urinalisis.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes69 views
This document provides information about urinalysis tests. It discusses the types of urine samples that can be collected, including early morning, random, 24-hour, and midstream samples. The document describes microscopic and chemical examinations of urine, including normal and abnormal colors, volumes, and presence of crystals, casts, glucose, bilirubin, ketones, specific gravity, blood, pH, and protein. Abnormal results can indicate conditions such as urinary tract infections, diabetes, liver and kidney diseases.
1 of 24
Download to read offline





















Recommended
URINE Analysis with normal structure of nephron and physical examination and ...



URINE Analysis with normal structure of nephron and physical examination and ...DeepshikhaSinghmar
Ėý
Urine analysisUrine analysis



Urine analysisnizar baginda
Ėý
Urine analysis provides important information about kidney and overall health. A urine sample can be analyzed through macroscopic, chemical, and microscopic examination. The macroscopic exam evaluates attributes like color, clarity, and specific gravity. Chemical tests detect substances like proteins, glucose, ketones, and blood. Microscopic analysis identifies casts, crystals, epithelial cells, and other elements in urine sediment. Urine dipsticks provide a convenient, first-line screening for various analytes through color-changing indicators. Collectively, a urine analysis can detect disorders of the kidneys, urinary tract, and other body systems.urine analysis sem āēŽāģ āēāģāēĪāēŪāģ āēāēĻāģāēĻāēĄāēŋāē 



urine analysis sem āēŽāģ āēāģāēĪāēŪāģ āēāēĻāģāēĻāēĄāēŋāē āēŪāēŋāēĨāģāēĻāģ āēāģāēĄ , āēāēĻāģāēĻāēĄāēŋāē āēāģāēĪāēŪāģ āēāģāēĄ
Ėý
Urine analysis is performed to examine urine composition and detect abnormalities. A 24-hour urine sample allows quantitative analysis of proteins, metabolites, and microorganisms. Urine is examined macroscopically for volume, color, odor, pH, and specific gravity. Chemical examination detects proteins, sugars, ketones, bilirubin, urobilinogen, and blood. Microscopic examination identifies crystals, casts, epithelial cells, and red and white blood cells. Urine dipsticks provide a convenient, rapid, qualitative analysis of various urine components.Urinalysis.ppt



Urinalysis.pptOnamiEmmanuel
Ėý
Urinalysis provides important information about overall health and diseases affecting the kidneys, urinary tract, and other body systems. It can detect disorders like diabetes, kidney disease, urinary tract infections, and drug abuse. Abnormalities in urine color, odor, volume, pH, specific gravity, protein, glucose, bilirubin, blood, and casts can indicate various underlying health issues. A urinalysis is a generally safe and noninvasive test that provides clinicians with valuable clues for diagnosis, monitoring disease progression, and screening for certain conditions.Common presentation and investigation of Kidney diseases



Common presentation and investigation of Kidney diseasesEzmeer Emiral
Ėý
This document provides an overview of the common presentations, investigations, and features of major renal diseases. It discusses the normal functions of the kidney and outlines typical symptoms of renal disease like dysuria, polyuria, oliguria, and hematuria. Specific conditions covered include glomerulonephritis, urinary tract infections, renal failure, polycystic kidney disease, and urinary tract obstruction. Investigations involve urine analysis, blood tests, imaging, and renal biopsy. Features, causes, and clinical presentations of various renal conditions are described in detail.glomerulonephritis.pdf



glomerulonephritis.pdfAnushriSrivastav
Ėý
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the glomeruli, the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste from the blood. There are two main types - acute glomerulonephritis, which has a sudden onset typically in children following a streptococcal infection, and chronic glomerulonephritis, which develops over time and can lead to long-term kidney damage. Acute glomerulonephritis causes kidney dysfunction seen as edema, high blood pressure, reduced urine output, and blood in the urine. Treatment focuses on rest, fluid management, antibiotics, and controlling blood pressure. Chronic glomerulonephritis can develop from acute or other causes and may cause few symptoms initiallyUrinSyndr_Lect#1_zoom+.pdfof urinary tract



UrinSyndr_Lect#1_zoom+.pdfof urinary tractrathoregavish80
Ėý
The document provides an overview of urinary system semiotics and urine syndrome. It discusses the main symptoms of kidney and urinary tract diseases, which include pain, edema, dysuria, arterial hypertension, and renal failure. It then examines each of these symptoms in more detail. For example, it describes the different types of pain seen in diseases like nephrolithiasis and pyelonephritis. It also outlines disorders of urination like polyuria, oliguria, and dysuria. The document concludes by presenting the case of a 52-year-old male patient complaining of fever, back pain, delayed urination, and morning edema, who has a medical history of similar symptoms for several years.1674029933129437.pptx



1674029933129437.pptxAdwaitPaithankar1
Ėý
This document discusses the management of patients with urinary syndrome. Urinary syndrome includes proteinuria, abnormal urinary sediment, hematuria, leukocyturia, and abnormal urinary casts. Proteinuria can be transient, microalbuminuria, or organic. Organic proteinuria is classified as pre-renal, renal, or post-renal. Hematuria is normal up to a certain level but indicates issues at higher levels. Leukocyturia indicates a urinary tract infection which can be sterile or non-sterile such as pyelonephritis. Tubulointerstitial nephritis is an immune-mediated kidney condition most often caused by medications and characterized by sterile pyuria, proteinuria,Urine detail examination



Urine detail examinationBahria University Medical & Dental College, Karachi, Pakistan
Ėý
This document summarizes the key components of a urine physical examination, including urine volume, color, appearance, specific gravity, osmolality, pH, and microscopic examination. Normal ranges are provided for each component, along with potential causes of abnormalities. The microscopic examination may reveal elements like white blood cells, red blood cells, epithelial cells, crystals, casts, bacteria, yeast, and other non-bacterial organisms that can indicate underlying renal, genitourinary, or systemic health issues. A urine physical examination provides important physical and microscopic findings to evaluate fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance and detect various diseases and disorders.Urine Analysis and Urine Culture.pptx



