Ureter
- 1. URETER The ureters are a pair of narrow,thick walled muscular tubes which convey urine from kidneys to the urinary bladder Lie deep to peritoneum,closely applied to the posterior abdominal wall in the upper part,and to the lateral pelvic part in the lower part DIMENSIONS Length-25 cm Diameter-3mm
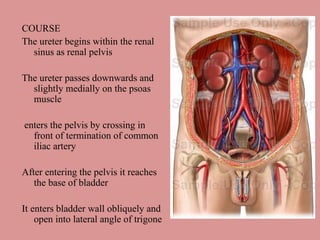
- 2. COURSE The ureter begins within the renal sinus as renal pelvis The ureter passes downwards and slightly medially on the psoas muscle enters the pelvis by crossing in front of termination of common iliac artery After entering the pelvis it reaches the base of bladder It enters bladder wall obliquely and open into lateral angle of trigone
- 3. 3 parts: PELVIS ABDOMINAL PELVIC
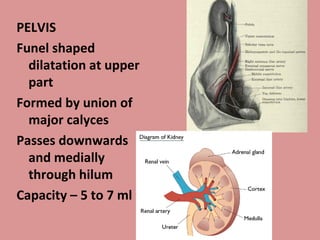
- 4. PELVIS Funel shaped dilatation at upper part Formed by union of major calyces Passes downwards and medially through hilum Capacity ŌĆō 5 to 7 ml
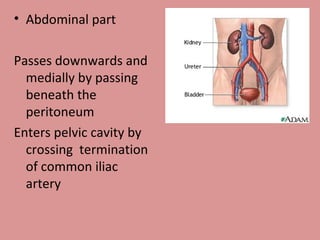
- 5. Abdominal part Passes downwards and medially by passing beneath the peritoneum Enters pelvic cavity by crossing termination of common iliac artery
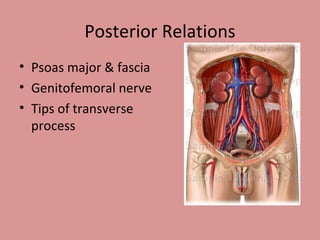
- 6. Posterior Relations Psoas major & fascia Genitofemoral nerve Tips of transverse process
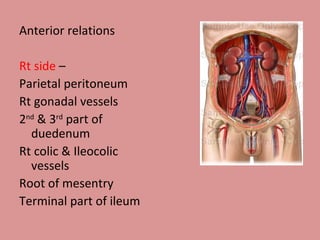
- 7. Anterior relations Rt side ŌĆō Parietal peritoneum Rt gonadal vessels 2 nd & 3 rd part of duedenum Rt colic & Ileocolic vessels Root of mesentry Terminal part of ileum
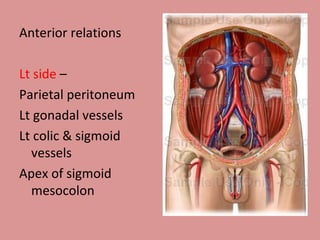
- 8. Anterior relations Lt side ŌĆō Parietal peritoneum Lt gonadal vessels Lt colic & sigmoid vessels Apex of sigmoid mesocolon
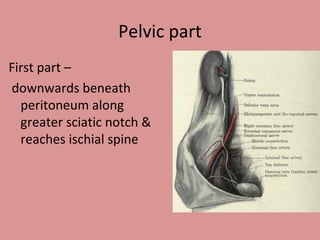
- 9. Pelvic part First part ŌĆō downwards beneath peritoneum along greater sciatic notch & reaches ischial spine
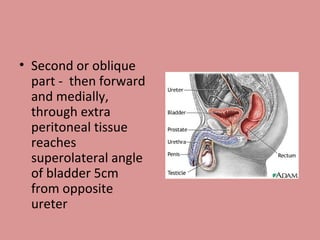
- 10. Second or oblique part - then forward and medially, through extra peritoneal tissue reaches superolateral angle of bladder 5cm from opposite ureter
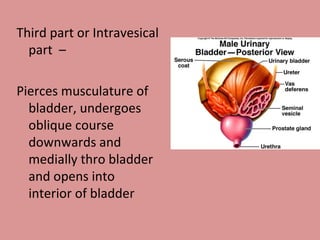
- 11. Third part or Intravesical part ŌĆō Pierces musculature of bladder, undergoes oblique course downwards and medially thro bladder and opens into interior of bladder
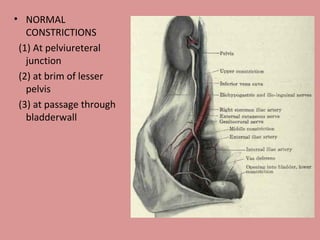
- 12. NORMAL CONSTRICTIONS (1) At pelviureteral junction (2) at brim of lesser pelvis (3) at passage through bladderwall
- 13. Factors preventing reflux of urine Oblique direction of intravesical part of ureter Trigonal muscle which by contraction maintains the obliquity of ureter Peristalsis of ureteral muscles at 2 to 5 times per minute. Urine is collected in bladder in jets, not continually
- 14. BLOOD SUPPLY Upper part ŌĆōrenal artery Middle part-aorta Pelvic part-vesical,middle rectal or uterine vessels NERVE SUPPLY Sympathetic- T10-L1 Parasympathetic- S2-S4