images.