Urine Analysis and Urine Culture.pptxKnowledgeDove
Ėý
WHAT IS URINEĖýANALYSIS?
Urine analysis, also called Urinalysis â one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine.
Also knows as Urine- R&M (routine & microscopy)
Is an array of tests performed on urine
WHY URINALYSIS?
GeneralĖýevaluation of health
Diagnosis of disease or disorders of the kidneys or urinary tract
Diagnosis of other systemic disease that affect kidney function
Monitoring of patients with diabetes
Screening for drug abuse (eg. Sulfonamide or aminoglycosides)
COLLECTION OF URINEĖýSPECIMENS
Improper collection---- may invalidate the results
Containers for collection of urine should be wide mouthed, clean and dry.
Analyzed within 2 hours of collection else requires refrigeration.
URINE CULTURE
Culture within 1 hour after collection or stored in a refrigerator at 4oC for no more than 18 hours.
Culture is performed when Polynephritis or Cystitis is suspected.
UTI is most frequent caused by E.Coli.
Other common agents are Enterobacter, Proteus, and Enterococcus faecalis.
URINALYSIS; WHAT TOĖýLOOK FOR?
âĒ Urinalysis consists of the following measurements:
Macroscopic or physical examination
Chemical examination
Microscopic examination of the sediment
Urine culture
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OFĖýURINE
Examination of physical characteristics:
Volume
Color
Odor
pH
Specific gravity
The refractometer or a reagent strip is used to measure specific gravity
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Normal- 1-2.5 L/day
Oliguria- Urine Output < 400ml/day
Dehydration
Shock
Acute glomerulonephritis
Renal Failure
Polyuria- Urine Output > 2.5 L/day
Increased water ingestion
Diabetes mellitus and insipidus.
Anuria- Urine output < 100ml/day
Seen in renal shut down Volume
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Normal
pale yellow in color due to pigments urochrome (different colour pigments in urine), urobilin (When urobilinogen- degraded product of bilirubin, is exposed to air, it is oxidized to urobilin, giving urine its yellow color) and uroerythrin (red pigment in urine).
Cloudiness
may be caused by excessive cellular material or protein, crystallization or precipitation of non pathological salts upon standing at room temperature or in the refrigerator.
Color
Colour of urine depending upon itâs constituents.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Abnormal Colors:
Colorless â diabetes, diuretics.
Deep Yellow â concentrated urine, excess bile pigments, jaundice Color
Blue-Green â Methylene Blue, Pseudomonas (Bactrium), Riboflavin (Vitamin B2, in FAD give Yellow Orange Color)
Pink-Orange-Red â Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Phenolphthalein, Porphyrins, Rifampicin (antibiotic against TB give orange color to urine)
Red-Brown-Black - Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Red Blood Cells, Homogentisic acid (Homogentisic acid present in Blood and its oxidized form alkapton are excreted in the urine, giving it an unusually dark color), L-DOPA (Levodopa, is the most effective drug for Parkinsonâs disease), Melanin (brown Pigment)
Urine analysis.ppt 



Urine analysis.ppt Nam Ly
Ėý
Urine analysis is a common medical diagnostic tool that can evaluate general health, diagnose diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, and monitor conditions like diabetes. A urine analysis involves macroscopic examination of properties like volume, color, odor, pH and specific gravity. Microscopic examination analyzes cellular elements and crystals in sediment. Chemical analysis tests for proteins, glucose, ketones, blood, and other substances. Abnormal results can indicate issues with the kidneys, urinary tract, liver or other organs. Precise diagnosis requires correlating clinical history with comprehensive urine analysis findings.Oliguria and anuria



Oliguria and anuriaAli Faris
Ėý
Oliguria is a low urine output defined as less than 1 mL/kg/hr in infants, less than 0.5 mL/kg/hr in children, and less than 300 mL daily in adults. It indicates an underlying disorder and can lead to acute renal failure if left untreated. Anuria is even less urine output at less than 50 mL/day. Causes of oliguria and anuria include pre-renal (low blood volume), renal (kidney damage), and post-renal (urinary tract obstruction). Evaluation and management depends on determining the cause through history, physical exam, urinalysis, and blood tests to guide volume replacement or other interventions to prevent further kidney injury.Urine analysis 



Urine analysis DarshanGandhi36
Ėý
1. Urinalysis provides important information for diagnosing and managing various renal and metabolic conditions. It involves examining the physical and chemical properties of a urine sample, as well as inspecting it microscopically.
2. The timing and method of urine collection depends on the tests being performed. A first morning midstream sample is preferred for routine analysis but random or postprandial samples are also used.
3. Normal urine has characteristics such as a yellow color, slight acidity, and absence of protein, glucose, and ketones. Abnormal findings provide clues to diseases like urinary tract infections or kidney disorders.Common urinary symptom



Common urinary symptomIPMS- KMU KPK PAKISTAN
Ėý
This document discusses polyuria, which is excessive urine output of greater than 3 liters per day in adults. Polyuria can be caused by physiological factors like excessive fluid intake or anxiety, or pathological factors like endocrine, renal, or psychiatric conditions. It may occur due to increased solute excretion (solute diuresis) or increased water excretion due to a defect in ADH production or renal responsiveness (water diuresis). Other conditions discussed include proteinuria, hematuria, and urinary retention. Causes, diagnostic testing, and treatment approaches are provided for each condition.Hematuria



Hematuriaabdur razzak
Ėý
Hematuria can be caused by various upper and lower urinary tract diseases. Common causes of glomerular hematuria include IgA nephropathy, Alport syndrome, and thin basement membrane disease. Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is associated with a preceding streptococcal infection. Membranous nephropathy presents with nephrotic syndrome. Goodpasture disease involves anti-GBM antibodies attacking the lungs and kidneys. Diagnosis involves urinalysis, renal biopsy, and identifying underlying causes or associations. Treatment depends on the specific condition but may include antibiotics, steroids, immunosuppressants, blood pressure control, and addressing complications.šÝšÝßĢ on Urine analysis and urine microscopy



