Vegetable seed rate
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes1,042 views
ALL VEGETABLE SEED RATE, commercial vegetable seed rate, Important vegetable seed
1 of 7
Downloaded 73 times






Ad
Recommended
Ground nut
Ground nutEkalavya Organic Agriculture Polytechnic (Ekalavya Grameena Vikas Foundation)
╠²
1. Groundnut, also known as peanut, is an important oil and protein crop grown primarily in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It is a self-pollinating, annual herbaceous legume.
2. Groundnut is predominantly grown in tropical and subtropical regions with rainfall between 500-1250 mm during the crop season. Ideal soil types are sandy loams with a pH between 5-5.5.
3. Groundnut seeds are usually sown in kharif season from June-July under rainfed conditions or in rabi/summer under irrigation. Proper sowing, weed, water and pest management are required to achieve optimal pod yields.Smart farming ppt.
Smart farming ppt.SirikornManeecharoen
╠²
This document defines smart farming as using modern technology to increase agricultural production and quality. It discusses the history of smart agriculture focusing on supporting development and food security. The objectives of smart farming are to sustainably increase yields and incomes while adapting to climate change and reducing emissions. The advantages include maximizing outputs with minimal resources, while disadvantages are reliance on continuous internet and farmers learning new technologies.Presentation on Pigeon Pea
Presentation on Pigeon PeaRitabrataSarkar3
╠²
The document provides information about the pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) crop. Some key details include:
- Pigeon pea is a perennial legume that is an important food crop in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, especially in South Asia.
- The variety being grown is NTL-724 over a plot size of 20m2 for a practical crop production course.
- Pigeon pea is rich in protein, iron, and other nutrients and is a staple food in India, where it is commonly eaten as dal.
- Details are provided about the sowing, growth stages, nutrient management, diseases, pests, and economics of pigeon peDiabetes Mellitus
Diabetes MellitusMD Abdul Haleem
╠²
This document provides an overview of diabetes mellitus (DM), including the three main types (Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes), signs and symptoms, complications, pathophysiology, oral manifestations, dental management considerations, emergency management, diagnosis, and treatment. DM is caused by either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or cells not responding properly to insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. The document compares and contrasts the characteristics of Type 1 and Type 2 DM.Power Point Presentation on Artificial Intelligence
Power Point Presentation on Artificial Intelligence Anushka Ghosh
╠²
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems that model and simulate human intelligence, with applications including virtual assistants like Siri and Google Now. The document covers the early history of AI, current advancements, and future challenges, highlighting its benefits and drawbacks. It concludes that AI, defined as the design of intelligent agents, has potential in various fields but also raises concerns about dependency and job displacement.Republic Act No. 11313 Safe Spaces Act (Bawal Bastos Law).pptx
Republic Act No. 11313 Safe Spaces Act (Bawal Bastos Law).pptxmaricelabaya1
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of the Safe Spaces Act, which aims to address gender-based sexual harassment. It defines harassment in public spaces, online, and work/educational settings. Acts considered harassment include catcalling, unwanted comments on appearance, stalking, and distributing intimate photos without consent. Those found guilty face penalties like imprisonment or fines. The law also requires employers and educational institutions to disseminate the law, prevent harassment, and address complaints through committees.Hypertension
HypertensionRatheeshkrishnakripa
╠²
This document defines hypertension and describes its types, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnostic evaluations, and management. Hypertension is defined as a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher and/or a diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or higher. It is managed primarily through lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise changes as well as pharmacological therapies including diuretics, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers. Nursing care involves monitoring the patient's condition, educating on lifestyle changes, and ensuring proper treatment adherence.Nursing process
Nursing processDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
╠²
The document discusses the nursing process, which includes assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It describes each component in detail. Assessment involves collecting client data through various methods. Nursing diagnosis identifies client problems based on the assessment. Planning establishes goals and interventions. Implementation carries out the planned interventions. Evaluation assesses client progress and intervention effectiveness. The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing individualized care.Mating designs..
