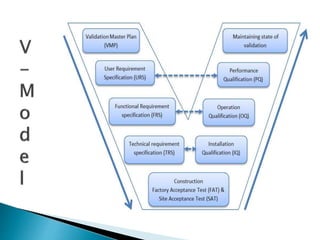
V Model
- 1. Validation Master Plan Mirza Danish Hussain Barlas Assistant Manager Business Development and Regulatory Affairs (Pharm-D , R.Ph, MBA Mkt, MBA Sc, CRCP)
- 3. ’üĮ A validation Master Plan (VMP) is a comprehensive document describing the applicable validation requirements for the facility, and providing a plan for the meeting those requirements. ’üĮ Scope: VMP includes all relevant aspects relating to the production of Pharmaceuticals in the production facility. The principle of validation, the organization of qualification and equipment are also described. It covers all facilities used in various production areas, storage, services and the rooms for staff. ’üĮ * In short, it is documented evidence that provides a high degree of assurance that a specific process will consistently produce a product the meets its predetermined specifications and quality attributes.
- 4. ’üĮ The user requirement(s) document (URD) or user requirement(s) specification is a document that specifies what the user expects the machine to be able to do.
- 5. ’üĮ A functional specification (or sometimes functional requirement specifications) is a formal document used to describe in detail a machines intended capabilities, appearance, and interactions with users.
- 6. ’üĮ A technical specification (or sometimes technical requirement specifications) is a formal document used to describe in detail the requirements for a machines use.
- 7. ’üĮ The first element of the validation of new facilities, systems or equipment is design qualification (DQ). ’üĮ The compliance of the design with GMP should be demonstrated and documented.
- 8. Installation qualification (IQ) should be performed on new or modified facilities, systems and equipment. IQ should include, but not be limited to the following: (a) installation of equipment, piping, services and instrumentation checked to current engineering drawings and specifications; (b) collection and collation of supplier operating and working instructions and maintenance requirements; (c) calibration requirements; (d) verification of materials of construction.
- 9. Operational qualification (OQ) should follow Installation qualification. OQ should include, but not be limited to the following: ’üĮ (a) tests that have been developed from knowledge of processes, systems and ’üĮ equipment; ’üĮ (b) tests to include a condition or a set of conditions encompassing upper and ower operating limits, sometimes referred to as ŌĆ£worst caseŌĆØ conditions. The completion of a successful Operational qualification should allow the finalization of calibration, operating and cleaning procedures, operator training and preventative maintenance requirements. It should permit a formal "release" of the facilities, systems and equipment
- 10. Performance qualification (PQ) should follow successful completion of ’üĮ Installation qualification and Operational qualification. ’üĮ PQ should include, but not be limited to the following: ’üĮ (a) tests, using production materials, qualified substitutes or simulated product, ’üĮ that have been developed from knowledge of the process and the facilities, systems or equipment;6 ’üĮ (b) tests to include a condition or set of conditions encompassing upper and lower operating limits. ’üĮ Although PQ is described as a separate activity, it may in some cases be ’üĮ appropriate to perform it in conjunction with OQ.