Unit 4 genetics and inheritance
1 like198 views
This document provides an overview of genetics and inheritance concepts taught in Campbell & Reece's chapters 14 and 15. It summarizes Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the basic principles of heredity, including dominant and recessive traits, segregation of alleles, and his laws of inheritance. The document also explains monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, sex determination, and inheritance of sex-linked genes.
1 of 41
























Ad
Recommended
Genetics and Inheritance
Genetics and InheritanceDylan Green
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics and inheritance concepts taught in Campbell & Reece's chapters 14 and 15. It begins by defining genetics as the study of heredity, then summarizes Gregor Mendel's pioneering experiments with pea plants which discovered the basic principles of heredity, including dominant and recessive traits, genotypes and phenotypes. The document explains how Mendel performed genetic crosses and formulated his laws of inheritance. It also covers additional genetics topics such as degrees of dominance, multiple alleles, pleiotropy, polygenic inheritance, sex determination, and inheritance of sex-linked genes.Unit 4 genetics and inheritance(2)
Unit 4 genetics and inheritance(2)siphesihle gloria Hlongwane
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics and inheritance concepts including:
- Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity through pea plant experiments including dominant and recessive traits.
- Genetic crosses can be used to determine the likelihood of offspring inheriting certain traits based on the parents' genotypes.
- Additional concepts covered include independent assortment, polygenic inheritance, sex determination, and sex-linked inheritance.Genetics and inheritance
Genetics and inheritanceSolomzi Nomvethe
Ėý
Genes are located on DNA and code for characteristics. Traits depend on both genes and environment. Mendel discovered genes through experiments with pea plants, showing traits are inherited as discrete units that assort and recombine independently. He found traits are dominant or recessive, and that alleles segregate and assort independently according to predictable statistical patterns. This laid the foundations for genetics.genetics and inheritance
genetics and inheritanceLuvo Maqungo
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics and inheritance concepts including:
- Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity through pea plant experiments and developed the laws of segregation and independent assortment.
- Genetic crosses can be used to determine the possible outcomes and traits of offspring. Monohybrid and dihybrid crosses examine one or two trait pairs.
- Genes exist in alleles that are dominant or recessive and determine an organism's genotype and phenotype. Sex is determined by X and Y chromosomes.Genetics and inheritance
Genetics and inheritanceNokuthula Hadebe
Ėý
This document discusses genetics and inheritance. It introduces Gregor Mendel as the father of genetics, who discovered the basic principles of heredity through his experiments breeding pea plants. It describes Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment. It also discusses sex determination and inheritance of sex-linked genes, noting disorders in humans caused by recessive alleles on the X chromosome like color blindness, Duchene muscular dystrophy, and hemophilia.Genetics and Heredity
Genetics and Heredityihmcbiology1213
Ėý
Here are some key points about sex-linked genetic disorders:
- Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder linked to the X chromosome. Males are affected more severely since they only have one X chromosome.
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy is an X-linked recessive disorder that causes progressive muscle degeneration and weakness. It primarily affects boys.
- Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder associated with an unusual structure on the X chromosome. It causes intellectual disabilities and specific physical characteristics.
- Color blindness, as mentioned in the passage, is a sex-linked trait carried on the X chromosome. Red-green color blindness is more common in males.
- Some other examples include hemophilia, DPrinciples of inheritance and variation
Principles of inheritance and variationHSE ZOOLOGY SHOWS
Ėý
Gregor Johann Mendel was the father of genetics. He conducted breeding experiments with pea plants and discovered the basic principles of heredity, including the laws of segregation and independent assortment. Through his experiments, he determined that traits are passed from parents to offspring via discrete units of inheritance called genes.7.genetics and inheritance
7.genetics and inheritancelmurdoch
Ėý
The document discusses genetics concepts like alleles, dominant and recessive traits, genotype and phenotype. It uses examples like pea plant height and mouse fur color to demonstrate inheritance patterns. Mendel's experiments with pea plants are cited to explain monohybrid crosses and how they were used to determine dominance relationships between alleles and predict offspring traits and genotypes.Genetics - Mendellian Principles of Heredity
Genetics - Mendellian Principles of HeredityChristine Joyce Javier
Ėý
The document discusses Gregor Mendel's experiments with garden peas, which led to the formulation of fundamental principles of heredity. It outlines Mendel's choice of garden peas for their observable traits, rapid reproduction, and self-pollination, and describes the results of his experiments that established the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. Key genetic terms and definitions, such as genes, alleles, and phenotype, are also provided to help understand the mechanics of heredity.Mendel law
Mendel lawfahadxahi
Ėý
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to establish the basic laws of inheritance. He found that traits from parents separate and recombine in predictable ways when passed to offspring. Mendel determined that traits are determined by discrete factors, now known as genes, which are inherited independently of each other. His work established the fundamental rules of genetics and heredity.Mendel's genetics
Mendel's genetics NOMSA TOLIBADI
Ėý
Gregor Mendel conducted the first recorded scientific study of heredity by breeding pea plants. Through his experiments, he discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes). Mendel determined that some traits are dominant and will mask recessive traits, and that traits are inherited independently of each other. His work established the basic principles of genetics and heredity.Mendel's laws 31 1 2011
Mendel's laws 31 1 2011Vasanthan vasudevan
Ėý
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who experimented with pea plants in the mid-19th century and is considered the father of genetics. Through his experiments crossing thousands of pea plants, he discovered the basic principles of heredity, including dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. His work showed that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes) that can be dominant or recessive.Mendelian genetics
Mendelian geneticsBahauddin Zakariya University lahore
Ėý
1. Mendel conducted breeding experiments with pea plants to study inheritance of traits such as flower color.
2. Through his experiments, he discovered that traits are inherited as discrete units (genes) which segregate and assort independently during reproduction according to his laws of inheritance.