Mating designs..PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi
╠²
The document outlines various mating designs used in plant breeding, highlighting their definitions, objectives, and factors influencing their selection. It contrasts several major mating designs, including biparental mating, polycross, top cross, and North Carolina designs, each with unique advantages and limitations. The analysis concludes that the appropriate choice of mating design is crucial for successful plant breeding and the identification of superior genotypes.Crop improvement / Space breeding
Crop improvement / Space breeding Dr. Pavan Kundur
╠²
Space breeding is a cutting-edge technique combining astronautics with agriculture, involving sending seeds into space to induce mutations that can enhance desirable traits in crops. China has pioneered this field, conducting various experiments leading to substantial increases in mutation rates and the development of high-yield, disease-resistant plant varieties. The method, although limited by technological support and investment, shows promise for significant agricultural advancements and requires further research into its practical applications.History of plant breeding
History of plant breedingRoshan Parihar
╠²
Thomas Fairchild was the first to create an artificial plant hybrid in 1717 between Sweet William and Carnation pink, called "Fairchild's Mule". Important developments in the pre-Mendelian era included domestication of major crops by 1000 BC, and the first description of the cell in 1665. The Mendelian era saw the rediscovery of Mendel's laws in 1900 and the development of the first commercial maize hybrid in 1917. The post-Mendelian era brought the discovery of cytoplasmic male sterility in rice in 1933 and transposable elements in 1950. Modern developments include the first transgenic plant in 1983, Bt cotton in 1987, and the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers'Rice Introduction, origin, floral description, floral formula and cultivation...
Rice Introduction, origin, floral description, floral formula and cultivation...Sindh Agriculture University Tandojam, Sindh Pakistan
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of rice, including its botanical characteristics, nutritional value, historical cultivation, and production statistics. It highlights global rice production, with China and India being the largest producers, and details the role of rice in Pakistan's agriculture and economy. Additionally, the document discusses rice varieties, cultivation areas, and by-products, emphasizing the importance of rice as a staple food.Population breeding in self pollinated crops
Population breeding in self pollinated cropsDarshana Ajith
╠²
The document describes Diallel Selective Mating (DSM), a population improvement approach involving parental diallel crosses, F1 diallel crosses, and selective mating series. DSM aims to accumulate desirable alleles, broaden the genetic base, and develop new cultivars through recurrent selection and intermating in segregating generations. It allows for introduction of new germplasm and isolation of pure lines at various stages of the breeding program. While effective for some autogamous crops, DSM requires a large number of crosses and is labor intensive.Short charts of Rabi Field crops
Short charts of Rabi Field cropsARUN RANKAWAT
╠²
This document provides information on 19 different crops including their botanical name, family, origin, varieties, sowing time and seed rate. Some of the major crops mentioned are wheat, barley, chickpea, mustard, potato, sugarcane, alfalfa, tobacco, sunflower, safflower and peas. For each crop, varieties suited to different regions of India are listed along with ideal sowing periods and recommended seeding rates.Breeding methods in sorghum
Breeding methods in sorghumarunchacko14
╠²
Sorghum is a crucial crop for over half a billion people, serving as food, fodder, feed, and fuel. Its cultivation is supported by its high nutritional value, multiple uses, and adaptability to harsh conditions, including drought resilience. Various breeding methods have been developed to enhance its traits, including resistance to diseases and pests, and to create hybrid varieties for improved yields.Cotton breeding
Cotton breedingShoukat Rather
╠²
Cotton is an important warm season crop grown for its fiber. It is a dicot plant that is often cross pollinated. The two main types are old world cotton which are diploid species, and new world cotton which are allo-tetraploid species. Breeding objectives for cotton include improved fiber yield and quality, early maturity, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Hybridization is the main breeding method used to combine desirable traits from different cotton varieties.Fertigation system
Fertigation systemIRADA Foundation
╠²
The document discusses fertigation, which is the process of applying fertilizers through irrigation systems. It covers the need for fertigation to address issues like soil fertility depletion. Key topics include characteristics of fertilizers suitable for fertigation like solubility, compatibility between fertilizers, and common fertigation equipment like fertilizer tanks, venturi injectors, and injection pumps. The document provides guidance on calculating fertilizer requirements and examples for determining the needed quantities based on recommended doses.Male sterility in vegetable crops
Male sterility in vegetable cropsMamtaChoudhary75
╠²
The document discusses male sterility in vegetable crops, which is crucial for hybrid seed production, first reported by J.K. Kaulreuter in 1763. It highlights various forms of male sterility, including genetic, cytoplasmic, and chemical, along with their implications for breeding strategies and hybridization in crops like tomato, onion, and chili. A case study demonstrates the effectiveness of using genic male sterility (ps 2) lines in improving hybrid seed yield, emphasizing the economic advantages of male sterile-based hybrid seeds over manual emasculation.Tomato Breeding
Tomato BreedingLav Kumar
╠²
Tomato has been extensively bred due to its short duration, easy cultivation, and large number of seeds per fruit. Breeding objectives include earliness, increased yield, fruit quality traits like size, color, and disease/stress resistance. Common breeding methods are introduction, pure line selection, pedigree, backcrossing, and heterosis breeding. Interspecific hybridization utilizes wild relatives for traits like disease resistance. New varieties have been developed with resistance to important diseases like bacterial wilt, nematodes, and viruses. Processing varieties have traits like uniform color, shape, acidity, and crack resistance.Detection of Genetically modified plants and Organic Seed production.