šÝšÝßĢ on Urine analysis and urine microscopyAdaobiOkubike1
Ėý
šÝšÝßĢ on urine analysis including microscopy and urinalysisrenal diseases



renal diseasesEric General
Ėý
This document discusses clinical manifestations and evaluation of renal disease in children. Common signs of renal disorders include edema, hematuria, abnormalities in urination, and flank or abdominal pain. Evaluation of renal disease involves examination of urine for red blood cells, proteins, and casts. Imaging tests like ultrasound and IVU can identify structural abnormalities. Glomerular diseases commonly cause hematuria while tubular disorders present with electrolyte abnormalities. Renal biopsy may be needed to diagnose conditions like Alport syndrome.Chapter 11 presentation



Chapter 11 presentationLaura Garcia
Ėý
Glycosuria, polyuria, and polydipsia are related conditions involving sugar in the urine, excessive urine production, and excessive thirst, respectively. Glycosuria is typically caused by diabetes but can also occur during pregnancy or with certain diseases. Polyuria is usually due to diabetes, kidney problems, medications, or excessive fluid intake. Polydipsia is often a symptom of diabetes or conditions causing fluid loss that triggers thirst. Testing of urine and blood can help identify underlying causes like diabetes, infections, or renal issues. Treatment focuses on managing the cause when possible.Kamal



KamalFarragBahbah
Ėý
This document provides information on urine analysis and examination. It discusses the importance of analyzing urine promptly after collection and outlines appropriate collection, storage, and examination methods. Physical, biochemical, and microscopic tests are described in detail. Key findings are interpreted, such as the clinical significance of various cells, casts, crystals, and substances that may be present in urine. Proper collection and handling of urine specimens is also reviewed. The document aims to serve as a guide for physicians on evaluating urine as an important diagnostic tool.03251163_jaundice_asc_port_hypertension.pptx



03251163_jaundice_asc_port_hypertension.pptxReshmaShajiPns1
Ėý
Jaundice is caused by high bilirubin levels in the blood and results in a yellowing of the skin and eyes. It can be classified as pre-hepatic, hepatic, or post-hepatic depending on whether the cause is upstream, within, or downstream of the liver. A bilirubin level over 35 Ξmol/L is needed for clinical jaundice. Causes include excessive bilirubin production from hemolysis, impaired liver function from infections, drugs or autoimmune diseases, or obstruction of bile flow from gallstones or tumors. A physical exam and lab tests are used to diagnose the type and cause of jaundice.Renal disease tutorial 



Renal disease tutorial drpallavip
Ėý
This document outlines an approach to renal diseases. It begins by listing common renal syndromes such as hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, nephritic syndrome, and acute/chronic renal failure. It then provides details on evaluating and differentiating each syndrome, including causes, diagnostic criteria, and key laboratory findings. Kidney biopsy indications are also outlined. The document aims to guide practitioners in diagnosing and classifying renal conditions based on presenting signs, symptoms and test results.CME On UGIB and Management of Decompensated Liver.pptx



CME On UGIB and Management of Decompensated Liver.pptxruthmalani
Ėý
UGIB management and decompensated liver failurejaundice 



jaundice Manisha Raika
Ėý
Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes, is caused by excessive levels of bilirubin in the blood. It can be a sign of liver or bile duct problems. The document discusses the differential diagnosis of jaundice by examining causes related to increased bilirubin production, impaired transport, or decreased excretion. A thorough physical exam and lab work are needed to determine the underlying etiology, such as viral hepatitis, gallstones, drugs, heart failure, or hepatic abscesses. Treatment involves addressing the specific cause and managing symptoms like pruritus.Child with jaundice 



Child with jaundice ROSHAN SHAH
Ėý
This document provides information about jaundice in children. It begins with learning objectives and definitions of jaundice and bilirubin metabolism. It then discusses the different types of jaundice including prehepatic, hepatic, and posthepatic. Physiological and pathological neonatal jaundice are described. Causes, clinical features, investigations, management approaches, and surgical treatment options for jaundice in children are summarized.CMHS DEPTOF NURSING SEMARA UNIVERSITY 2023



CMHS DEPTOF NURSING SEMARA UNIVERSITY 2023Obsa2
Ėý
This document provides an outline and lecture content on the management of patients with cardiovascular disorders. It covers topics such as coronary vascular diseases including atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, and myocardial infarction. For each topic, it discusses pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic testing, medical management, and nursing interventions. It aims to educate nursing students on caring for patients experiencing these common cardiovascular conditions.5. Health Planning.pptx



5. Health Planning.pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document discusses health sector planning. It defines health planning as the process of defining community health problems, identifying needs and resources, establishing priority goals, and setting out actions to reach those goals. The document outlines the planning process, which includes situation analysis, priority setting, option appraisal, identifying obstacles, designing strategies, and developing a plan of action. It also discusses planning tools like SWOT analysis and the roles of various stakeholders in the planning process.More Related Content
Similar to urinalisis.pptx (20)
1674029933129437.pptx



1674029933129437.pptxAdwaitPaithankar1
Ėý
This document discusses the management of patients with urinary syndrome. Urinary syndrome includes proteinuria, abnormal urinary sediment, hematuria, leukocyturia, and abnormal urinary casts. Proteinuria can be transient, microalbuminuria, or organic. Organic proteinuria is classified as pre-renal, renal, or post-renal. Hematuria is normal up to a certain level but indicates issues at higher levels. Leukocyturia indicates a urinary tract infection which can be sterile or non-sterile such as pyelonephritis. Tubulointerstitial nephritis is an immune-mediated kidney condition most often caused by medications and characterized by sterile pyuria, proteinuria,Urine detail examination