3. Mendel's work laid the foundations of classical genetics although it was not widely recognized until rediscovered later.mendelian genetics
mendelian geneticsMarko Polo Manzano
Ėý
This document discusses Mendelian genetics and Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants. It covers key concepts such as genotype and phenotype, Mendel's experimental design using true-breeding pea traits, his findings on monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, and the principles of segregation and independent assortment. It also discusses how Mendelian genetics applies to inheritance patterns in humans through pedigree analysis and examples of genetic traits.Mendelism
MendelismWasiu Adeseji
Ėý
This document provides an outline and overview of Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the fundamental laws of inheritance. It discusses genetics prior to Mendel, Mendel's experiments crossing true-breeding pea plants, his establishment of the principles of dominance/recessiveness and segregation of alleles, and how his principles can be applied to understand human genetics through the use of pedigrees. The document serves to introduce Mendelism and Mendel's pivotal role in establishing the foundations of genetics.Law of independent assortment_TRISHA
Law of independent assortment_TRISHATrisha Salanatin
Ėý
The document discusses the Law of Independent Assortment, which states that the separation and distribution of genes to gametes during meiosis is independent between different chromosome pairs. Specifically, it notes that each gamete will contain only one gene for seed height and one for color from separate chromosomes, and that the four combinations of these genes will occur with roughly equal frequency. It also provides background that Mendel's groundbreaking work on genetics went ignored for 34 years until its rediscovery in 1900.Genetics And Mendel
Genetics And MendelJames H. Workman
Ėý
Gregor Mendel studied inheritance patterns of traits in pea plants in the 1800s. He found that traits like seed shape, color, and flower position were controlled by discrete factors (now called genes) that are passed from parents to offspring without blending. Some forms of these genes are dominant and mask the appearance of recessive genes in the first hybrid generation, but the recessive genes still exist and can be expressed in later generations. Mendel's discoveries established the foundations of classical genetics and heredity.Developing Branding Solutions for 2013
Developing Branding Solutions for 2013Thomas Daly
Ėý
The document presents a comprehensive overview of branding solutions for SharePoint 2013, focusing on various aspects such as branding assets, deploying custom master pages, and creating composed looks. It details key concepts like modules, feature receivers, and tools for improved SharePoint development. Additionally, it provides insights on styling with CSS and JavaScript, and offers practical examples of implementation strategies across different SharePoint environments.Building SharePoint 2013 Apps - Architecture, Authentication & Connectivity API
Building SharePoint 2013 Apps - Architecture, Authentication & Connectivity APISharePointRadi
Ėý
This document provides an overview of building SharePoint 2013 apps, including their architecture, authentication, and connectivity APIs. It discusses the app infrastructure and how apps work, authentication models for apps, and the Connectivity API for accessing SharePoint data from apps. The presentation also covers server-side and client-side app hosting models, app shapes including full pages and parts, and the app manifest and package.4.4
4.4AliyaSH
Ėý
ÐÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―Ņ ŅаŅŅОаŅŅÐļÐēаÐĩŅ ОÐĩŅÐūÐīŅ ÐēÐļзŅаÐŧÐļзаŅÐļÐļ ÐļÐ―ŅÐūŅОаŅÐļÐļ Ðē ŅÐĩКŅŅÐūÐēŅŅ
ÐīÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―ŅаŅ
, ÐēКÐŧŅŅаŅ Ð―ŅОÐĩŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ, ОаŅКÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ðļ ÐžÐ―ÐūÐģÐūŅŅÐūÐēÐ―ÐĩÐēŅÐĩ ŅÐŋÐļŅКÐļ, ŅÐ°ÐąÐŧÐļŅŅ Ðļ ÐģŅаŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐĩ ÐļзÐūÐąŅаÐķÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ. ÐÐ― ÐūÐŋÐļŅŅÐēаÐĩŅ ÐŋŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ÐūŅÐūŅОÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐīÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅŅ
Ðļ ÐēаÐķÐ―ÐūŅŅŅ ŅŅŅŅКŅŅŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ ÐļÐ―ŅÐūŅОаŅÐļÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐŧŅŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐĩÐĩ ÐēÐūŅÐŋŅÐļŅŅÐļŅ. ÐКÐŧŅŅÐĩÐ―Ņ ÐŋŅÐļОÐĩŅŅ ŅазÐŧÐļŅÐ―ŅŅ
ŅÐūŅОаŅÐūÐē ŅÐŋÐļŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ŅÐ°ÐąÐŧÐļŅ, а ŅаКÐķÐĩ ÐēÐūзОÐūÐķÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ŅÐĩÐīаКŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ ÐģŅаŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļŅ
ÐūÐąŅÐĩКŅÐūÐē Ðē ŅÐĩКŅŅÐūÐēŅŅ
ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐūŅаŅ
.The Whole Enchilada
The Whole Enchiladadavidshah
Ėý
The document appears to be a presentation about building a mobile app for ordering from Ohio City Burrito. It discusses using an agile approach with acceptance test-driven development (ATDD) and continuous collaboration between developers and product owners. Live coding is demonstrated for writing automated tests and code to display menu items and prices in the app.Deep dive into feature versioning in SharePoint 2010
Deep dive into feature versioning in SharePoint 2010Jeremy Thake
Ėý
This document discusses feature versioning and upgrade support in SharePoint 2010. It begins by explaining that some objects like fields and content types are easier to upgrade than others like workflows. It then covers imperative and declarative approaches to upgrading features. The declarative method uses attributes like VersionRange and UpgradeActions to specify upgrade logic. The document demonstrates upgrading features declaratively and imperatively in PowerShell. It provides tips on handling definitions and instances during upgrades and considerations for sandboxed solutions and assembly versions. References for further information are also included.Study: The Future of VR, AR and Self-Driving Cars
Study: The Future of VR, AR and Self-Driving CarsLinkedIn
Ėý
The research examines the integration of wearable technology, self-driving cars, and AI into everyday life. While 35% of respondents use wearables, their adoption increases with seniority and age, notably with higher usage in Brazil compared to the UK and Australia. Interest in purchasing self-driving cars and VR headsets varies significantly by age and region, with younger individuals showing greater openness, while concerns about AI are present but less acute among those interested in these technologies.genetics and inheritance
genetics and inheritanceOluhle Mantyi
Ėý
This document provides information about genetics and inheritance from a grade 12 lesson. It discusses:
1. What genetics is and how it relates to heredity and similarities/differences between parents and offspring.
2. Gregory Mendel's pioneering genetics experiments in the 1800s using pea plants which discovered the basic principles of heredity and inheritance through generations. He demonstrated dominant and recessive traits and that genes exist in different alleles.
3. How to solve genetic cross problems by determining the genotypes and phenotypes of parents and predicting offspring based on dominant and recessive traits. It provides examples of monohybrid and dihybrid cross problems involving traits like plant height, eye color in rabbits, and seed shapeUNIT 4 GENETICS AND INHERITANCE (2).pptx
UNIT 4 GENETICS AND INHERITANCE (2).pptxOluhle Mantyi
Ėý
This document provides information about genetics and inheritance from a grade 12 lesson. It discusses:
1. What genetics is and how it relates to heredity and similarities/differences between parents and offspring.
2. Gregory Mendel's pioneering genetics experiments in the 1800s using pea plants which discovered the basic principles of heredity and inheritance through generations. He demonstrated dominant and recessive traits and that genes exist in different alleles.