Detection of Genetically modified plants and Organic Seed production.NSStudents
╠²
The document discusses the detection and identification of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in crops, emphasizing the importance of PCR methods for these processes. It provides methodologies for organic seed production, including soil management, weed management, and pest control, alongside the concerns of transgene contamination. The text outlines various strategies to ensure compliance with GMO regulations while maintaining organic farming practices.Underutilized Vegetable Crops
Underutilized Vegetable Crops Dr.Sunil Prajapati
╠²
This document discusses underutilized vegetable crops and their potential. It begins by explaining that while over 75,000 edible plant species exist globally, only around 150 are widely cultivated. It then discusses the nutritional value of various vegetables and common nutrient deficiencies. The concept of underutilized vegetable crops (UUVCs) is introduced as crops that are locally important but lack national recognition. UUVCs have potential for food security, income generation, and environmental benefits. Some constraints to their development include lack of awareness, research, and marketing support. The document concludes by listing examples of UUVCs from Central India along with their uses.Weed management using remote sensing
Weed management using remote sensingveerendra manduri
╠²
This document discusses the use of remote sensing technologies in precision agriculture for effective weed management, highlighting the inefficiencies of traditional herbicide spraying methods. It emphasizes the role of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in detecting and mapping weeds, particularly in crops like sugarcane, by analyzing their spectral reflectance characteristics. The document also outlines various methodologies, including object-based image analysis and texture-based classification techniques, to enhance weed detection accuracy.Maintenance breeding
Maintenance breedingPawan Nagar
╠²
Maintenance breeding is the branch of plant breeding that deals with producing and maintaining breeder seed to preserve the genetic purity and identity of plant varieties. It involves continuously producing fresh breeder seed through methods like growing isolated plots and bulk selection to remove off-types. Proper handling and roguing of the breeder seed crop is crucial. The breeder seed is then used to produce foundation seed while maintaining a carry-over stock to safeguard against losses. Maintenance breeding helps purify varieties and parental lines, prevent genetic deterioration, support quality seed production, and prolong the life of varieties.Sesame
SesameVarsha Gayatonde
╠²
Sesame is an important oilseed crop cultivated worldwide for its edible oil. It originated in tropical Africa but is now widely grown in Asia, Africa, and other warm regions. Sesame is an annual herb with opposite leaves, solitary flowers in the leaf axils, and capsular fruits containing numerous seeds. It is predominantly self-pollinated but some natural cross-pollination occurs via insects. Traditional breeding methods include bagging flowers to encourage selfing or emasculation and hand-pollination to facilitate crossing.Physical Purity Testing.pdf
Physical Purity Testing.pdfKumari Rajani
╠²
The document outlines the concept and procedures for physical purity testing of seed samples, providing guidelines for classifying components such as pure seeds, other crop seeds, weed seeds, and inert matter according to specific standards. It details the methodology for conducting tests, sample preparation, component separation, weighing, and reporting results in accordance with international seed testing rules. Additionally, it includes standards for certification and guidelines for identifying objectionable weed seeds and diseases affecting crops.cropping system
cropping systemChoudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar
╠²
The document discusses various cropping systems, highlighting their significance in agriculture, including mono cropping, multiple cropping, and sustainable practices. It explains techniques like intercropping, agroforestry, organic farming, and the importance of maintaining soil fertility through crop rotation. Additionally, it addresses ecological practices such as contour farming and permaculture that contribute to sustainable agricultural development.Breeding assignment on clonal selection
Breeding assignment on clonal selectionOrissa university of agricultural and technology
╠²
This document discusses clonal selection and its use in fruit breeding. It defines clones as progeny from a single plant produced through asexual reproduction. Clones are homogeneous, heterozygous, and maintain genetic variation through environmental effects rather than genetics. Clonal selection is useful for conserving heterosis over many generations. Superior clones can be isolated from local varieties, introduced varieties, or intercrossed populations. The breeding procedure involves multi-year selection and testing of clones from initial populations to identify superior clones for release as new varieties. Clonal selection is effective for genetic improvement in asexually propagated crops but clones are highly prone to new diseases and cannot create new genetic variability.Lentil
LentilJatinder Singh
╠²
This document provides information about lentils (Lens culinaris), including:
1. Lentils are an important pulse crop grown mainly in Canada, India, Turkey, US, and Australia, with India producing about 0.6 million tons annually.