Urine detail examinationBahria University Medical & Dental College, Karachi, Pakistan
Ėý
This document summarizes the key components of a urine physical examination, including urine volume, color, appearance, specific gravity, osmolality, pH, and microscopic examination. Normal ranges are provided for each component, along with potential causes of abnormalities. The microscopic examination may reveal elements like white blood cells, red blood cells, epithelial cells, crystals, casts, bacteria, yeast, and other non-bacterial organisms that can indicate underlying renal, genitourinary, or systemic health issues. A urine physical examination provides important physical and microscopic findings to evaluate fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance and detect various diseases and disorders.Urine Analysis and Urine Culture.pptx



Urine Analysis and Urine Culture.pptxKnowledgeDove
Ėý
WHAT IS URINEĖýANALYSIS?
Urine analysis, also called Urinalysis â one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine.
Also knows as Urine- R&M (routine & microscopy)
Is an array of tests performed on urine
WHY URINALYSIS?
GeneralĖýevaluation of health
Diagnosis of disease or disorders of the kidneys or urinary tract
Diagnosis of other systemic disease that affect kidney function
Monitoring of patients with diabetes
Screening for drug abuse (eg. Sulfonamide or aminoglycosides)
COLLECTION OF URINEĖýSPECIMENS
Improper collection---- may invalidate the results
Containers for collection of urine should be wide mouthed, clean and dry.
Analyzed within 2 hours of collection else requires refrigeration.
URINE CULTURE
Culture within 1 hour after collection or stored in a refrigerator at 4oC for no more than 18 hours.
Culture is performed when Polynephritis or Cystitis is suspected.
UTI is most frequent caused by E.Coli.
Other common agents are Enterobacter, Proteus, and Enterococcus faecalis.
URINALYSIS; WHAT TOĖýLOOK FOR?
âĒ Urinalysis consists of the following measurements:
Macroscopic or physical examination
Chemical examination
Microscopic examination of the sediment
Urine culture
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OFĖýURINE
Examination of physical characteristics:
Volume
Color
Odor
pH
Specific gravity
The refractometer or a reagent strip is used to measure specific gravity
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Normal- 1-2.5 L/day
Oliguria- Urine Output < 400ml/day
Dehydration
Shock
Acute glomerulonephritis
Renal Failure
Polyuria- Urine Output > 2.5 L/day
Increased water ingestion
Diabetes mellitus and insipidus.
Anuria- Urine output < 100ml/day
Seen in renal shut down Volume
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Normal
pale yellow in color due to pigments urochrome (different colour pigments in urine), urobilin (When urobilinogen- degraded product of bilirubin, is exposed to air, it is oxidized to urobilin, giving urine its yellow color) and uroerythrin (red pigment in urine).
Cloudiness
may be caused by excessive cellular material or protein, crystallization or precipitation of non pathological salts upon standing at room temperature or in the refrigerator.
Color
Colour of urine depending upon itâs constituents.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Abnormal Colors:
Colorless â diabetes, diuretics.
Deep Yellow â concentrated urine, excess bile pigments, jaundice Color
Blue-Green â Methylene Blue, Pseudomonas (Bactrium), Riboflavin (Vitamin B2, in FAD give Yellow Orange Color)
Pink-Orange-Red â Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Phenolphthalein, Porphyrins, Rifampicin (antibiotic against TB give orange color to urine)
Red-Brown-Black - Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Red Blood Cells, Homogentisic acid (Homogentisic acid present in Blood and its oxidized form alkapton are excreted in the urine, giving it an unusually dark color), L-DOPA (Levodopa, is the most effective drug for Parkinsonâs disease), Melanin (brown Pigment)
Urine analysis.ppt 



Urine analysis.ppt Nam Ly
Ėý
Urine analysis is a common medical diagnostic tool that can evaluate general health, diagnose diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, and monitor conditions like diabetes. A urine analysis involves macroscopic examination of properties like volume, color, odor, pH and specific gravity. Microscopic examination analyzes cellular elements and crystals in sediment. Chemical analysis tests for proteins, glucose, ketones, blood, and other substances. Abnormal results can indicate issues with the kidneys, urinary tract, liver or other organs. Precise diagnosis requires correlating clinical history with comprehensive urine analysis findings.Oliguria and anuria



Oliguria and anuriaAli Faris
Ėý
Oliguria is a low urine output defined as less than 1 mL/kg/hr in infants, less than 0.5 mL/kg/hr in children, and less than 300 mL daily in adults. It indicates an underlying disorder and can lead to acute renal failure if left untreated. Anuria is even less urine output at less than 50 mL/day. Causes of oliguria and anuria include pre-renal (low blood volume), renal (kidney damage), and post-renal (urinary tract obstruction). Evaluation and management depends on determining the cause through history, physical exam, urinalysis, and blood tests to guide volume replacement or other interventions to prevent further kidney injury.Urine analysis 



Urine analysis DarshanGandhi36
Ėý
1. Urinalysis provides important information for diagnosing and managing various renal and metabolic conditions. It involves examining the physical and chemical properties of a urine sample, as well as inspecting it microscopically.
2. The timing and method of urine collection depends on the tests being performed. A first morning midstream sample is preferred for routine analysis but random or postprandial samples are also used.
3. Normal urine has characteristics such as a yellow color, slight acidity, and absence of protein, glucose, and ketones. Abnormal findings provide clues to diseases like urinary tract infections or kidney disorders.Common urinary symptom



Common urinary symptomIPMS- KMU KPK PAKISTAN
Ėý
This document discusses polyuria, which is excessive urine output of greater than 3 liters per day in adults. Polyuria can be caused by physiological factors like excessive fluid intake or anxiety, or pathological factors like endocrine, renal, or psychiatric conditions. It may occur due to increased solute excretion (solute diuresis) or increased water excretion due to a defect in ADH production or renal responsiveness (water diuresis). Other conditions discussed include proteinuria, hematuria, and urinary retention. Causes, diagnostic testing, and treatment approaches are provided for each condition.Hematuria



