Upcat 2009 handout
- 1. UPCAT REVIEWER 2009 ~AJDRC (arrajeuneze@yahoo.com) : UPCAT Lecturer SCIENCES Solar System Mang Mercury Nearest to the sun, thin atmosphere Victor Venus Hottest planet, greenhouse effect, retrogade Espinosa Earth Planet of life Mag Mars The red planet Jogging Jupiter Largest planet, with rings Sa Saturn 100 rings Umaga Uranus Rotates on side, retrogade Ng Neptune Has rings Pumayat Pluto (not a planet anymore) Principles of biology ŌĆó Cell theory. Cell Theory is the study of everything that involves cells.All living organisms are made of at least one cell, the basic unit of function in all organisms. In addition, the core mechanisms and chemistry of all cells in all organisms are similar, and cells emerge only from preexisting cells that multiply through cell division. The study of cell theory will tell you how cells are made, how they reproduce, how they interact with their environment, what it is composed of, and how the materials that make up a cell work and there interaction with the other sections of the cells. ŌĆó Evolution. Through natural selection and genetic drift, a population's inherited traits change from generation to generation. ŌĆó Gene theory. A living organism's traits are encoded in DNA, the fundamental component of genes. In addition, traits are passed on from one generation to the next by way of these genes. All information flows from the genotype to the phenotype, the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of the organism. Although the phenotype expressed by the gene may adapt to the environment of the organism, that information is not transferred back to the genes. Only through the process of evolution do genes change in response to the environment. ŌĆó Homeostasis. The physiological processes that allow an organism to maintain its internal environment notwithstanding its external environment. Levels of Biological Organization Subatomic Particle - Atom - Molecule - Organelle ŌĆō Cell (unit of life) - Tissue - Organ - Organ System - Organism - Population - Community - Ecosystem - Biosphere. Classification of Matter 1
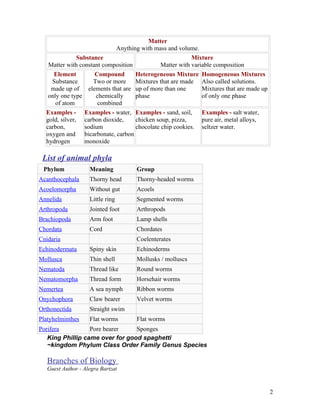
- 2. Matter Anything with mass and volume. Substance Mixture Matter with constant composition Matter with variable composition Element Compound Heterogeneous Mixture Homogeneous Mixtures Substance Two or more Mixtures that are made Also called solutions. made up of elements that are up of more than one Mixtures that are made up only one type chemically phase of only one phase of atom combined Examples - Examples - water, Examples - sand, soil, Examples - salt water, gold, silver, carbon dioxide, chicken soup, pizza, pure air, metal alloys, carbon, sodium chocolate chip cookies. seltzer water. oxygen and bicarbonate, carbon hydrogen monoxide List of animal phyla Phylum Meaning Group Acanthocephala Thorny head Thorny-headed worms Acoelomorpha Without gut Acoels Annelida Little ring Segmented worms Arthropoda Jointed foot Arthropods Brachiopoda Arm foot Lamp shells Chordata Cord Chordates Cnidaria Coelenterates Echinodermata Spiny skin Echinoderms Mollusca Thin shell Mollusks / molluscs Nematoda Thread like Round worms Nematomorpha Thread form Horsehair worms Nemertea A sea nymph Ribbon worms Onychophora Claw bearer Velvet worms Orthonectida Straight swim Platyhelminthes Flat worms Flat worms Porifera Pore bearer Sponges King Phillip came over for good spaghetti ~kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Branches of Biology Guest Author - Alegra Bartzat 2
- 3. Branches of Biology Agriculture - study of producing crops from the land, with an emphasis on practical applications Anatomy - the study of the animal form, with an emphasis on human bodies Biochemistry - the study of the chemical reactions required for life to exist and function, usually a focus on the cellular level Biotechnology - a new and sometimes controversial branch of biology that studies the manipulation of living matter, including genetic modification Botany - the study of plants Cell Biology - the study of the cell as a complete unit, and the molecular and chemical interactions that occur within a living cell. Ecology - the study