3. How to solve genetic cross problems by determining the genotypes and phenotypes of parents and predicting offspring based on dominant and recessive traits. It provides examples of monohybrid and dihybrid cross problems involving traits like plant height, eye color in rabbits, and seed shapeB4FA 2012 Nigeria: Principles of Genetics - Charles Amadi
B4FA 2012 Nigeria: Principles of Genetics - Charles Amadib4fa
Ėý
The lecture by Amadi Charles provides an overview of genetics, including key principles established by Gregor Mendel, such as the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. It discusses various inheritance patterns beyond Mendelian genetics, like incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, and sex-linked traits. The document also highlights the importance of genetic simulations for research efficiency and introduces genetic simulation programs available for educational purposes.grade 5 science genetics and heredity.pptx
grade 5 science genetics and heredity.pptxAhmed Samir
Ėý
The document outlines the fundamentals of genetics and heredity, emphasizing the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring, concepts such as dominant and recessive alleles, and Gregor Mendel's pioneering work in this area. It explains key terms like alleles, homozygous, and heterozygous, and introduces tools like Punnett squares for predicting genetic outcomes. Additionally, it discusses Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment, sex-linked disorders, and includes examples of genetic disorders.mendelian genetics 2 &non mendelian.pptx
mendelian genetics 2 &non mendelian.pptxJonasCabusbusan1
Ėý
The document provides an overview of genetics, focusing on inheritance patterns and seminal work by Gregor Mendel involving monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. Key concepts include genetic terminology, Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment, as well as applications to human genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis. It concludes with a summary of Mendel's principles and their significance in understanding heredity.More Related Content
What's hot (9)
Genetics - Mendellian Principles of Heredity
Genetics - Mendellian Principles of HeredityChristine Joyce Javier
Ėý
The document discusses Gregor Mendel's experiments with garden peas, which led to the formulation of fundamental principles of heredity. It outlines Mendel's choice of garden peas for their observable traits, rapid reproduction, and self-pollination, and describes the results of his experiments that established the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. Key genetic terms and definitions, such as genes, alleles, and phenotype, are also provided to help understand the mechanics of heredity.Mendel law
Mendel lawfahadxahi
Ėý
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to establish the basic laws of inheritance. He found that traits from parents separate and recombine in predictable ways when passed to offspring. Mendel determined that traits are determined by discrete factors, now known as genes, which are inherited independently of each other. His work established the fundamental rules of genetics and heredity.Mendel's genetics
Mendel's genetics NOMSA TOLIBADI
Ėý
Gregor Mendel conducted the first recorded scientific study of heredity by breeding pea plants. Through his experiments, he discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes). Mendel determined that some traits are dominant and will mask recessive traits, and that traits are inherited independently of each other. His work established the basic principles of genetics and heredity.Mendel's laws 31 1 2011
Mendel's laws 31 1 2011Vasanthan vasudevan
Ėý
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who experimented with pea plants in the mid-19th century and is considered the father of genetics. Through his experiments crossing thousands of pea plants, he discovered the basic principles of heredity, including dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. His work showed that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes) that can be dominant or recessive.Mendelian genetics
Mendelian geneticsBahauddin Zakariya University lahore
Ėý
1. Mendel conducted breeding experiments with pea plants to study inheritance of traits such as flower color.
2. Through his experiments, he discovered that traits are inherited as discrete units (genes) which segregate and assort independently during reproduction according to his laws of inheritance.
3. Mendel's work laid the foundations of classical genetics although it was not widely recognized until rediscovered later.mendelian genetics
mendelian geneticsMarko Polo Manzano
Ėý
This document discusses Mendelian genetics and Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants. It covers key concepts such as genotype and phenotype, Mendel's experimental design using true-breeding pea traits, his findings on monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, and the principles of segregation and independent assortment. It also discusses how Mendelian genetics applies to inheritance patterns in humans through pedigree analysis and examples of genetic traits.Mendelism
MendelismWasiu Adeseji
Ėý
This document provides an outline and overview of Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the fundamental laws of inheritance. It discusses genetics prior to Mendel, Mendel's experiments crossing true-breeding pea plants, his establishment of the principles of dominance/recessiveness and segregation of alleles, and how his principles can be applied to understand human genetics through the use of pedigrees. The document serves to introduce Mendelism and Mendel's pivotal role in establishing the foundations of genetics.Law of independent assortment_TRISHA
Law of independent assortment_TRISHATrisha Salanatin
Ėý
The document discusses the Law of Independent Assortment, which states that the separation and distribution of genes to gametes during meiosis is independent between different chromosome pairs. Specifically, it notes that each gamete will contain only one gene for seed height and one for color from separate chromosomes, and that the four combinations of these genes will occur with roughly equal frequency. It also provides background that Mendel's groundbreaking work on genetics went ignored for 34 years until its rediscovery in 1900.Genetics And Mendel
Genetics And MendelJames H. Workman
Ėý
Gregor Mendel studied inheritance patterns of traits in pea plants in the 1800s. He found that traits like seed shape, color, and flower position were controlled by discrete factors (now called genes) that are passed from parents to offspring without blending. Some forms of these genes are dominant and mask the appearance of recessive genes in the first hybrid generation, but the recessive genes still exist and can be expressed in later generations. Mendel's discoveries established the foundations of classical genetics and heredity.Viewers also liked (7)
Developing Branding Solutions for 2013
Developing Branding Solutions for 2013Thomas Daly
Ėý
The document presents a comprehensive overview of branding solutions for SharePoint 2013, focusing on various aspects such as branding assets, deploying custom master pages, and creating composed looks. It details key concepts like modules, feature receivers, and tools for improved SharePoint development. Additionally, it provides insights on styling with CSS and JavaScript, and offers practical examples of implementation strategies across different SharePoint environments.Building SharePoint 2013 Apps - Architecture, Authentication & Connectivity API
Building SharePoint 2013 Apps - Architecture, Authentication & Connectivity APISharePointRadi
Ėý
This document provides an overview of building SharePoint 2013 apps, including their architecture, authentication, and connectivity APIs. It discusses the app infrastructure and how apps work, authentication models for apps, and the Connectivity API for accessing SharePoint data from apps. The presentation also covers server-side and client-side app hosting models, app shapes including full pages and parts, and the app manifest and package.4.4
4.4AliyaSH
Ėý
ÐÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―Ņ ŅаŅŅОаŅŅÐļÐēаÐĩŅ ОÐĩŅÐūÐīŅ ÐēÐļзŅаÐŧÐļзаŅÐļÐļ ÐļÐ―ŅÐūŅОаŅÐļÐļ Ðē ŅÐĩКŅŅÐūÐēŅŅ
ÐīÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―ŅаŅ
, ÐēКÐŧŅŅаŅ Ð―ŅОÐĩŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ, ОаŅКÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ðļ ÐžÐ―ÐūÐģÐūŅŅÐūÐēÐ―ÐĩÐēŅÐĩ ŅÐŋÐļŅКÐļ, ŅÐ°ÐąÐŧÐļŅŅ Ðļ ÐģŅаŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐĩ ÐļзÐūÐąŅаÐķÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ. ÐÐ― ÐūÐŋÐļŅŅÐēаÐĩŅ ÐŋŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ÐūŅÐūŅОÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐīÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅŅ
