urine formtion.pptx
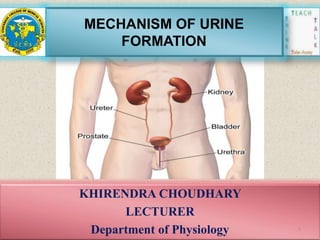
- 1. MECHANISM OF URINE FORMATION KHIRENDRA CHOUDHARY LECTURER Department of Physiology 1
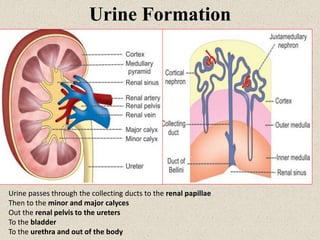
- 2. Urine Formation Urine passes through the collecting ducts to the renal papillae Then to the minor and major calyces Out the renal pelvis to the ureters To the bladder To the urethra and out of the body
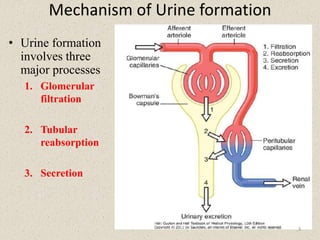
- 3. Mechanism of Urine formation âĒ Urine formation involves three major processes 1. Glomerular filtration 2. Tubular reabsorption 3. Secretion 3
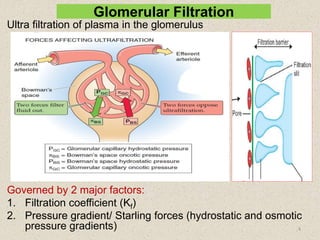
- 4. Glomerular Filtration Ultra filtration of plasma in the glomerulus Governed by 2 major factors: 1. Filtration coefficient (Kf) 2. Pressure gradient/ Starling forces (hydrostatic and osmotic pressure gradients) 4
- 5. GLOMERULAR FILTRAION RATE ïąIt is the amount of plasma filtered by all nephrons of both the kidney in a unit time i.e. per min or per day 125ml/min or 180 lit /day ïąAn important measurement in the evaluation of kidney function ïąThe kidney filter in one day an amount equal to-4 times the body water-15 times the ECF-60 times the plasma volume. 5
- 6. DYNAMICS OF FILTERATION NFP= sum of opposing forces and favouring forces Favouring forces= hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillary ( PGC=50) colloid osmotic pressure in bowmans space (áīŦBS=0) Opposing forces = Glomerular capillary oncotic pressure (áīŦGC= 30) hydrostatic pressure in bowmans space (PBS =10) NFP= favoring forces â opposing forces = ( 50+0) â (30 +10) = 10 mm of Hg 6 GFR NFP KF
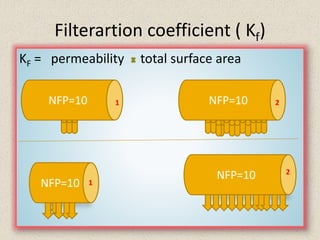
- 7. Filterartion coefficient ( Kf) KF = permeability total surface area 7 NFP=10 NFP=10 NFP=10 NFP=10 2 1 1 2
- 8. FILTRATION FRACTION Filtration fraction is the fraction (portion) of the renal plasma, which becomes the filtrate. It is the ratio between glomerular filtration rate & renal plasma flow . It is expressed in percentage. Filtration fraction = GFR/Renal plasma flowà 100 125 mL/min / 650 mL/min à 100 = 19.2%. Normal filtration fraction varies from 15% to 20%. 8
- 9. FACTORS AFECTING GFR 1) Renal Blood Flow 2) Glomerular Capillary Pressure 3) Colloidal Osmotic Pressure 4) Hydrostatic Pressure in Bowman Capsule 5) Constriction of Afferent Arteriole 6) Constriction of Efferent Arteriole 7) Systemic Arterial Pressure 8) Sympathetic Stimulation 9) Surface Area of Capillary Membrane 10) Permeability of Capillary Membrane 11) Contraction of Glomerular Mesangial Cells 12) Hormonal and Other Factors 9
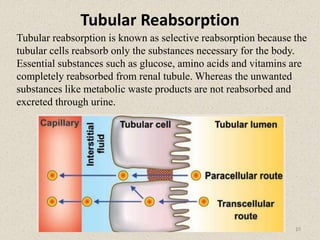
- 10. Tubular Reabsorption 10 Tubular reabsorption is known as selective reabsorption because the tubular cells reabsorb only the substances necessary for the body. Essential substances such as glucose, amino acids and vitamins are completely reabsorbed from renal tubule. Whereas the unwanted substances like metabolic waste products are not reabsorbed and excreted through urine.
- 11. Tubular Reabsorption Reabsorption of the substances occurs in almost all the segments of tubular portion of nephron. 1. Substances Reabsorbed from ProximalConvoluted Tubule About 7/8 of the filtrate (about 88%) is reabsorbed in proximal convoluted tubule. The brush border of epithelial cells in proximal convoluted tubule increases the surface area and facilitates the reabsorption. Substances reabsorbed are glucose, amino acids, sodium, potassium, calcium, bicarbonates, chlorides, phosphates, urea, uric acid and water. 2. Substances Reabsorbed from Loop of Henle sodium and chloride. 3. Substances Reabsorbed from Distal Convoluted Tubule Sodium, calcium, bicarbonate and water are reabsorbed from distal convoluted tubule 11
- 12. Tubular secretion Tubular secretion is the process by which the substances are transported from blood into renal tubules. It is also called tubular excretion Substances secreted are âĒ 1. Paraaminohippuric acid (PAH) âĒ 2. Diodrast âĒ 3. 5hydroxyindoleaceticacid (5HIAA) âĒ 4. Amino derivatives âĒ 5. Penicillin. 12
- 13. Summary 13
- 14. 14