of the ecosystem as a complete unit, with an emphasis on how species and groups of species interact with other living beings and non-living elements. Entomology - the study of insects Ethology - the study of animal behavior. Genetics - the study of genes and heredity. Herpetology - the study of reptiles Histology - The study of cells and tissue, a microscopic branch of anatomy. Ichthyology - the study of fish Mammology - the study of mammals Marine Biology - the study of ocean ecosystems, plants, animals, and other living beings. on alleviating or curing the body from states of disease Microbiology - the study of microscopic organisms (microorganisms) and their interactions with other living things Molecular Biology - the study of biology and biological functions at the molecular level, some cross over with biochemistry Mycology - the study of fungi Neurobiology - the study of the nervous system, including anatomy, physiology, even pathology Oceanography - the study of the ocean, including ocean life, environment, geography, weather, and other aspects influencing the ocean. See Marine Biology Ornithology - the study of birds Paleontology - the study of fossils and sometimes geographic evidence of prehistoric life 3
- 4. Pathobiology or pathology - the study of diseases, and the causes, processes, nature, and development of disease Parisitology - the study of parasites and parasitism Physiology - the study of the functioning of living organisms and the organs and parts of living organisms Virology - the study of viruses and some other virus-like agents, usually considered part of microbiology or pathology Zoology - the study of animals and animal life, including classification, physiology, development, and behavior (See also Entomology, Ethology, Herpetology, Ichthyology, Mammology, Ornithology 4
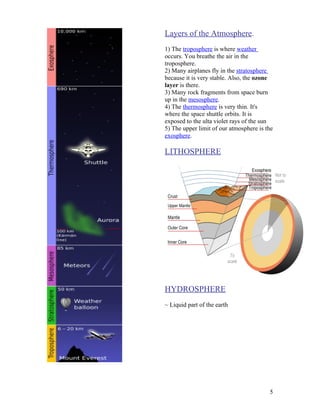
- 5. Layers of the Atmosphere. 1) The troposphere is where weather occurs. You breathe the air in the troposphere. 2) Many airplanes fly in the stratosphere because it is very stable. Also, the ozone layer is there. 3) Many rock fragments from space burn up in the mesosphere. 4) The thermosphere is very thin. It's where the space shuttle orbits. It is exposed to the ulta violet rays of the sun 5) The upper limit of our atmosphere is the exosphere. LITHOSPHERE HYDROSPHERE ~ Liquid part of the earth 5
- 6. UPCAT REVIEWER ~AJDRC (arrajeuneze@yahoo.com) : UPCAT Lecturer MATHEMATICS Polynomial Identities a 2 - b 2 = (a+b)(a-b) (Difference of squares) a 3 +b 3 = (a +b)(a 2- ab + b 2) (Sum and Difference of Cubes) a 3 -b 3 = (a -b)(a 2+ab + b 2) (Sum and Difference of Cubes) Complex numbers i 4k = 1; i (4k+1) = i; i (4k+2) = -1; i (4k+3) = -i (k = integer) Area Formulas Note: "ab" means "a" multiplied by "b". "a2" means "a squared", which is the same as "a" times "a". square = a 2 trapezoid = h/2 (b1 + b2) rectangle = ab circle = pi r 2 parallelogram = bh ellipse = pi r1 r2 one half times the base length times triangle = the height of the triangle equilateral triangle = regular polygon = (1/2) n sin(360┬░/n) S2 when n = # of sides and S = length from center to a corner 6
- 7. Volume Formulas cube = a 3 pyramid = (1/3) b h rectangular prism = a b c cone = (1/3) b h = 1/3 pi r 2 h irregular prism = b h sphere = (4/3) pi r 3 cylinder = b h = pi r 2 h Conversion of Decimal to fraction Note the following pattern for repeating decimals: 0.22222222... = 2/9 0.54545454... = 54/99 0.298298298... = 298/999 Division by 9's causes the repeating pattern. Note the pattern if zeros precede the repeating decimal: 0.022222222... = 2/90 0.00054545454... = 54/99000 0.00298298298... = 298/99900 Adding zero's to the denominator adds zero's before the repeating decimal. Polygon Formulas (N = # of sides and S = length from center to a corner) Area of a regular polygon = (1/2) N sin(360┬░/N) S2 Sum of the interior angles of a polygon = (N - 2) x 180┬░ The number of diagonals in a polygon = 1/2 N(N-3) The number of triangles (when you draw all the diagonals from one vertex) in a polygon = (N - 2) Information collected by Arra Corpuz. Home service Tutor 2008-present; UP Diliman BS Mathematics (1st year). 09175386393 7