Ðļ ÐēаÐķÐ―ÐūŅŅŅ ŅŅŅŅКŅŅŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ ÐļÐ―ŅÐūŅОаŅÐļÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐŧŅŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐĩÐĩ ÐēÐūŅÐŋŅÐļŅŅÐļŅ. ÐКÐŧŅŅÐĩÐ―Ņ ÐŋŅÐļОÐĩŅŅ ŅазÐŧÐļŅÐ―ŅŅ
ŅÐūŅОаŅÐūÐē ŅÐŋÐļŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ŅÐ°ÐąÐŧÐļŅ, а ŅаКÐķÐĩ ÐēÐūзОÐūÐķÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ŅÐĩÐīаКŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ ÐģŅаŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļŅ
ÐūÐąŅÐĩКŅÐūÐē Ðē ŅÐĩКŅŅÐūÐēŅŅ
ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐūŅаŅ
.The Whole Enchilada
The Whole Enchiladadavidshah
Ėý
The document appears to be a presentation about building a mobile app for ordering from Ohio City Burrito. It discusses using an agile approach with acceptance test-driven development (ATDD) and continuous collaboration between developers and product owners. Live coding is demonstrated for writing automated tests and code to display menu items and prices in the app.Deep dive into feature versioning in SharePoint 2010
Deep dive into feature versioning in SharePoint 2010Jeremy Thake
Ėý
This document discusses feature versioning and upgrade support in SharePoint 2010. It begins by explaining that some objects like fields and content types are easier to upgrade than others like workflows. It then covers imperative and declarative approaches to upgrading features. The declarative method uses attributes like VersionRange and UpgradeActions to specify upgrade logic. The document demonstrates upgrading features declaratively and imperatively in PowerShell. It provides tips on handling definitions and instances during upgrades and considerations for sandboxed solutions and assembly versions. References for further information are also included.Study: The Future of VR, AR and Self-Driving Cars
Study: The Future of VR, AR and Self-Driving CarsLinkedIn
Ėý
The research examines the integration of wearable technology, self-driving cars, and AI into everyday life. While 35% of respondents use wearables, their adoption increases with seniority and age, notably with higher usage in Brazil compared to the UK and Australia. Interest in purchasing self-driving cars and VR headsets varies significantly by age and region, with younger individuals showing greater openness, while concerns about AI are present but less acute among those interested in these technologies.Ad
Similar to Unit 4 genetics and inheritance (20)
genetics and inheritance
genetics and inheritanceOluhle Mantyi
Ėý
This document provides information about genetics and inheritance from a grade 12 lesson. It discusses:
1. What genetics is and how it relates to heredity and similarities/differences between parents and offspring.
2. Gregory Mendel's pioneering genetics experiments in the 1800s using pea plants which discovered the basic principles of heredity and inheritance through generations. He demonstrated dominant and recessive traits and that genes exist in different alleles.
3. How to solve genetic cross problems by determining the genotypes and phenotypes of parents and predicting offspring based on dominant and recessive traits. It provides examples of monohybrid and dihybrid cross problems involving traits like plant height, eye color in rabbits, and seed shapeUNIT 4 GENETICS AND INHERITANCE (2).pptx
UNIT 4 GENETICS AND INHERITANCE (2).pptxOluhle Mantyi
Ėý
This document provides information about genetics and inheritance from a grade 12 lesson. It discusses:
1. What genetics is and how it relates to heredity and similarities/differences between parents and offspring.
2. Gregory Mendel's pioneering genetics experiments in the 1800s using pea plants which discovered the basic principles of heredity and inheritance through generations. He demonstrated dominant and recessive traits and that genes exist in different alleles.
3. How to solve genetic cross problems by determining the genotypes and phenotypes of parents and predicting offspring based on dominant and recessive traits. It provides examples of monohybrid and dihybrid cross problems involving traits like plant height, eye color in rabbits, and seed shapeB4FA 2012 Nigeria: Principles of Genetics - Charles Amadi
B4FA 2012 Nigeria: Principles of Genetics - Charles Amadib4fa
Ėý
The lecture by Amadi Charles provides an overview of genetics, including key principles established by Gregor Mendel, such as the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. It discusses various inheritance patterns beyond Mendelian genetics, like incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, and sex-linked traits. The document also highlights the importance of genetic simulations for research efficiency and introduces genetic simulation programs available for educational purposes.grade 5 science genetics and heredity.pptx
grade 5 science genetics and heredity.pptxAhmed Samir
Ėý
The document outlines the fundamentals of genetics and heredity, emphasizing the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring, concepts such as dominant and recessive alleles, and Gregor Mendel's pioneering work in this area. It explains key terms like alleles, homozygous, and heterozygous, and introduces tools like Punnett squares for predicting genetic outcomes. Additionally, it discusses Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment, sex-linked disorders, and includes examples of genetic disorders.mendelian genetics 2 &non mendelian.pptx
mendelian genetics 2 &non mendelian.pptxJonasCabusbusan1
Ėý
The document provides an overview of genetics, focusing on inheritance patterns and seminal work by Gregor Mendel involving monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. Key concepts include genetic terminology, Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment, as well as applications to human genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis. It concludes with a summary of Mendel's principles and their significance in understanding heredity.G8 Science Q4- Week 3-Patterns-of-Inheritance.ppt
G8 Science Q4- Week 3-Patterns-of-Inheritance.pptElliePamaPastrana
Ėý
The document discusses patterns of inheritance in genetics, focusing on Mendelian genetics, which explores how traits are inherited from one generation to the next through genes. It defines key concepts such as alleles, dominant and recessive traits, and Mendel's laws of heredity, which include the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. Furthermore, it explains the processes of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses using examples of traits such as earlobe shape and hair color.Genetics Powerpoint.pptx
Genetics Powerpoint.pptxFolusoOyolola
Ėý
Genetics is the study of heredity and genes. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1800s that formed the basis of genetics. Through his work, he discovered the principles of inheritance, including that traits are determined by units now called genes, genes occur in different forms called alleles, dominant alleles mask recessive alleles, and alleles assort independently during gamete formation. Mendel's principles can be used to predict the results of genetic crosses and the inheritance of traits.Genetics..............................ppt
Genetics..............................pptrheapalmaortego
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics and key concepts from Gregor Mendel's experiments. It introduces Mendel's work with pea plants and how he established the principles of heredity through monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. His work demonstrated that traits are inherited through discrete units called genes. The document also defines important genetic terminology and concepts such as dominant/recessive alleles, genotypes, phenotypes and Punnett squares. It discusses how Mendel's principles apply universally, using the example of cystic fibrosis inheritance in humans. The principle of independent assortment and exceptions like incomplete dominance in snapdragons are also summarized.introduction to genetics final.pptx
introduction to genetics final.pptxAhmedYousseryBatan
Ėý
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1850s and 1860s to study inheritance of traits. Through his experiments with over 28,000 pea plants, he discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete factors, now known as genes. Mendel identified that for each trait, organisms inherit one gene from each parent, and that some genes are dominant and will always be expressed while others are recessive and only expressed when the dominant gene is not present. His work formed the basis of classical genetics and established the laws of segregation and independent assortment.Chapter 5 principles of inheritance and variation
Chapter 5 principles of inheritance and variationmohan bio
Ėý
- Mendelian genetics deals with the study of heredity and variation through experiments in pea plants by Gregor Mendel.
