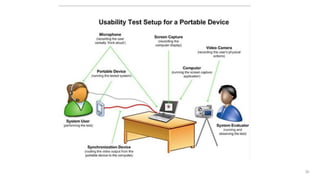
Usability testing
- 2. 2
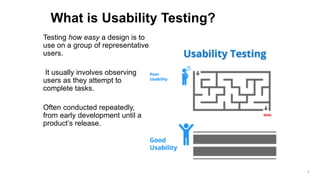
- 3. Testing how easy a design is to use on a group of representative users. It usually involves observing users as they attempt to complete tasks. Often conducted repeatedly, from early development until a product’s release. What is Usability Testing? 3
- 4. Comparative Usability Testing : Used to compare the usability of one website with another. Explorative Usability Testing : Explorative usability testing can establish what content and functionality a new product should include to meet the needs of its users. Usability Evaluation This is a test of a new or updated service either pre or post-launch. Different types of usability testing or reasons to conduct usability research 4
- 5. • feedback direct from the target audience makes the project team focused. • internal debates can be resolved by testing the issue to see how users react to the different options being discussed. • issues and potential problems are highlighted before the product is launched. • it increases the likelihood of usage and repeat usage. • it minimises the risk of the product failing. • users are better able to reach their goals, which results in the business meeting its targets. Why usability testing? 5
- 6. 6
- 7. 7
- 8. 8
- 9. 9
- 10. 10
- 11. 11
- 12. 12
- 13. 13
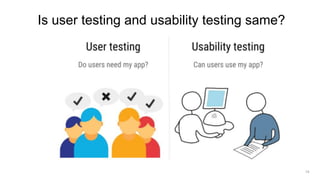
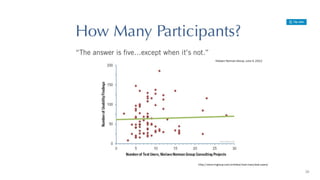
- 14. Is user testing and usability testing same? 14
- 15. Definition of Utility = whether it provides the features you need. Definition of Usability = how easy & pleasant these features are to use. Definition of Useful = usability + utility. 15
- 16. The five components of usability CP2408 - Design Thinking and Creative IT Industries 16 1. Learnability 2. Efficiency 3. Memorability 4. Errors 5. Satisfaction If your customers can’t easily use your application, they won’t bother to try and learn it. They will just go elsewhere.
- 17. 17
- 18. 18
- 19. • What features do you actually need to put into your product? • How easy and pleasant are these features to use? • Are these features even useful? Now you can answer following 19
- 20. 20
- 21. 21
- 22. 22
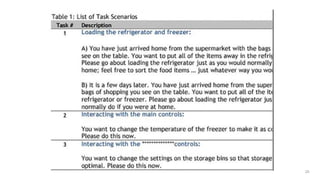
- 23. 23 Design task scenarios Depends on product, lab or field Identification & negotiation with users Team plan, roles according to the place of test
- 24. 24
- 25. 25
- 26. 26
- 27. 27
- 28. 28
- 29. 29
- 30. 30
- 31. 31
- 32. 32
- 33. 33
- 34. 34
- 35. 35
- 36. 36
- 37. 37
- 38. 38
- 39. How to behave with your users? 39
- 40. 40
- 41. 41
- 42. 42
- 43. 43
- 44. 44
- 45. 45
- 46. 46
- 47. 47
- 49. • Objectives of the test • Tasks that will be performed • Test Documents (content form, orientation script, pre & post-test questionnaires) • Test Participants • Test Method To test the usability of a mobile application, you need: 49
- 50. • Explore important areas: • The app’s roadmap • Users and markets for whom the app is targeted • The app’s competitors • Timing and scope The Objectives of the Usability Test 50
- 51. 51
- 52. 52
- 53. Translating technical knowledge into everyday language is a skill CP2408 - Design Thinking and Creative IT Industries 53 ● We need communication skills that bridge the gap between technical realities and client aspirations ● A good approach is to speak in plain english ○ Find ways to translate technical details and limitations into easily understandable concepts ● Also, use metaphors - provide clarity about a complex notion by comparing it to something commonplace ○ E.g. A computer network is like the postal system… ○ E.g. Mobile app notifications are like how magazine subscriptions work...
- 54. Beyond usability to Amazing Experience Design Functionality + Usability = Good Experience Good experience + Thoughtfulness = Amazing Experience CP2408 - Design Thinking and Creative IT Industries 54
- 55. Building Amazing Experiences • Doesn’t have to be complicated • Combine functionality, usability and thoughtfulness • Immerse yourself in your user’s world • Understand the whole story • Imagine your Grandpa using the product • Show some personality and fun! • Simplify to let your thoughtfulness shine CP2408 - Design Thinking and Creative IT Industries 55
- 56. Assume a beginner’s mindset Ask What-How-Why Ask the 5 whys Conduct interviews with empathy Empathise methods 56
- 57. Designing without empathy: Google glass 57
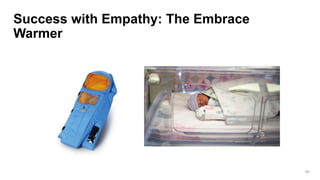
- 58. Success with Empathy: The Embrace Warmer 58