Hematuriaabdur razzak
Ėý
Hematuria can be caused by various upper and lower urinary tract diseases. Common causes of glomerular hematuria include IgA nephropathy, Alport syndrome, and thin basement membrane disease. Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is associated with a preceding streptococcal infection. Membranous nephropathy presents with nephrotic syndrome. Goodpasture disease involves anti-GBM antibodies attacking the lungs and kidneys. Diagnosis involves urinalysis, renal biopsy, and identifying underlying causes or associations. Treatment depends on the specific condition but may include antibiotics, steroids, immunosuppressants, blood pressure control, and addressing complications.šÝšÝßĢ on Urine analysis and urine microscopy



šÝšÝßĢ on Urine analysis and urine microscopyAdaobiOkubike1
Ėý
šÝšÝßĢ on urine analysis including microscopy and urinalysisrenal diseases



renal diseasesEric General
Ėý
This document discusses clinical manifestations and evaluation of renal disease in children. Common signs of renal disorders include edema, hematuria, abnormalities in urination, and flank or abdominal pain. Evaluation of renal disease involves examination of urine for red blood cells, proteins, and casts. Imaging tests like ultrasound and IVU can identify structural abnormalities. Glomerular diseases commonly cause hematuria while tubular disorders present with electrolyte abnormalities. Renal biopsy may be needed to diagnose conditions like Alport syndrome.Chapter 11 presentation



Chapter 11 presentationLaura Garcia
Ėý
Glycosuria, polyuria, and polydipsia are related conditions involving sugar in the urine, excessive urine production, and excessive thirst, respectively. Glycosuria is typically caused by diabetes but can also occur during pregnancy or with certain diseases. Polyuria is usually due to diabetes, kidney problems, medications, or excessive fluid intake. Polydipsia is often a symptom of diabetes or conditions causing fluid loss that triggers thirst. Testing of urine and blood can help identify underlying causes like diabetes, infections, or renal issues. Treatment focuses on managing the cause when possible.Kamal



KamalFarragBahbah
Ėý
This document provides information on urine analysis and examination. It discusses the importance of analyzing urine promptly after collection and outlines appropriate collection, storage, and examination methods. Physical, biochemical, and microscopic tests are described in detail. Key findings are interpreted, such as the clinical significance of various cells, casts, crystals, and substances that may be present in urine. Proper collection and handling of urine specimens is also reviewed. The document aims to serve as a guide for physicians on evaluating urine as an important diagnostic tool.03251163_jaundice_asc_port_hypertension.pptx



03251163_jaundice_asc_port_hypertension.pptxReshmaShajiPns1
Ėý
Jaundice is caused by high bilirubin levels in the blood and results in a yellowing of the skin and eyes. It can be classified as pre-hepatic, hepatic, or post-hepatic depending on whether the cause is upstream, within, or downstream of the liver. A bilirubin level over 35 Ξmol/L is needed for clinical jaundice. Causes include excessive bilirubin production from hemolysis, impaired liver function from infections, drugs or autoimmune diseases, or obstruction of bile flow from gallstones or tumors. A physical exam and lab tests are used to diagnose the type and cause of jaundice.Renal disease tutorial 



Renal disease tutorial drpallavip
Ėý
This document outlines an approach to renal diseases. It begins by listing common renal syndromes such as hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, nephritic syndrome, and acute/chronic renal failure. It then provides details on evaluating and differentiating each syndrome, including causes, diagnostic criteria, and key laboratory findings. Kidney biopsy indications are also outlined. The document aims to guide practitioners in diagnosing and classifying renal conditions based on presenting signs, symptoms and test results.CME On UGIB and Management of Decompensated Liver.pptx



CME On UGIB and Management of Decompensated Liver.pptxruthmalani
Ėý
UGIB management and decompensated liver failurejaundice 



jaundice Manisha Raika
Ėý
Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes, is caused by excessive levels of bilirubin in the blood. It can be a sign of liver or bile duct problems. The document discusses the differential diagnosis of jaundice by examining causes related to increased bilirubin production, impaired transport, or decreased excretion. A thorough physical exam and lab work are needed to determine the underlying etiology, such as viral hepatitis, gallstones, drugs, heart failure, or hepatic abscesses. Treatment involves addressing the specific cause and managing symptoms like pruritus.Child with jaundice 



Child with jaundice ROSHAN SHAH
Ėý
This document provides information about jaundice in children. It begins with learning objectives and definitions of jaundice and bilirubin metabolism. It then discusses the different types of jaundice including prehepatic, hepatic, and posthepatic. Physiological and pathological neonatal jaundice are described. Causes, clinical features, investigations, management approaches, and surgical treatment options for jaundice in children are summarized.More from Obsa2 (20)
CMHS DEPTOF NURSING SEMARA UNIVERSITY 2023



CMHS DEPTOF NURSING SEMARA UNIVERSITY 2023Obsa2
Ėý
This document provides an outline and lecture content on the management of patients with cardiovascular disorders. It covers topics such as coronary vascular diseases including atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, and myocardial infarction. For each topic, it discusses pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic testing, medical management, and nursing interventions. It aims to educate nursing students on caring for patients experiencing these common cardiovascular conditions.5. Health Planning.pptx



5. Health Planning.pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document discusses health sector planning. It defines health planning as the process of defining community health problems, identifying needs and resources, establishing priority goals, and setting out actions to reach those goals. The document outlines the planning process, which includes situation analysis, priority setting, option appraisal, identifying obstacles, designing strategies, and developing a plan of action. It also discusses planning tools like SWOT analysis and the roles of various stakeholders in the planning process.entrepreneurship



entrepreneurshipObsa2
Ėý
This document outlines the contents of an entrepreneurship course, including 7 chapters on topics such as the nature of entrepreneurship, business planning, business formation, product development, marketing, financing, and managing growth. It then provides details on Chapter 1 which defines key terms like entrepreneurship and entrepreneur. It describes the characteristics and qualities of successful entrepreneurs, and their role in economic development. The chapter also covers creativity, innovation, and identifying business opportunities.Chapter five Aminots.ppt