- Mendel discovered the laws of inheritance through experiments showing traits are inherited in dominant and recessive patterns.
- His work was later combined with the chromosomal theory of inheritance which showed genes are located on chromosomes and segregate during gamete formation according to Mendel's laws.mendelian genetics and hereditynnnn.pptx
mendelian genetics and hereditynnnn.pptxRamirezRejeanO
Ėý
The document is a lecture on genetics that covers core concepts such as Mendelâs principles of inheritance, genetic terminology, and various types of genetic crosses including monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. It explains Mendel's discoveries through studies on pea plants and introduces the concept of incomplete dominance. Additionally, it discusses genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis and Gaucher disease, as well as the significance of sex cell formation and allele segregation.mendelian genetics (1) (1).ppt
mendelian genetics (1) (1).pptSyedSaaqib1
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics and key concepts from Gregor Mendel's experiments. It introduces Mendel's work with pea plants, the principles of inheritance he established including dominance, segregation and independent assortment. It explains genetic crosses such as monohybrid and dihybrid through the use of Punnett squares. The document also discusses examples of genetic inheritance patterns in humans including cystic fibrosis and Gaucher disease. It concludes with a brief overview of concepts beyond Mendelian genetics like incomplete dominance.Mendelians bhya jevaha hdjdjbbbus god.ppt
Mendelians bhya jevaha hdjdjbbbus god.pptthakreyouraj100
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics concepts including:
- Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the principles of heredity and inheritance patterns
- Key genetics terms like genotype, phenotype, alleles, homozygous, heterozygous
- How Mendel used monohybrid and dihybrid crosses to study single and double trait inheritance through Punnett squares
- His principles of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment
- Examples of genetic inheritance patterns in humans like cystic fibrosis and Gaucher disease
- Exceptions to Mendelian genetics through incomplete dominance seen in snapdragon flower colorHeredity
HeredityLevi Nebres
Ėý
This document provides an overview of genetics and heredity. It discusses how traits are passed from parents to offspring through alleles and genes. It introduces key genetics concepts and terminology such as dominant and recessive traits, genotypes, phenotypes, homozygous and heterozygous. The document outlines Gregor Mendel's pioneering experiments with pea plants in the 1860s, which laid the foundations for modern genetics through his discovery of dominant and recessive traits and his laws of inheritance. It also explains tools used in genetics like Punnett squares, pedigree charts, and the roles of chromosomes and sex determination in heredity.Mendelian's Genetics: Monohybrid, Dyhybrid, Trihybrid
Mendelian's Genetics: Monohybrid, Dyhybrid, Trihybridmain23001654
Ėý
monohybrid cross, dyhybrid cross, punette square, mendelian genetics, mendelian ratio, Patterns of inheritance, Test cross
Beyond Mendelian Genetics â incomplete dominance, Introduction to Genetics and heredity
Gregor Mendel â a brief bio
Genetic terminology (glossary), genotype, phenotype,
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian GeneticsMauiGemSerao
Ėý
This lecture covers the basics of genetics including an introduction to Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants, genetic terminology, monohybrid and dihybrid crosses using Punnett squares, Mendel's principles of inheritance, and concepts beyond Mendel like incomplete dominance. Key points covered include Mendel discovering the basic principles of heredity through studying traits in pea plants, how dominant and recessive alleles are inherited in monohybrid and dihybrid crosses according to his principles, and the concept of incomplete dominance in traits like flower color.4.5 Theoretical Genetics
4.5 Theoretical GeneticsPatricia Lopez
Ėý
This document provides an overview of theoretical genetics concepts including:
1) It defines key genetics terms and concepts discovered by Gregor Mendel through his pea plant experiments, including genes, alleles, dominance, segregation, and Punnett squares.
2) It explains Mendel's principles of inheritance including segregation and independent assortment of alleles and how this determines genotype and phenotype probabilities.
3) It discusses extensions of Mendelian genetics including co-dominance, multiple alleles, genetic linkage, sex-linkage, and examples like blood types and hemophilia.Genetics and Inheritance
Genetics and InheritanceReginald V. Finley Sr. M.Ed.
Ėý
The document provides a comprehensive overview of genetics and inheritance, focusing on key concepts such as genes, alleles, dominant and recessive traits, and the principles of segregation and independent assortment. It details Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants, explaining how he formulated the foundation of heredity through concepts like purebreds, hybrids, complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and co-dominance, as well as dihybrid crosses. Additionally, the document discusses multi-allele systems, sex linkage, and polygenic inheritance, providing definitions and explanations for various genetic terms and concepts.Chapter 9 notes
Chapter 9 notesmjnepa
Ėý
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in his monastery garden to study heredity and the transmission of traits from parents to offspring. He observed seven traits in pea plants that each had two contrasting variants. Through controlled pollination experiments over multiple generations, he discovered that traits are transmitted through discrete factors, now known as genes. His work established the laws of segregation and independent assortment, laying the foundation for modern genetics.Ad
Recently uploaded (15)
Experience the Charm of Bur Dubai Living
Experience the Charm of Bur Dubai Livinggeorgemmmlaws
Ėý
Discover the unique blend of history, culture, and modern convenience that makes Bur Dubai one of the most vibrant neighborhoods in the heart of Dubai. From traditional souks and heritage sites to trendy cafÃĐs and waterfront living, Bur Dubai offers something for everyone. Whether you're a resident, newcomer, or visitor, this dynamic area provides a rich lifestyle experience shaped by community, accessibility, and authentic charm. Join us as we explore what it's like to live in Bur Dubai â where the past meets the present in the most captivating ways.Light Up the Night with a Luxe Candle Party Experience
Light Up the Night with a Luxe Candle Party ExperienceWick & Pour
Ėý
Light up the night with a luxe candle party experience that blends elegance, creativity, and ambiance. Craft your own signature candles, sip on fine drinks, and enjoy a cozy, glamorous atmosphere with friends. Perfect for celebrations or a unique night out, this unforgettable event offers relaxation, laughter, and glowing memories that linger long after the flame fades.Al Barari Living Where Nature Meets Elegance
Al Barari Living Where Nature Meets Elegancegeorgemmmlaws
Ėý
Al Barari Living showcases one of Dubaiâs most exclusive and nature-inspired residential communities. Designed as a green oasis in the heart of the city, Al Barari is known for its luxurious villas, landscaped gardens, and commitment to sustainable living. From organic eateries and wellness centers to tranquil water features and botanical beauty, Al Barari is more than a home â it's a lifestyle built around peace, privacy, and elegance.JUNE 15 Blessed FAMILIES series 2025.pptx
JUNE 15 Blessed FAMILIES series 2025.pptxJose Ramos
Ėý
Used for FATHERS DAY and KINGSMEN Sunday at HLM 715amLOTEnacional 9amAYALA 1030am 2pmSMX 5pmAYALAVietnamâs Healthcare Visionary Joins Global CEO Ranks: Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, CEO...