2. Lentils have a diploid chromosome number of 2n=2x=14. Their center of origin is the Near East and they were first domesticated there.
3. Breeding objectives for lentils include increasing yield, improving seed size/color/quality for different market classes, and improving resistance to diseases, insects, drought, and lodging.Brooding and rearing manegement pdf
Brooding and rearing manegement pdfRavi Yadav
╠²
The document outlines management practices for brooding and rearing poultry, covering stages from 1 to 20 weeks. It details specific weight and housing requirements for broilers, growers, and layers, along with lighting considerations for egg production. The process is segmented into brooding (1-4 weeks), rearing (4-8 weeks), and growing phases (9-20 weeks) with transition points for different stages.Agro climatic zone of India by ICAR 05-Nov-2022.pdf
Agro climatic zone of India by ICAR 05-Nov-2022.pdfRavi Yadav
╠²
The document outlines various agricultural zones in India, detailing their geographical and climatic characteristics along with key crops. It describes 15 distinct zones, including the Western Himalayan, Eastern Himalayan, Gangetic Plains, and Plateau regions, each with specific rainfall and temperature patterns. The information highlights the major crops suited to each zone and the challenges faced, such as waterlogging and low irrigation intensity.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Mating designs..
Mating designs..PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi
╠²
The document outlines various mating designs used in plant breeding, highlighting their definitions, objectives, and factors influencing their selection. It contrasts several major mating designs, including biparental mating, polycross, top cross, and North Carolina designs, each with unique advantages and limitations. The analysis concludes that the appropriate choice of mating design is crucial for successful plant breeding and the identification of superior genotypes.Crop improvement / Space breeding
Crop improvement / Space breeding Dr. Pavan Kundur
╠²
Space breeding is a cutting-edge technique combining astronautics with agriculture, involving sending seeds into space to induce mutations that can enhance desirable traits in crops. China has pioneered this field, conducting various experiments leading to substantial increases in mutation rates and the development of high-yield, disease-resistant plant varieties. The method, although limited by technological support and investment, shows promise for significant agricultural advancements and requires further research into its practical applications.History of plant breeding
History of plant breedingRoshan Parihar
╠²
Thomas Fairchild was the first to create an artificial plant hybrid in 1717 between Sweet William and Carnation pink, called "Fairchild's Mule". Important developments in the pre-Mendelian era included domestication of major crops by 1000 BC, and the first description of the cell in 1665. The Mendelian era saw the rediscovery of Mendel's laws in 1900 and the development of the first commercial maize hybrid in 1917. The post-Mendelian era brought the discovery of cytoplasmic male sterility in rice in 1933 and transposable elements in 1950. Modern developments include the first transgenic plant in 1983, Bt cotton in 1987, and the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers'Rice Introduction, origin, floral description, floral formula and cultivation...
Rice Introduction, origin, floral description, floral formula and cultivation...Sindh Agriculture University Tandojam, Sindh Pakistan
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of rice, including its botanical characteristics, nutritional value, historical cultivation, and production statistics. It highlights global rice production, with China and India being the largest producers, and details the role of rice in Pakistan's agriculture and economy. Additionally, the document discusses rice varieties, cultivation areas, and by-products, emphasizing the importance of rice as a staple food.Population breeding in self pollinated crops
Population breeding in self pollinated cropsDarshana Ajith
╠²
The document describes Diallel Selective Mating (DSM), a population improvement approach involving parental diallel crosses, F1 diallel crosses, and selective mating series. DSM aims to accumulate desirable alleles, broaden the genetic base, and develop new cultivars through recurrent selection and intermating in segregating generations. It allows for introduction of new germplasm and isolation of pure lines at various stages of the breeding program. While effective for some autogamous crops, DSM requires a large number of crosses and is labor intensive.Short charts of Rabi Field crops
Short charts of Rabi Field cropsARUN RANKAWAT
╠²
This document provides information on 19 different crops including their botanical name, family, origin, varieties, sowing time and seed rate. Some of the major crops mentioned are wheat, barley, chickpea, mustard, potato, sugarcane, alfalfa, tobacco, sunflower, safflower and peas. For each crop, varieties suited to different regions of India are listed along with ideal sowing periods and recommended seeding rates.Breeding methods in sorghum
