Unit 2.8 relative velocity method and rubbing velocity
- 1. Relative velocity method and rubbing velocity
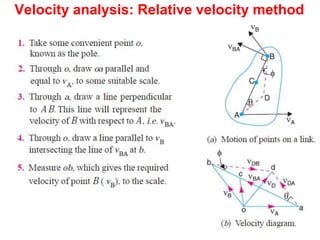
- 2. Velocity analysis: Relative velocity method
- 3. Velocity analysis: Rubbing velocity at a pin joint
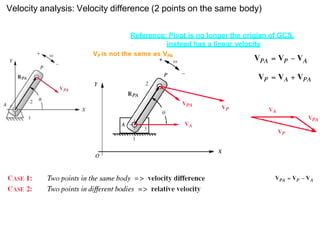
- 4. Velocity analysis: Velocity difference (2 points on the same body) Reference: Pivot is no longer the origian of GCS, instead has a linear velocity
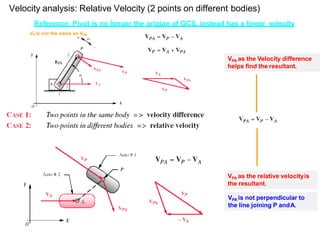
- 5. Reference: Pivot is no longer the origian of GCS, instead has a linear velocity When P and A are not on the same body, the resultant vector Is different. VPA as the Velocity difference helps find the resultant. VPA as the relative velocityis the resultant. VPA is not perpendicular to the line joining P andA. Velocity analysis: Relative Velocity (2 points on different bodies)
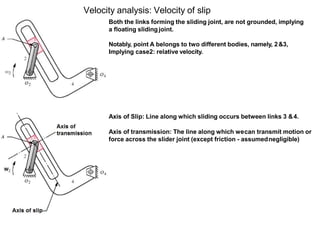
- 6. Velocity analysis: Velocity of slip Both the links forming the sliding joint, are not grounded, implying a floating sliding joint. Notably, point A belongs to two different bodies, namely, 2&3, Implying case2: relative velocity. Axis of Slip: Line along which sliding occurs between links 3 &4. Axis of transmission: The line along which wecan transmit motion or force across the slider joint (except friction - assumednegligible)
- 7. Velocity analysis: Velocity of slip Intuition: The axis of 3 & 4 have a fixed geometric relationship, hence the rate of change of ╬Ė3 ╬Ė4 will remain the same: Žē3=Žē4 VA3=VA2
- 8. Velocity analysis: Velocity of slip Perpendicular to O2A Sense as Žē2
- 9. Velocity analysis: Velocity of slip