Unitc manufacturing basic-machine_processes
- 1. Basic MachineBasic Machine ProcessesProcesses Competency D403.00Competency D403.00 Identify the basic conceptsIdentify the basic concepts of the manufacturingof the manufacturing processes.processes.
- 2. Basic Machine ProcessesBasic Machine Processes Objective D403.01Objective D403.01 Explain the conceptsExplain the concepts of the manufacturingof the manufacturing process.process.
- 3. ManufacturingManufacturing ’ü« Arrived from the Latin word ŌĆ£manu factusŌĆØ, meaning ŌĆ£made by handŌĆØ. ’ü« Manufacturing is the process of converting raw materials into products.
- 4. WHY STUDYWHY STUDY MANUFACTURING PROCESSES?MANUFACTURING PROCESSES? The designer and the drafter must have a working knowledge of the various processes that could produce a part in order to: lower cost and reduce production time.
- 5. Three Phases Of TheThree Phases Of The Manufacturing ProcessManufacturing Process 1. Product design. 2. Selection of materials. 3. Selection of production methods and techniques.
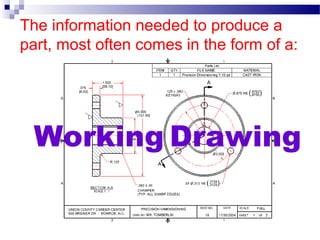
- 6. The information needed to produce a part, most often comes in the form of a: Working Drawing
- 7. Three Main Stages Of TheThree Main Stages Of The Production Of A Machined PartProduction Of A Machined Part Rough Forming Casting, Forging, Welding Finishing Drilling, machining, surfacing Assembling The assembly of parts
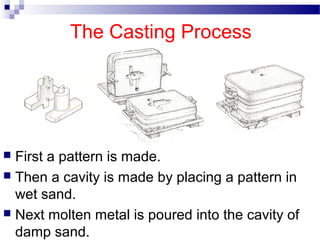
- 8. The Casting Process ’ü« First a pattern is made. ’ü« Then a cavity is made by placing a pattern in wet sand. ’ü« Next molten metal is poured into the cavity of damp sand.
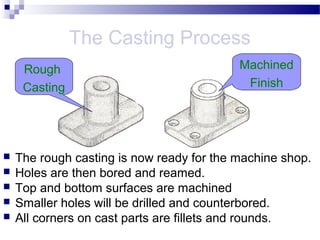
- 9. The Casting Process ’ü« The rough casting is now ready for the machine shop. ’ü« Holes are then bored and reamed. ’ü« Top and bottom surfaces are machined ’ü« Smaller holes will be drilled and counterbored. ’ü« All corners on cast parts are fillets and rounds. Rough Casting Machined Finish
- 10. Forging Process ’ü« Forging is produced by using heavy mechanical presses or hammering heated bars of metal between dies. ’ü« Advantages of forging over sand casting are that forged parts are much stronger and less brittle.
- 11. Welding Welding is the fusion or joining of two pieces of metal by means of heat, with or without the application of pressure. Cast Welded
- 12. ManufacturingManufacturing MaterialsMaterials Fall into three general categories: 1. Metal 2. Plastic 3. Inorganic materials
- 13. Metals are classified as:Metals are classified as: ’ü« Ferrous - contain iron and steel. ’ü« Nonferrous - do not have iron content (such as copper and aluminum). ’ü« Alloys - mixture of two or more metals.
- 14. Inorganic Materials Include:Inorganic Materials Include: ŌĆó Carbon and graphite - have low tensile strength (ability to be stretched). ŌĆó Ceramics are clay and glass materials. (resistant to heat, chemicals, & corrosion).
- 15. Heat-Treating:Heat-Treating: ’ü« Annealing ŌĆō is the process generally used to soften metal by heating followed by slow cooling. ’ü« Hardening ŌĆō requires heating and then rapid cooling in oil or water.
- 16. Plastics Processing The plastics industry represents one of the major manufacturing segments. ’ü« Thermoplastic ŌĆō becoming or remaining soft and moldable when subjected to heat. ’ü« Thermosetting ŌĆō becoming permanently hard and unmoldable when once subjected to heat.
- 17. Typical Plastic Processing Operations Include: ’é¦ Extrusion ’é¦ Blow Molding ’é¦ Injection Molding ’é¦ Thermoforming
- 18. ExtrudingExtruding The process of producing shapes by forcing hot metal through a die that has and opening of the desired shape.
- 19. Blow Molding Used in the production of bottles, automotive ductwork, hollow toy components, and door panels.
- 20. Injection Molding Used to manufacture products such as housings for electronic implements, automotive components, food storage containers, and components for medical applications. . ┬Ā ┬Ā ┬Ā
- 21. Thermoforming ’ü« Used in the manufacturing of thin-walled packages for the food industry. ’ü« Manufactured primarily by injection molding.
- 22. CAD in Manufacturing ’ü« The process of developing a design drawing on a CAD system and producing it on a computerized machine is called CAD/CAM. ’ü« The process of converting the CAD drawing into a preprogrammed, coded instructions is called Computer Numerical Control (CNC). ’ü« The advantages of the (CNC) is, better production and control, increased productivity, decreased labor and lower production costs.
- 23. The Machinist Steel Ruler ’ü« Commonly used measuring tool for getting rough measurements on a part. ’ü« The smallest division on the fractional scale is 1/64ŌĆØ (.016).
- 24. Vernier CaliperVernier Caliper ’ü« Precise measuring. ’ü« Decimal, fractional, or metric. ’ü« Often used by drafters to record dimensions from a machined prototype or part.
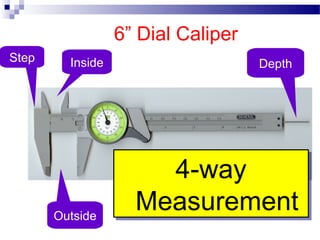
- 25. 6ŌĆØ Dial Caliper Inside Inside Outside DepthStep 4-way Measurement 4-way Measurement
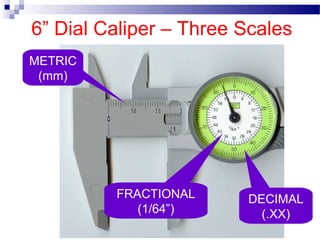
- 26. 6ŌĆØ Dial Caliper ŌĆō Three Scales METRIC (mm) DECIMAL (.XX) FRACTIONAL (1/64ŌĆØ)