Breeding methods in sorghumarunchacko14
╠²
Sorghum is a crucial crop for over half a billion people, serving as food, fodder, feed, and fuel. Its cultivation is supported by its high nutritional value, multiple uses, and adaptability to harsh conditions, including drought resilience. Various breeding methods have been developed to enhance its traits, including resistance to diseases and pests, and to create hybrid varieties for improved yields.Cotton breeding
Cotton breedingShoukat Rather
╠²
Cotton is an important warm season crop grown for its fiber. It is a dicot plant that is often cross pollinated. The two main types are old world cotton which are diploid species, and new world cotton which are allo-tetraploid species. Breeding objectives for cotton include improved fiber yield and quality, early maturity, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Hybridization is the main breeding method used to combine desirable traits from different cotton varieties.Fertigation system
Fertigation systemIRADA Foundation
╠²
The document discusses fertigation, which is the process of applying fertilizers through irrigation systems. It covers the need for fertigation to address issues like soil fertility depletion. Key topics include characteristics of fertilizers suitable for fertigation like solubility, compatibility between fertilizers, and common fertigation equipment like fertilizer tanks, venturi injectors, and injection pumps. The document provides guidance on calculating fertilizer requirements and examples for determining the needed quantities based on recommended doses.Male sterility in vegetable crops
Male sterility in vegetable cropsMamtaChoudhary75
╠²
The document discusses male sterility in vegetable crops, which is crucial for hybrid seed production, first reported by J.K. Kaulreuter in 1763. It highlights various forms of male sterility, including genetic, cytoplasmic, and chemical, along with their implications for breeding strategies and hybridization in crops like tomato, onion, and chili. A case study demonstrates the effectiveness of using genic male sterility (ps 2) lines in improving hybrid seed yield, emphasizing the economic advantages of male sterile-based hybrid seeds over manual emasculation.Tomato Breeding
Tomato BreedingLav Kumar
╠²
Tomato has been extensively bred due to its short duration, easy cultivation, and large number of seeds per fruit. Breeding objectives include earliness, increased yield, fruit quality traits like size, color, and disease/stress resistance. Common breeding methods are introduction, pure line selection, pedigree, backcrossing, and heterosis breeding. Interspecific hybridization utilizes wild relatives for traits like disease resistance. New varieties have been developed with resistance to important diseases like bacterial wilt, nematodes, and viruses. Processing varieties have traits like uniform color, shape, acidity, and crack resistance.Detection of Genetically modified plants and Organic Seed production.
Detection of Genetically modified plants and Organic Seed production.NSStudents
╠²
The document discusses the detection and identification of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in crops, emphasizing the importance of PCR methods for these processes. It provides methodologies for organic seed production, including soil management, weed management, and pest control, alongside the concerns of transgene contamination. The text outlines various strategies to ensure compliance with GMO regulations while maintaining organic farming practices.Underutilized Vegetable Crops
Underutilized Vegetable Crops Dr.Sunil Prajapati
╠²
This document discusses underutilized vegetable crops and their potential. It begins by explaining that while over 75,000 edible plant species exist globally, only around 150 are widely cultivated. It then discusses the nutritional value of various vegetables and common nutrient deficiencies. The concept of underutilized vegetable crops (UUVCs) is introduced as crops that are locally important but lack national recognition. UUVCs have potential for food security, income generation, and environmental benefits. Some constraints to their development include lack of awareness, research, and marketing support. The document concludes by listing examples of UUVCs from Central India along with their uses.Weed management using remote sensing
Weed management using remote sensingveerendra manduri
╠²
This document discusses the use of remote sensing technologies in precision agriculture for effective weed management, highlighting the inefficiencies of traditional herbicide spraying methods. It emphasizes the role of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in detecting and mapping weeds, particularly in crops like sugarcane, by analyzing their spectral reflectance characteristics. The document also outlines various methodologies, including object-based image analysis and texture-based classification techniques, to enhance weed detection accuracy.Maintenance breeding
Maintenance breedingPawan Nagar
╠²