Vietnamâs Healthcare Visionary Joins Global CEO Ranks: Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, CEO...Gorman Bain Capital
Ėý
In a major nod to Vietnamâs growing clout in regional healthcare, Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, CEO and Board Member of Prima Medical Center Saigon, has been spotlighted this week by the Global CEO Community among the most influential new members across Asia-Pacific leadership circles.
Dr. Bao appears alongside power players such as Vivek Aranha of AIA, Anson Li of Kroll, and Tommy Wong of Mercedes-Benz HK in the June 18 issue of CXO WEEKLY (Vol. 425), a roundup of top-tier executive movements curated by global leadership advisor Gary Lam.
But Dr. Baoâs inclusion stands out for one key reason: he is the only hospital CEO on the listârepresenting not just healthcare, but a bold new vision of cross-border medical innovation driven from Vietnam.
Under his leadership, Prima Saigon has earned acclaim as one of Asiaâs Top 10 Hospitals, blending international clinical standards with tech-forward infrastructure. Dr. Bao, who brings a rare mix of medical insight and financial strategy (MBA, CFA, CMT, FMVA among his titles), has also recently been ranked #7 among Vietnamâs Top 200 Healthcare Influencers on LinkedIn.
While other executives on the list are making headlines in finance, consulting, and technology, Dr. Bao is drawing attention to Vietnamâs emerging role in medical tourism, digital health, and integrated patient-centered care. His voice is increasingly shaping thought leadership on topics like healthcare equity and hospital digital transformation across Southeast Asia.
His presence in this elite league of CEOs reflects more than personal achievementâit marks the global recognition of Vietnamâs maturing healthcare sector, and the growing importance of leaders who can translate local challenges into regional innovation.
As Asiaâs healthcare systems race to modernize post-pandemic, names like Dr. Tran Quoc Bao arenât just part of the conversationâtheyâre setting the agenda.History of Ayurveda: Ancient Roots to Global Healing
History of Ayurveda: Ancient Roots to Global HealingVedic Meet
Ėý
Discover the complete history of Ayurveda, from its Vedic origins to modern global recognition. Learn how this ancient healing system continues to transform lives today.
Eleanora Kurban - Solo Hiking Safety Tips
Eleanora Kurban - Solo Hiking Safety TipsEleanora Kurban
Ėý
Solo hiking offers a unique way to connect with nature. When solo hiking, safety is paramount. Understanding dangers and mitigating them may make an intimidating journey more enjoyable.
10 Kid-Friendly Fairy Garden Designs with Sparkling Trails
10 Kid-Friendly Fairy Garden Designs with Sparkling Trailscivil hospital parasia
Ėý
Creating a fairy garden is a delightful way to spark your childâs imagination and encourage outdoor play. These miniature landscapes filled with whimsical fairy houses, tiny plants, and glowing trails offer a magical escape right in your backyard or balcony. Adding sparkling paths made with glow-in-the-dark stones takes the enchantment to the next level, especially for evening garden strolls..Live a life without any regrets and be someone who will be respected by everyone
Live a life without any regrets and be someone who will be respected by everyonesmartninja1947
Ėý
Be happy be healthyKOTA DORIA DUPATTA PRESENTATION UPLOAD part
KOTA DORIA DUPATTA PRESENTATION UPLOAD partprekshachittorasingl
Ėý
Kota Doria dupattas are lightweight and sheer, known for their unique checkered weave made from cotton and silk. Originating from Kota, Rajasthan, these dupattas are celebrated for their breathability and elegant drape, making them a popular choice for both casual and formal wear. The fabric's distinctive texture and intricate patterns, often achieved through block printing or tie-dye techniques, add to their appeal. Experience the Charm of Al Muhaisnah, Dubai
Experience the Charm of Al Muhaisnah, Dubaigeorgemmmlaws
Ėý
Al Muhaisnah is a dynamic and diverse residential area in Dubai, known for its vibrant community and strategic location in the northeastern part of the city. This neighbourhood offers a mix of affordable housing options, including villas and apartments, catering largely to families and working professionals. With essential amenities such as schools, parks, mosques, and shopping centers, Al Muhaisnah provides a practical and culturally rich living environment. The areaâs accessibility to major highways makes it convenient for commuters, while ongoing development projects highlight its growing potential for real estate investment. This presentation explores Al Muhaisnahâs unique characteristics, community lifestyle, and its role in Dubaiâs urban landscape.technology and productivity power point presentation
technology and productivity power point presentationFernandoMateodePablo2
Ėý
technology and productivity power point Danang's Medical Tourism - A Promising Frontier for Asiaâs Health and Wellnes...
Danang's Medical Tourism - A Promising Frontier for Asiaâs Health and Wellnes...Gorman Bain Capital
Ėý
As global travelers increasingly seek meaningful, wellness-oriented experiences, DanangâVietnamâs coastal gemâis emerging as a compelling destination for high-quality medical tourism. Recognized for its scenic beaches, cultural richness, and modern infrastructure, the city is now preparing for a major breakthrough in health-related travel.
To gain deeper insights into this evolution, Forbes spoke with Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, a prominent leader in Asiaâs healthcare and wellness industry, about Danangâs strategy and what the city must do to unlock its full potential in medical tourism.
________________________________________
Building a Strong Foundation for High-Quality Healthcare Travel
"Medical tourism is not a casual venture," says Dr. Tran. "It demands a robust ecosystemâstate-of-the-art medical equipment, highly qualified healthcare professionals, strong aesthetic and wellness services, and even integration of traditional medicine practices." According to him, Danang is poised to deliver on these requirements.
The city has already ratified a strategic plan for developing medical tourism, aiming to blend its vibrant travel offerings with health services such as diagnostics, wellness retreats, cosmetic procedures, and traditional medicine therapies. âWhat makes Danang stand out is its unique ability to integrate healthcare with world-class tourism experiences,â Dr. Tran explains.
________________________________________
Is Danang Late to the Game? Not Quite.
When asked whether Danangâs entry into the medical tourism sector is delayed, Dr. Tran disagrees. âItâs not about who moves firstâit's about who builds the most sustainable and quality-driven ecosystem. The timing is right,â he affirms.
With global demand for wellness and medical travel surging post-pandemic, Danangâs entry coincides with a pivotal moment. âPatients and wellness travelers are now more focused on holistic health and value-for-money experiences. Danang, with its favorable cost structure and rising medical standards, is well-positioned,â he adds.
________________________________________
What Tourists Are Seeking
Though data specific to medical tourism usage is sparse, Dr. Tran notes a growing trend: âWe see strong demand for cosmetic enhancements, health screenings, physical conditioning programs, and traditional medicine experiences. These are areas where Vietnamâand especially Danangâhas a comparative advantage.â
These services are bolstered by a skilled medical workforce, advanced medical technology, and the allure of beachside recovery and relaxationâa major draw for health-conscious travelers.