Chapter five Aminots.pptObsa2
Ėý
The document summarizes amniotes and their evolution. It discusses:
1) Amniotes are tetrapods with an amniotic egg, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. The amniotic egg allowed reproduction on land.
2) Modern amniotes are classified as synapsids (mammals), anapsids (turtles), or diapsids (reptiles and birds). Diapsids split into lepidosaurs and archosaurs.
3) Reptiles evolved from amphibians and gained adaptations like scaly skin, internal fertilization, and efficient lungs and kidneys for land survival.CH 4.pptx



CH 4.pptxObsa2
Ėý
The document discusses employee recruitment, selection, and orientation processes. It defines recruitment as finding and attracting job applicants, and selection as choosing candidates that best fit open positions. Recruitment sources can be internal, like promotions, or external through advertising. The selection process involves screening applications, testing candidates, interviewing, reference and background checks, medical exams, and final approval. Orientation socializes new hires by familiarizing them with company policies, culture, jobs, and expectations. The goal is to quickly integrate new employees and increase productivity.OR-Chapter One (1).pdf



OR-Chapter One (1).pdfObsa2
Ėý
This chapter introduces operations research as a quantitative approach to decision making. It discusses the history of operations research emerging during World War II to help manage scarce resources. Operations research is defined as applying scientific methods to complex problems involving systems of people, machines, materials and money. The chapter outlines the nature, features, and significance of operations research in decision making. It also introduces modeling as used in operations research to analyze systems through representations that maintain essential elements.3. Unit-Three.ppt



3. Unit-Three.pptObsa2
Ėý
This document provides an overview of health care production and markets. It begins by outlining the key concepts to be covered, including demand and supply, elasticity, equilibrium, and market failure. It then defines some important economic terms like ceteris paribus. The document goes on to explain demand, including the law of demand and determinants of demand. It also covers supply, the law of supply, and factors that can shift the supply curve. Finally, it discusses market equilibrium and sources of market failure in health care markets.4. Unit- Four.pptx



4. Unit- Four.pptxObsa2
Ėý
The document discusses health care financing. It begins by outlining the objectives of describing national health accounts, the three functions of health care financing, and sources of financing. It then explains national health accounts and their use in tracking health expenditure trends. The three main functions of health care financing are described as resource mobilization, risk pooling, and resource allocation. Various sources of resource mobilization are outlined like general tax revenue, insurance schemes, and out-of-pocket payments. Criteria for assessing financial mechanisms and strategies for health sector reform like user fee systems and improving resource allocation are also summarized.6. Met of CHO.pptx



6. Met of CHO.pptxObsa2
Ėý
metabolism of carbohydrate presentation from samara university
college of medicine and health scienceCHAPTER âTHREE.pptx



CHAPTER âTHREE.pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document discusses various natural and man-made disasters including their definitions, causes, health impacts, and public health interventions. It covers deforestation, drought, epidemics, pest infestations, floods, earthquakes, different types of pollution, fires, and explosions. For each disaster, it provides details on magnitude, impacts such as deaths, injuries, and diseases, and recommendations for management and protective measures before, during, and after the event. The public health interventions focus on surveillance, health education, ensuring safe water and sanitation, and continuity of medical care.Animal Feed and Nutrition (Ch3).pptx



Animal Feed and Nutrition (Ch3).pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document discusses feedstuff classification and anti-nutritional factors. It classifies feeds as roughages or concentrates based on fiber and nutrient content. Roughages like pastures and crop residues are low in nutrients. Concentrates include energy sources like grains and protein sources like oilseed meals. Many protein concentrates contain anti-nutritional factors that can reduce nutrient availability if not properly heat treated. The document provides detailed examples and characteristics of various roughages and concentrates as well as classes of feed additives.Ecology_Chapt_4[1].pptx![Ecology_Chapt_4[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt41-220827095144-8fd17933-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Ecology_Chapt_4[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt41-220827095144-8fd17933-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Ecology_Chapt_4[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt41-220827095144-8fd17933-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Ecology_Chapt_4[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt41-220827095144-8fd17933-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Ecology_Chapt_4[1].pptxObsa2
Ėý
Plant communities are groups of interacting plant populations that occupy a common habitat. They can be characterized by their physiognomy, species richness, and other attributes. Historically, there have been three paradigms for understanding plant communities: Clements' view of communities as stable, climax superorganisms; Gleason's individualistic view of communities as arbitrary sections along environmental gradients; and the modern synthesis that communities are dynamic and influenced by both environmental factors and historical processes. Plant species distributions are constrained by abiotic factors like climate and soils as well as biotic interactions like mutualism and competition, causing non-random assemblages along environmental gradients. Habitats provide the biotic and abiotic context for plant niches within communitiesEcology_Chapt_5[1].pptx![Ecology_Chapt_5[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt51-220827093138-ae3aa5ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Ecology_Chapt_5[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt51-220827093138-ae3aa5ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Ecology_Chapt_5[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt51-220827093138-ae3aa5ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Ecology_Chapt_5[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ecologychapt51-220827093138-ae3aa5ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Ecology_Chapt_5[1].pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document discusses ecosystem classification and structure. It defines ecosystems as consisting of biotic and abiotic components that interact. Ecosystems are classified into terrestrial and aquatic types. Terrestrial ecosystems include forests, grasslands, tundras and deserts, while aquatic ecosystems include freshwater and marine. The structure of ecosystems includes producers, consumers and decomposers. Energy enters ecosystems through photosynthesis and flows through trophic levels as organisms consume each other.2.Chapter Two.pptx