Maintenance breeding is the branch of plant breeding that deals with producing and maintaining breeder seed to preserve the genetic purity and identity of plant varieties. It involves continuously producing fresh breeder seed through methods like growing isolated plots and bulk selection to remove off-types. Proper handling and roguing of the breeder seed crop is crucial. The breeder seed is then used to produce foundation seed while maintaining a carry-over stock to safeguard against losses. Maintenance breeding helps purify varieties and parental lines, prevent genetic deterioration, support quality seed production, and prolong the life of varieties.Sesame
SesameVarsha Gayatonde
╠²
Sesame is an important oilseed crop cultivated worldwide for its edible oil. It originated in tropical Africa but is now widely grown in Asia, Africa, and other warm regions. Sesame is an annual herb with opposite leaves, solitary flowers in the leaf axils, and capsular fruits containing numerous seeds. It is predominantly self-pollinated but some natural cross-pollination occurs via insects. Traditional breeding methods include bagging flowers to encourage selfing or emasculation and hand-pollination to facilitate crossing.Physical Purity Testing.pdf
Physical Purity Testing.pdfKumari Rajani
╠²
The document outlines the concept and procedures for physical purity testing of seed samples, providing guidelines for classifying components such as pure seeds, other crop seeds, weed seeds, and inert matter according to specific standards. It details the methodology for conducting tests, sample preparation, component separation, weighing, and reporting results in accordance with international seed testing rules. Additionally, it includes standards for certification and guidelines for identifying objectionable weed seeds and diseases affecting crops.cropping system
cropping systemChoudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar
╠²
The document discusses various cropping systems, highlighting their significance in agriculture, including mono cropping, multiple cropping, and sustainable practices. It explains techniques like intercropping, agroforestry, organic farming, and the importance of maintaining soil fertility through crop rotation. Additionally, it addresses ecological practices such as contour farming and permaculture that contribute to sustainable agricultural development.Breeding assignment on clonal selection
Breeding assignment on clonal selectionOrissa university of agricultural and technology
╠²
This document discusses clonal selection and its use in fruit breeding. It defines clones as progeny from a single plant produced through asexual reproduction. Clones are homogeneous, heterozygous, and maintain genetic variation through environmental effects rather than genetics. Clonal selection is useful for conserving heterosis over many generations. Superior clones can be isolated from local varieties, introduced varieties, or intercrossed populations. The breeding procedure involves multi-year selection and testing of clones from initial populations to identify superior clones for release as new varieties. Clonal selection is effective for genetic improvement in asexually propagated crops but clones are highly prone to new diseases and cannot create new genetic variability.Lentil
LentilJatinder Singh
╠²
This document provides information about lentils (Lens culinaris), including:
1. Lentils are an important pulse crop grown mainly in Canada, India, Turkey, US, and Australia, with India producing about 0.6 million tons annually.
2. Lentils have a diploid chromosome number of 2n=2x=14. Their center of origin is the Near East and they were first domesticated there.
3. Breeding objectives for lentils include increasing yield, improving seed size/color/quality for different market classes, and improving resistance to diseases, insects, drought, and lodging.Rice Introduction, origin, floral description, floral formula and cultivation...
Rice Introduction, origin, floral description, floral formula and cultivation...Sindh Agriculture University Tandojam, Sindh Pakistan
╠²
More from Ravi Yadav (19)
Brooding and rearing manegement pdf
Brooding and rearing manegement pdfRavi Yadav
╠²
The document outlines management practices for brooding and rearing poultry, covering stages from 1 to 20 weeks. It details specific weight and housing requirements for broilers, growers, and layers, along with lighting considerations for egg production. The process is segmented into brooding (1-4 weeks), rearing (4-8 weeks), and growing phases (9-20 weeks) with transition points for different stages.Agro climatic zone of India by ICAR 05-Nov-2022.pdf
Agro climatic zone of India by ICAR 05-Nov-2022.pdfRavi Yadav
╠²
The document outlines various agricultural zones in India, detailing their geographical and climatic characteristics along with key crops. It describes 15 distinct zones, including the Western Himalayan, Eastern Himalayan, Gangetic Plains, and Plateau regions, each with specific rainfall and temperature patterns. The information highlights the major crops suited to each zone and the challenges faced, such as waterlogging and low irrigation intensity.Ravi yadav
Ravi yadavRavi Yadav
╠²
The document lists various fruits and nuts, including coconut, cashew nut, almond, and many others. It provides scientific names for each listed item. The variety reflects a diverse range of edible plants.Ravi yadav