________________________________________
Competitive Advantages in a Global Arena
According to Dr. Tran, Danangâs key strengths lie in affordability, accessibility, and quality care. âCompared to other regional medical hubs like Bangkok or Seoul, Danang offers a more cost-effective experience without sacrificing safety or expertise,â he says. Vietnamâs Healthcare Visionary Joins Global CEO Ranks: Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, CEO...
Vietnamâs Healthcare Visionary Joins Global CEO Ranks: Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, CEO...Gorman Bain Capital
Ėý
Danang's Medical Tourism - A Promising Frontier for Asiaâs Health and Wellnes...
Danang's Medical Tourism - A Promising Frontier for Asiaâs Health and Wellnes...Gorman Bain Capital
Ėý
Unit 4 genetics and inheritance
- 1. UNIT 4: GENETICS AND INHERITANCE Campbell & Reece: Chapters 14 and 15
- 2. 1. WHAT IS GENETICS âĒ Genetics: The study of heredity. âĒ Heredity is the relations between successive generations. âĒ Why do children look a little bit like their parents but also different? âĒ What is responsible for these similarities and differences?
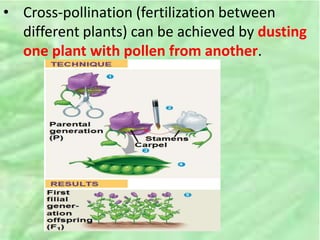
- 3. 2. MENDELâS GENETICS âĒ Gregory Mendel is the father of Genetics. âĒ Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity by breeding garden peas in carefully planned experiments. âĒ Advantages of pea plants for genetic study: Cross-pollination (fertilization between different plants) can be achieved by dusting one plant with pollen from another.
- 4. âĒ Cross-pollination (fertilization between different plants) can be achieved by dusting one plant with pollen from another.
- 5. âĒ He also used varieties that were true-breeding (organisms with only one variety of a type e.g. red flowers can only produce red flowers) âĒ In a typical experiment, Mendel mated two contrasting, true-breeding varieties, a process called hybridization âĒ The true-breeding parents are the P generation. âĒ The hybrid offspring of the P generation are called the F1 generation âĒ When F1 individuals self-pollinate, the F2 generation is produced
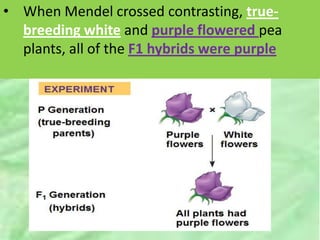
- 6. âĒ When Mendel crossed contrasting, true- breeding white and purple flowered pea plants, all of the F1 hybrids were purple
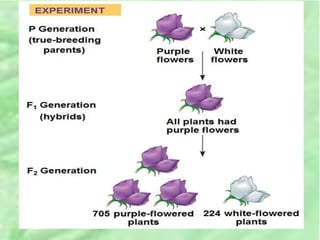
- 7. âĒ When Mendel crossed the F1 hybrids, many of the F2 plants had purple flowers, but some had white âĒ Mendel discovered a ratio of about three to one, purple to white flowers, in the F2 generation.
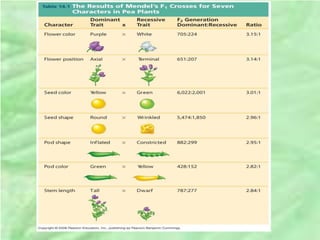
- 9. âĒ Mendel reasoned that only the purple flower factor was affecting flower color in the F1 hybrids. âĒ Mendel called the purple flower color a dominant trait and the white flower color a recessive trait âĒ What Mendel called a âheritable factorâ is what we now call a gene âĒ He did 7 other crosses using different traits and found the same phenomenon.
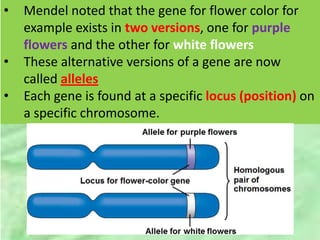
- 11. âĒ Mendel noted that the gene for flower color for example exists in two versions, one for purple flowers and the other for white flowers âĒ These alternative versions of a gene are now called alleles âĒ Each gene is found at a specific locus (position) on a specific chromosome.
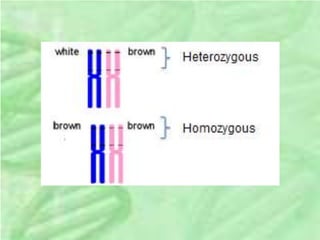
- 12. âĒ The two alleles at a locus on a homologous chromosome pair may be identical, as in the true-breeding plants â they are then said to be homozygous for that trait/gene. âĒ Alternatively, the two alleles at a locus may differ â they are said to be heterozygous for that gene/trait. âĒ If the two alleles at a locus differ, then one (the dominant allele) determines the organismâs appearance (we refer to it as its phenotype), and the other (the recessive allele) has no noticeable effect on
- 14. âĒ Mendel then formulated the law of segregation, states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate (segregate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes âĒ Thus, an egg or a sperm gets only one of the two alleles that are present in the somatic cells of an organism.
- 15. âĒ An organism traits are indicated via its genotype and phenotype. ïķ Genotype: The genetic composition of the gene, indicated by letters e.g. GG, Gg, gg. (A capital letter represents a dominant allele, and a lowercase letter represents a recessive allele) ïķ Phenotype: The external appearance of the gene e.g. Brown hair, white hair.
- 16. 3. GENETIC CROSSES âĒ HOW CAN WE NOW MORE OF LESS DETERMINE WHAT WILL BE THE OUTCOME IF 2 ORGANISMS HAVE A BABY?
- 17. TWO TYPES OF GENETIC CROSSES âĒ MONOHYBRID CROSSES: A cross between 2 organisms where we only look an one pair of contrasting traits. âĒ DIHYBRID CROSS: A cross between 2 organisms where we look at two pairs of contrasting traits at the same time.
- 18. MONOHYBRID CROSS -EXAMPLE âĒ Determine the outcome/ F1 generation of a cross between a homozygous tall plant and a homozygous short plant. Tall plants are dominant over short plants.