2.Chapter Two.pptxObsa2
Ėý
Natural and human-caused disasters can have widespread social and public health consequences. Natural disasters are caused by forces of climate and geology and include events like earthquakes, floods, fires, and storms. Human-caused disasters result from activities such as explosions, fires, and technological accidents. The consequences of disasters include widespread human and economic losses, population displacement, increased risk of communicable diseases due to issues like lack of sanitation and overcrowding, food shortages and malnutrition, and long-term mental health impacts for survivors.1.Chapter one .pptx



1.Chapter one .pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document provides an overview of disaster prevention and preparedness for public health students. It defines key terms like disaster, hazard, vulnerability, risk assessment, mitigation, prevention, preparedness, warning, response, reconstruction and rehabilitation. The learning objectives are to understand disasters and their causes, impacts on health, and appropriate preventive and control measures. Common disaster types in Ethiopia and how disasters disproportionately affect marginalized groups are also discussed.SENSE_ORGANS_physiology[1].pptx![SENSE_ORGANS_physiology[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/senseorgansphysiology1-220821145046-6193b3ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![SENSE_ORGANS_physiology[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/senseorgansphysiology1-220821145046-6193b3ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![SENSE_ORGANS_physiology[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/senseorgansphysiology1-220821145046-6193b3ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![SENSE_ORGANS_physiology[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/senseorgansphysiology1-220821145046-6193b3ac-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
SENSE_ORGANS_physiology[1].pptxObsa2
Ėý
Sense organs allow animals to monitor their internal and external environments by detecting stimuli via specialized receptor cells. There are five main types of receptors that respond to mechanical, thermal, light, chemical, and painful stimuli. Receptors are classified as extroceptors on the surface, visceroceptors for internal organs, or proprioceptors for body position. Special sense organs like the eye, ear, nose and tongue contain concentrated sensory cells and detect vision, sound, smell and taste respectively. The eye contains three tunics - fibrous, vascular and nervous - that house light-sensitive retinal cells. Accessory structures like the eyelids and muscles help move and protect the eyeball.biochemist 5.pptx



biochemist 5.pptxObsa2
Ėý
Cellular metabolism involves enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions that break down nutrients to acquire energy for cellular functions. It consists of catabolic pathways that break down molecules and release energy (catabolism), and anabolic pathways that use energy to synthesize complex molecules (anabolism). The main catabolic pathway is cellular respiration, which includes glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and partially breaks down glucose, producing ATP. The Krebs cycle and electron transport chain occur in the mitochondria and completely oxidize pyruvate and other fuel molecules, generating much more ATP through oxidative phosphorylation as electrons are transferred to oxygen.bioch 4.pptx



bioch 4.pptxObsa2
Ėý
The Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a key metabolic pathway that oxidizes acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, producing carbon dioxide and high-energy electron carriers NADH and FADH2. The cycle consists of 8 steps that occur in the mitochondrial matrix and produces ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Regulation of the cycle occurs through three irreversible steps that are controlled by allosteric enzymes responding to energy levels in the cell.Introduction to ECOLOGY.ppt