Ravi yadavRavi Yadav
╠²
The document discusses Sclerotinia stem rot, a significant disease affecting sunflowers and other crops, characterized by symptoms such as lesions and sclerotia formation on various plant parts. Sclerotinia sclerotium, the causal organism, has a monocyclic lifecycle that thrives in moist conditions, leading to widespread plant tissue invasion. Management strategies include crop rotation, avoiding planting near previously infested areas, and controlling broad-leaved weeds.Result seminar potato ravi
Result seminar potato raviRavi Yadav
╠²
The document presents a study conducted by Ravi Yadav on the effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium on potato growth and yield at the College of Agriculture, Tikamgarh. The experiment involved twelve treatments evaluated for their impact on various growth parameters, including emergence percentage, plant height, number of leaves, and fresh weight. Data were collected during the Rabi season of 2019-20, with findings aimed at establishing the optimal nutrient combination for enhancing potato production.Randomized block experiment with excel ravi yadav
Randomized block experiment with excel ravi yadavRavi Yadav
╠²
Data Analysis ToolPak ,Microsoft add-ins,Data Analysis RBD,Data Analysis RBD Agriculture, RBD Problem Statement,Data Analysis RBD Exemple, Randomized Block ANOVA With Excel,Use of CD-ROM Database
Use of CD-ROM DatabaseRavi Yadav
╠²
The document discusses the use of CD-ROM databases in the College of Agriculture, Tikamgarh, detailing their history, advantages, disadvantages, and objectives of a study on user awareness and usage. It highlights the transition from compact discs for audio to digital data storage, the technical standards for CD-ROMs, and the evaluation of their usage patterns by postgraduate students. Additionally, it outlines the development and management of a collection of 28 data banks made available through CD-ROM technology, along with an analysis of user demographics.Compacted soil
Compacted soilRavi Yadav
╠²
Soil compaction results from increased bulk density or decreased porosity due to applied loads, adversely impacting agricultural yield and the environment. Major causes include heavy machinery use, inappropriate tillage practices, and livestock trampling, and management strategies focus on avoidance and rehabilitation through biological, chemical, and technical methods. Public policies have been established to combat land degradation and promote sustainable agricultural practices.Eroded soil
Eroded soilRavi Yadav
╠²
Eroded soils result from soil erosion, which is the loss of valuable topsoil through wind and water action, leading to decreased fertility and increased agricultural costs. Major causes of erosion include heavy rainfall, wind, recreational activities, improper land use, and lack of vegetation, with harmful effects on soil structure and productivity. Management practices such as crop rotation, contour cultivation, and no-till planting can mitigate soil erosion and preserve soil health.Survey and sampling and forcasting
Survey and sampling and forcastingRavi Yadav
╠²
Integrated Pest Management requires regular pest surveys, surveillance, and forecasting. Surveys involve collecting detailed pest population information in a given area at a particular time. Surveillance is an ongoing process to monitor pest populations and occurrences over time through methods like fixed plot surveys. This provides information on existing and new pest species, population levels, and damage. Forecasting predicts future pest infestation levels based on surveillance data and environmental factors, helping farmers time control measures appropriately. Proper pest surveys, surveillance, and forecasting are essential components of an effective IPM strategy.Preparation of Solution of Acids
Preparation of Solution of AcidsRavi Yadav
╠²
The document is an assignment from Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya covering the preparation of acid solutions, including types like percentage and normal solutions. It outlines procedures for creating NaCl and sulfuric acid solutions, emphasizing careful measurement and the importance of adding acid to water slowly to avoid dangerous reactions. Key definitions such as solute, solvent, saturation, and types of dilutions are also provided.Experimental Design-512,JNKVV,Hindi Notes
Experimental Design-512,JNKVV,Hindi Notes Ravi Yadav
╠²
Experimental Design-512, JNKVV, Hindi Notes, RBD IN HINDI,CRD IN HINDI,LSD IN HINDI, MISSING PLOT TECH. IN HINDI, STATISTIC NOTES IN HINDIExperimental Design-512,JNKVV,Hindi Notes
Experimental Design-512,JNKVV,Hindi Notes Ravi Yadav
╠²
Experimental Design-512, JNKVV, Hindi Notes, RBD IN HINDI,CRD IN HINDI,LSD IN HINDI, MISSING PLOT TECH. IN HINDI, STATISTIC NOTES IN HINDIsynopsis of potato experiment
synopsis of potato experiment Ravi Yadav
╠²
1. The student Ravi Yadav is conducting research on the effect of nitrogen and potassium on the growth and yield of potato.
2. The study will evaluate 12 treatments with varying levels of nitrogen (N0, N1, N2, N3) and potassium (K0, K1, K2) on the potato variety Kufri Badshah.