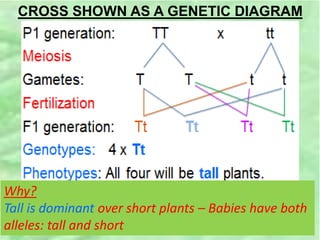
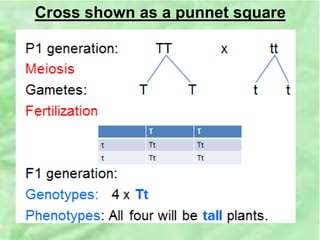
- 19. STEPS TO SOLVE A CROSS PROBLEM 1. What trait are we looking at? 2. Choose a letter to represent the trait. 3. See if you can identify which trait is dominant â allocate the capital letter to that trait. 4. Identify the recessive trait and allocate a lower case letter to that trait. 5. Determine the genotypes of the parents. â Homozygous dominant â Two capital letters e.g. GG Homozygous recessive â Two lower case letter. E.g. gg Heterozygous â One capital letter and one lower case letter e.g. Gg 1. Start with cross
- 20. SOLUTION 1. Trait â Size of plant. 2. Letter chosen to represent size of plant = T/t 3. Tall plants are dominant. (Given in problem) â Given the â âTâ (capital T) 4. Short plants are recessive â given the âtâ (lower case t) 5. One parent is homozygous tall â TT other parent is homozygous short - tt
- 21. CROSS SHOWN AS A GENETIC DIAGRAM Why? Tall is dominant over short plants â Babies have both alleles: tall and short
- 22. Cross shown as a punnet square
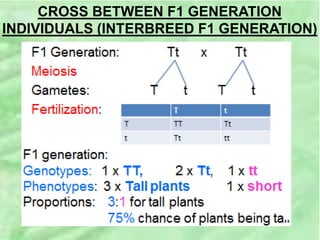
- 23. CROSS BETWEEN F1 GENERATION INDIVIDUALS (INTERBREED F1 GENERATION)
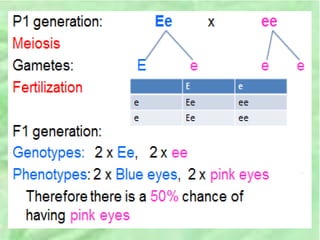
- 24. MONOHYBRID CROSS âEXAMPLE 2 A heterozygous blue eyed rabbit is crossed with a rabbit with pink eyes. What is the possibility of the babies being born with pink eyes?
- 25. SOLUTION 1. Trait: eye colour of rabbit. 2. Letter used: E/e 3. Dominant trait: Blue eyes (Why? The first rabbit is heterozygous â both alleles â but blue is being expressed in rabbit eyes.) = E 4. Recessive trait: pink eyes = e 5. Rabbit one â heterozygous: Ee Rabbit two â homozygous: ee (why?) The only way that a rabbit can have pink eyes expressed externally is if both alleles code for pink eyes.
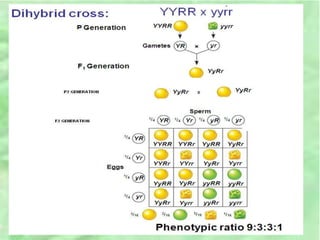
- 27. EXAMPLE OF A DIHYBRID CROSS Determine the F2 generation of a cross between yellow round seeded peas and wrinkled green seeded peas. Yellow and round seeds are dominant.
- 29. âĒ Using a dihybrid cross, Mendel developed the law of independent assortment âĒ The law of independent assortment states that each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation. âĒ Strictly speaking, this law applies only to genes on different, nonhomologous chromosomes âĒ Genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together.
- 30. 4. DEGREES OF DOMINANCE âĒComplete dominance One allele suppresses the expression of the other allele. âĒ Incomplete dominance: phenotype of F1 hybrids is somewhere between the phenotypes of the 2 parental varieties â neither allele completely dominant (White x Red = Pink) âĒ Codominance, 2 dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. (Red and white flowers = White and red
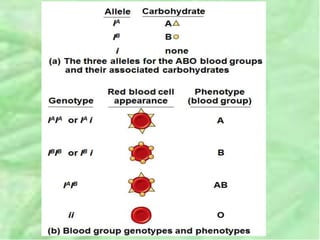
- 31. 5. MULTIPLE ALLELES ïą Most genes exist in populations in more than two allelic forms. ïą For example, the four phenotypes of the ABO blood group in humans are determined by three alleles for the enzyme (I) that attaches A or B carbohydrates to red blood cells: IA, IB, and i. ïą The enzyme encoded by the IA allele adds the A carbohydrate, whereas the enzyme encoded by the IB allele adds the B carbohydrate; the enzyme encoded by the i allele adds neither.
- 33. 6. PLEIOTROPY ï§ Most genes have multiple phenotypic effects, a property called pleiotropy ï§ For example, pleiotropic alleles are responsible for the multiple symptoms of certain hereditary diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and sickle-cell disease
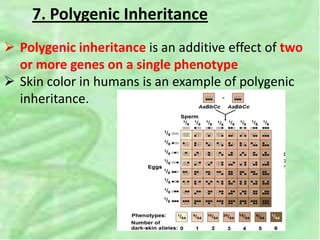
- 34. 7. Polygenic Inheritance ï Polygenic inheritance is an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotype ï Skin color in humans is an example of polygenic inheritance.
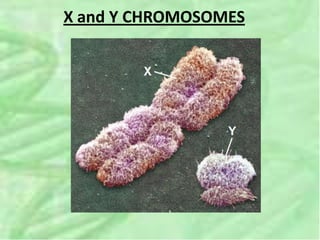
- 35. 8. DETERMINING THE SEX OF A BABY ï In humans and other mammals, there are two varieties of sex chromosomes: a larger X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome ï Only the ends of the Y chromosome have regions that are homologous with the X chromosome ï The SRY gene on the Y chromosome codes for the development of testes.
- 36. X and Y CHROMOSOMES
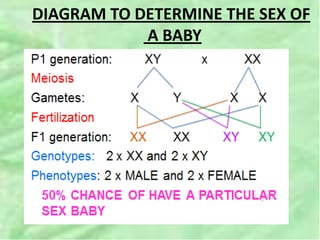
- 37. ï Females are XX, and males are XY ï Each ovum contains an X chromosome, while a sperm may contain either an X or a Y chromosome.
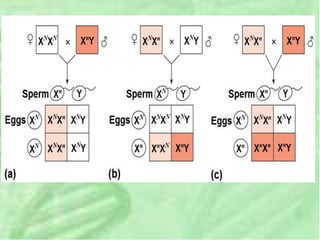
- 38. DIAGRAM TO DETERMINE THE SEX OF A BABY
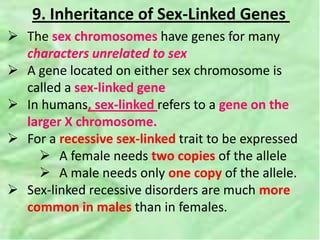
- 39. 9. Inheritance of Sex-Linked Genes ï The sex chromosomes have genes for many characters unrelated to sex ï A gene located on either sex chromosome is called a sex-linked gene ï In humans, sex-linked refers to a gene on the larger X chromosome. ï For a recessive sex-linked trait to be expressed ï A female needs two copies of the allele ï A male needs only one copy of the allele. ï Sex-linked recessive disorders are much more common in males than in females.
- 41. Some disorders caused by recessive alleles on the X chromosome in humans: âĒ Color blindness âĒ Duchenne muscular dystrophy âĒ Hemophilia
