Unit-ii-Queue ADT.pptx
- 1. Queue
- 2. 6/4/2023 CS 201 What is a Queue? âĒ Like stacks, queues are lists. With a queue, however, insertion is done at one end whereas deletion is done at the other end. âĒ Queues implement the FIFO (first-in first-out) policy. E.g., a printer/job queue! âĒ Two basic operations of queues: âĒ dequeue: remove an item/element from front âĒ enqueue: add an item/element at the back dequeue enqueue
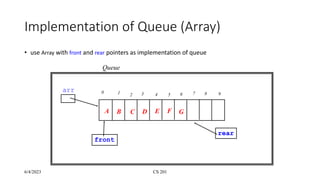
- 3. 6/4/2023 CS 201 Implementation of Queue (Array) âĒ use Array with front and rear pointers as implementation of queue Queue arr 0 1 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 A B C D E F G front rear
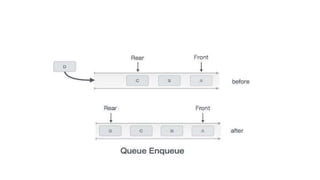
- 4. Enqueue Operation âĒ Queues maintain two data pointers, front and rear. The following steps should be taken to enqueue (insert) data into a queue â Step 1 â Check if the queue is full. Step 2 â If the queue is full, produce overflow error and exit. Step 3 â If the queue is not full, increment rear pointer to point the next empty space. Step 4 â Add data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing. Step 5 â return success.
- 6. procedure enqueue(data) if queue is full return overflow endif rear â rear + 1 queue[rear] â data return true end procedure
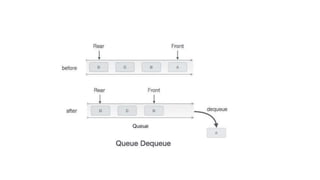
- 7. Dequeue Operation âĒ Accessing data from the queue is a process of two tasks â access the data where front is pointing and remove the data after access. The following steps are taken to perform dequeue operation â âĒ Step 1 â Check if the queue is empty. âĒ Step 2 â If the queue is empty, produce underflow error and exit. âĒ Step 3 â If the queue is not empty, access the data where front is pointing. âĒ Step 4 â Increment front pointer to point to the next available data element. âĒ Step 5 â Return success.
- 9. procedure dequeue if queue is empty return underflow end if data = queue[front] front â front + 1 return true end procedure
- 10. Check full bool isfull() { if(rear == MAXSIZE - 1) return true; else return false; }
- 11. Check empty bool isempty() { if(front < 0 || front > rear) return true; else return false; }
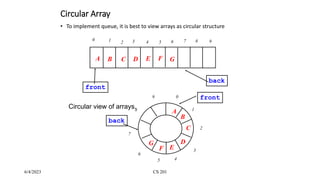
- 12. 6/4/2023 CS 201 Circular Array âĒ To implement queue, it is best to view arrays as circular structure 0 1 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 A B C D E F G front back front back A B C D E F G 0 1 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 Circular view of arrays.
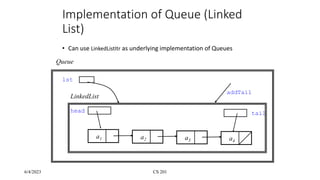
- 13. 6/4/2023 CS 201 Implementation of Queue (Linked List) âĒ Can use LinkedListItr as underlying implementation of Queues a1 a2 a3 a4 head tail Queue lst LinkedList addTail
- 14. âĒ dequeue: remove an item/element from front ( tail pointer) - Delete first âĒ enqueue: add an item/element at the rear ( head pointer) insert first



![procedure enqueue(data)
if queue is full
return overflow
endif
rear â rear + 1
queue[rear] â data
return true
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-ii-queueadt-230604123745-2f53de58/85/Unit-ii-Queue-ADT-pptx-6-320.jpg)

![procedure dequeue
if queue is empty
return underflow
end if
data = queue[front]
front â front + 1
return true
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-ii-queueadt-230604123745-2f53de58/85/Unit-ii-Queue-ADT-pptx-9-320.jpg)