Introduction to ECOLOGY.pptObsa2
Ėý
Here are the key differences between scramble and contest competition within a population:
- Scramble competition: All individuals within a population compete equally for limited resources. There is no aggressive interaction between individuals over resources.
- Contest competition: Certain dominant individuals within a population are able to monopolize access to resources through aggressive interactions like fighting. Subordinate individuals have reduced access to resources.
So in summary, scramble competition is non-aggressive and equal, while contest competition involves aggression and dominance hierarchies that give some individuals preferential access to resources over others. These differences in the mechanisms of intra-specific competition can influence population dynamics and traits under natural selection.RNA_VIRUSES_(1)(1)[1].pptx![RNA_VIRUSES_(1)(1)[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rnaviruses111-220820222315-dc52963b-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![RNA_VIRUSES_(1)(1)[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rnaviruses111-220820222315-dc52963b-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![RNA_VIRUSES_(1)(1)[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rnaviruses111-220820222315-dc52963b-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![RNA_VIRUSES_(1)(1)[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rnaviruses111-220820222315-dc52963b-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
RNA_VIRUSES_(1)(1)[1].pptxObsa2
Ėý
This document provides information on various RNA viruses. It discusses positive strand RNA viruses like coronaviruses, which cause diseases such as COVID-19, MERS and SARS. It also covers negative strand RNA viruses including orthomyxoviruses (influenza viruses), paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses and filoviruses. It provides details on virus structure, genome and diseases caused, for virus families like Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Reoviridae and Birnaviridae, which contain double stranded RNA genomes.Recently uploaded (20)
Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
Ėý
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
Ėý
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningUnit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
Ėý
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
Ėý
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatComprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde
Ėý
ðĒ Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
ðŽ Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
ð What Youâll Learn in This Presentation
â
History & Evolution of Antibiotics
â
Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
â
Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
â
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
â
Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
â
Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
â
Clinical Applications & Challenges.
ð Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
ð Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
ð Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatFull-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatMeeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
Ėý
NAPD Annual Symposium
âEquity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?âMastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
Ėý
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
â
Soft Tissue Therapy â The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
â
Sports Taping Techniques â Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
â
Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia â A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatRRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON
Ėý
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ėý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxHow to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.urinalisis.pptx
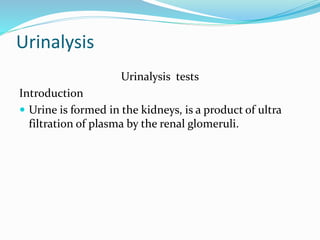
- 1. Urinalysis Urinalysis tests Introduction ï Urine is formed in the kidneys, is a product of ultra filtration of plasma by the renal glomeruli.
- 2. Urine sample ï Early morning sample-qualitative ï Random sample- routine ï 24hrs sample- quantitative ï Midstream sample-UTI ï Post prandial sample-D.M
- 3. Urine examination ï Macroscopic examination ï Chemical examination ï Microscopic examination
- 4. Color & appearance ï Normal= clear & pale yellow 1. Colourless- dilution, diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus, diuretics 2. Milky-purulent genitourinary tract infection 3. Orange-fever, excessive sweating 4. Red-haematuria 5. Brown/ black- melanin
- 5. Urinary volume ï Normal = 600-1550ml/day ï Polyuria- >2000ml ï Oliguria-<400ml ï Anuria-complete cessation of urine(<200ml) ï Nocturia-excretion of urine by a adult of >500ml with a specific gravity of <1.018 at night (characteristic of chronic glomerulonephritis)
- 6. Causes of polyuria ï Diabetes mellitus ï Diabetes insipidus ï Polycystic kidney ï Chronic renal failure ï Diuretics ï Intravenous saline/glucose
- 7. oliguria ï Dehydration-vomiting, diarrhoea, excessive sweating ï Renal ischemia ï Acute tubular necrosis ï Obstruction to the urinary tract ï Acute renal failure
- 8. Chemical tests- 1. Protein Causes of proteinuria ï Prerenal causes-Heavy exercise,Fever,hypertension, multiple myeloma, ecalmpsia ï Renal âacute & chronic glomerulonephritis,Renal tubular dysfunction,Polycystic kidney, nephrotic syndrome ï Post renal- acute & chronic cystitis, tuberculosis cystitis
- 9. 2. Bilirubin Test- fouchetâs test. ï Causes ïLiver diseases-injury,hepatitis ïObstruction to biliary tract 3. Urobilinogen ï est- ehrlich test ï Causes-hemolytic anemia's Bile salts- Hayâs test Cause- obstruction to bile flow (obstructive jaundice)
- 10. 3. Urobilinogen ï Test- ehrlich test ï Causes-hemolytic anemia's ï Bile salts- Hayâs test Cause- obstruction to bile flow (obstructive jaundice)
- 11. 4. Blood RBCs-Causes of hematuria ï Pre renal- bleeding diathesis, hemoglobinopathies, malignant hypertension. ï Renal- trauma, acute & chronic glomerulonephritis, renal tumors ï Post renal â severe UTI, calculi, trauma, tumors of urinary tract
- 12. Crystals in urine Crystals in acidic urine ïUric acid ïCalcium oxalate ïCystine ïLeucine Crystals in alkaline urine ïAmmonium magnesium phosphates(triple phosphate crystals) ïCalcium carbonate
- 13. Different crystals (indicative of renal disfunction) ï
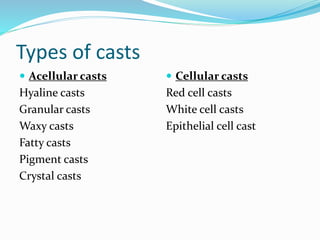
- 14. Types of casts ï Acellular casts Hyaline casts Granular casts Waxy casts Fatty casts Pigment casts Crystal casts ï Cellular casts Red cell casts White cell casts Epithelial cell cast
- 15. Fatty casts ï Formed by the breakdown of lipid-rich epithelial cells, these are hyaline casts with fat globule inclusions They can be present in various disorders, including ï nephrotic syndrome, ï diabetic or lupus nephropathy, ï Acute tubular necrosis
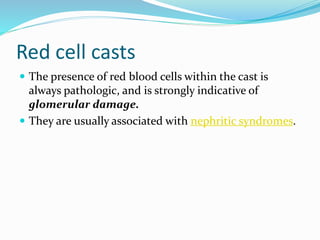
- 16. Red cell casts ï The presence of red blood cells within the cast is always pathologic, and is strongly indicative of glomerular damage. ï They are usually associated with nephritic syndromes.
- 17. White blood cell casts ï Indicative of inflammation or infection (especially when there is a pus), ï pyelonephritis ï acute allergic interstitial nephritis, ï nephrotic syndrome, or ï post-streptococcal acute glomerulonephritis
- 18. Negative Trace (100 mg/dL) + (250 mg/dL) ++ (500 mg/dL) +++ (1000 mg/dL) ++++ (2000+ mg/dL) The Urine Glucose Dipstick: Significance â Diabetes mellitus â Renal glycosuria Normal concentration: 15 mg/dl
- 19. Negative + (weak) ++ (moderate) +++ (strong) The Urine Bilirubin Dipstick: Bilirubin : is a break down of aged RBC or hemoglobin-result in yellowish color-it is excretd in urine and bile Significance -jaundice (direct bilirubin) ï§ Hepatitis, cirrhosis, other liver disorders ï§ Biliary obstruction
- 20. Negative Trace (5 mg/dL) + (15 mg/dL) ++ (40 mg/dL) +++ (80 mg/dL) ++++ (160+ mg/dL) The Urine Ketones Dipstick: Ketones: are produced by the liver as part of fatty acid metabolism/when lack of glucose occured Significance - Diabetic ketoacidosis - Prolonged fasting (starvation)
- 21. 1.000 1.005 1.010 1.015 1.020 1.025 1.030 It measures the concentration of all chemical particles of urine Normal-1.016-1.022 Significance - Diabetes insipidus (a disorder of the pituitary gland that causes the body to produce large amounts of urine). Urine Specific Gravity
- 22. Negative Moderate Trace + (weak) ++ (moderate) +++ (strong) The Urine Blood Dipstick: Significance - Hematuria ï§ Renal problem ï§ Glomerulonephritis ï§ Tumors
- 23. 5.0 6.0 6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 The Urine pH Dipstick: Significance - Acidic (less than 4.5) - Alkaline (greater than 8.0): renal tubular acidosis (>5.5) âĒ respiratory or metabolic acidosis/ketosis respiratory or metabolic alkalosis âĒ renal tubular acidosis âĒ renal calculi /renal stoneformation
- 24. Negative Trace + (30 mg/dL) ++ (100 mg/dL) +++ (300 mg/dL) ++++ (2000 mg/dL) The Urine Protein Dipstick: Significance - Proteinuria:- indicative of early kidney damage ï§ Tubular damage ï§ Glomerular damage








