Value chain analysis
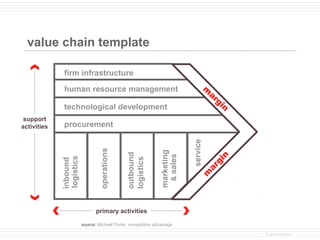
- 1. value chain template firm infrastructure human resource management m ar gi technological development n support activities procurement service operations marketing outbound & sales n logistics logistics inbound gi ar m primary activities source: Michael Porter, competitive advantage © provenmodels
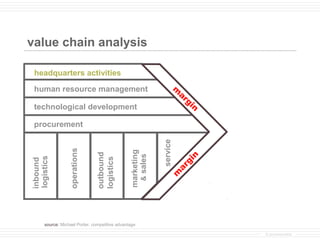
- 2. value chain analysis headquarters activities human resource management m ar gi technological development n procurement service operations marketing outbound & sales n logistics logistics inbound gi ar m source: Michael Porter, competitive advantage © provenmodels
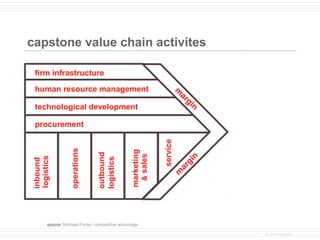
- 3. capstone value chain activites firm infrastructure human resource management m ar gi technological development n procurement service operations marketing outbound & sales logistics n logistics inbound gi ar m source: Michael Porter, competitive advantage © provenmodels
- 4. objective value chain analysis • the objective is to analyse competitive advantage by disintegrating an organisation into discrete activities or processes and examine how each activity contributes to the organisation’s relative cost position or the customer’s comparative willingness to pay. the analysis provides: • insight into why the firm does or does not have added value; • a way to identify opportunities to improve added value; • an understanding how added value may change over time. source: Pankaj Ghemawat, strategy and the business landscape © provenmodels
- 5. value chain analysis process process: 1. setup: classify an organisation’s activities based on the value chain. Single out individual activities which: • Have different economics; • Have a high potential impact of differentiation; • Represent a significant or growing proportion of costs. 1. cost analysis: managers examine the costs associated with (the most important) activities to understand why and how their cost base differs from competitors. Defining relevant cost drivers helps to estimate competitor’s positions and to assess the own organisation’s flexibility; 2. value analysis: managers analyse how each activity generates customer willingness to pay. Customer willingness often varies per customer segment; 3. strategic decision making: consider changes in activities so that costs are lowered or customer willingness is increased. Identify linkages, relationships between value activities, within the chain. The more complex the linkage the higher chance it will provide a competitive advantage. The competitor’s profiles need to be taken into account when repositioning oneself. source: Pankaj Ghemawat, strategy and the business landscape © provenmodels
- 6. tips for value chain analysis • focus on the important activities; those that matter to the strategic position; • make a clear distinction between annual recurring cost and one time investments; • keep track of all assumptions that underline the allocation of costs over the activity groups; • use sensitivity analysis to validate the assumptions underlying the value chain analysis in order to assess which assumptions really matter; • value chain analysis allows for the inclusions of multiple drivers per activity. • only include drivers that vary across competitors; • do not focus on differences between total cost levels, but on costs per activity. Activities provide competitive advantage; • research should focus on customers willingness to pay for an activity as part of a product’s profile instead of only a customers desire; • reduce the list of customer needs to a manageable number. source: Pankaj Ghemawat, strategy and the business landscape © provenmodels
- 7. tips for value chain analysis • focus on the important activities; those that matter to the strategic position; • make a clear distinction between annual recurring cost and one time investments; • keep track of all assumptions that underline the allocation of costs over the activity groups; • use sensitivity analysis to validate the assumptions underlying the value chain analysis in order to assess which assumptions really matter; • value chain analysis allows for the inclusions of multiple drivers per activity. • only include drivers that vary across competitors; • do not focus on differences between total cost levels, but on costs per activity. Activities provide competitive advantage; • research should focus on customers willingness to pay for an activity as part of a product’s profile instead of only a customers desire; • reduce the list of customer needs to a manageable number. source: Pankaj Ghemawat, strategy and the business landscape © provenmodels