3. Key growth parameters like plant height, leaves per plant, and biomass will be recorded along with yield attributes and economic analysis to determine the optimal combination of nitrogen and potassium for maximizing potato growth and yield.Production Technology for Papaya
Production Technology for Papaya Ravi Yadav
╠²
Papaya is a significant tropical fruit known for its high nutritional value and adaptability, leading to a substantial increase in production, especially in India. It is cultivated primarily in states like Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, with a notable rise in commercial demand for both fresh fruit and papain. Various cultivated varieties exhibit distinct characteristics, and optimal production practices, including planting techniques, fertilization, and harvesting, are crucial for maximizing yield and fruit quality.Market Promotion strategy
Market Promotion strategyRavi Yadav
╠²
The document is an assignment on market promotion submitted by a student at the JNKVV College of Agriculture, detailing various elements of market promotion such as personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, and publicity. It highlights the merits and demerits of each marketing method and emphasizes the importance of educating customers and increasing brand recognition. Additionally, the assignment includes acknowledgments and a bibliography of sources utilized.new technique of guava production on different varieties in hindi
new technique of guava production on different varieties in hindiRavi Yadav
╠²
introduction, guava production in a different state, different varieties characteristics with pictures, production, management, to development for seed propagation, nursery development in the greenhouse, grafting method in the Hindi language Dormancy
DormancyRavi Yadav
╠²
The document discusses seed dormancy, defining it as a period where seeds cannot germinate despite favorable conditions, and details its classification into primary, secondary, and physiological dormancy. Factors causing dormancy include hard seed coats, temperature requirements, light sensitivity, and the presence of growth inhibitors. Various methods to overcome dormancy are also highlighted, such as mechanical scarification, stratification, and treatment with growth hormones.Dormancy ppt ravi
Dormancy ppt raviRavi Yadav
╠²
The document discusses dormancy in plants, seeds, trees, bacteria, and viruses. It defines dormancy as a temporary suspension of growth and metabolic activity that helps conserve energy and is often associated with environmental conditions. It provides examples of different types of dormancy like physical dormancy caused by an impermeable seed coat, physiological dormancy preventing embryo growth until chemical changes, and morphological dormancy where the embryo is underdeveloped. Hard seed coats, temperature requirements, immature embryos, and growth inhibitory chemicals are mentioned as some causes of dormancy.Ad
Vegetable seed rate
- 1. JNKVV COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE TIKAMGARH (M.P.) TOPIC = ALLVEGETABLE SEED RATE SUBMITTEDTO SUBMITTED BY DR.V.K.SINGH RAVIYADAV
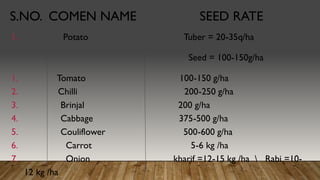
- 2. S.NO. COMEN NAME SEED RATE 1. Potato Tuber = 20-35q/ha Seed = 100-150g/ha 1. Tomato 100-150 g/ha 2. Chilli 200-250 g/ha 3. Brinjal 200 g/ha 4. Cabbage 375-500 g/ha 5. Couliflower 500-600 g/ha 6. Carrot 5-6 kg /ha 7. Onion kharif =12-15 kg /ha Rabi =10- 12 kg /ha
- 3. S.NO. COMEN NAME SEED RATE 9. Garlic 5 q /ha 10. Okra summere = 18-22 kg / ha Kharif = 8-10 kg /ha 11. Knol -knol 1-1.5 kg /ha 12. Sprputing brocoli 400- 500 g/ha 13. Raddish 9-12 kg/ ha 14. Turnip 3-4 kg /ha
- 4. S. NO. COMMEN NAME SEED RATE 15. Cucumber 2.5-3.5 kg /ha 16. Water melon 3.5-5 kg /ha 17. Musk melon 3-7 kg/ ha 18. Bottle gourd 3-4 kg/ha 19. Ridge gourd 3.5-5 kg/ha 20. Sponge gourd 2.5 -3.5 kg /ha 21. Pumpkin 1-5 kg/ha
- 5. S .NO. COMMEN NAME SEED RATE 22. Pea 100-120 kg /ha 23. Cowpea 25 kg/ha 24. Cluster bean 25-30 kg/ha 25. Lettuce 4-5 q / ha 26. Amaranthus 1.5 -2 kg/ha 27. Ash gourd 3.5 -4 kg /ha 28. Beet root 7.5 -8 kg /ha
- 6. S. NO. COMMEN NAME SEED RATE 28. Bitter gourd 4.5 -5 kg/ ha 29. Drumstick 500 g/ha 30. French bean 50-70 kg/ha 31. Spinach 37-45 kg/ha
- 7. Thank you
