Venture capital p pt
- 2. VENTURE CAPITAL Prepared by: Snehal Butani (13) Zankhana Thakurdesai (113)
- 3. Meaning & Definition of Venture Capital âĒ In Narrow sense, the capital which is available for financing the new business venture is called venture capital. âĒ â Venture Capital termed as long-term funds in equity or semi-equity form to finance hi- tech projects involving high risk and yet having strong potential of high profitability.â
- 4. Featured of Venture Capital âĒ New Venture âĒ Continuous Involvement âĒ Mode of Investment âĒ Objectives âĒ High risk-return approach âĒ Nature of firms âĒ liquidity
- 5. FUNDING STAGES IN VC INVESTING
- 6. Form of venture Capital Venture Capital Conventional loan Conditional Loan Income Notes
- 7. Initial public offer(IPOs) Trade sale Promoter buy back Acquisition by another company
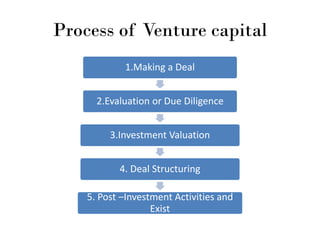
- 8. Process of Venture capital 1.Making a Deal 2.Evaluation or Due Diligence 3.Investment Valuation 4. Deal Structuring 5. Post âInvestment Activities and Exist
- 9. Advantages of Venture Capital âĒ It injects Long term equity finance which provides a solid capital base for future growth. âĒ It could encourage new breed of entrepreneurs to take-up risk. âĒ The venture capitalist is a business partner, sharing both the risks and rewards.
- 10. âĒ The Venture capitalist is able to provide practical advice and assistance to the company. âĒ The venture capitalist also has a network of contacts in many areas that can add value to the company, such as in recruiting key personnel, providing contacts in international markets, introductions to strategic partners.
- 11. âĒInsufficient understanding of venture capital as commercial activity. âĒSupport to the venture capital industry, by the govt. is inadequate âĒMarket limitations hinder the growth of venture capital industry. âĒThe inadequacy of the legal frame work of venture capital industry. Disadvantages of Venture Capital
- 12. The concept of VC was formally introduced in India in 1987 by IDBI. The government levied a 5 per cent success on all know-how import payments to create the venture fund. ICICI started VC activity in the same year Later on ICICI floated a separate VC company - TDICI
- 13. Rules & Regulations of Venture Capital in India As per SEBI Guidelines SEBI (Venture Capital Fund) Regulations, 1996. The following are the various provisions
- 14. âĒ A venture capital fund may be set up by a company or a trust, after a certificate of registration is granted by SEBI on an application made to it. On receipt of the certificate of registration, it shall be binding on the venture capital fund to abide by the provisions of the SEBI Act. âĒ A VCF may raise money from any investor, Indian, Non- resident Indian or foreign, provided the money accepted from any investor is not less than Rs 5 lakhs. The VCF shall not issue any document or advertisement inviting offers from the public for subscription of its security or units
- 15. âĒ SEBI regulations permit investment by venture capital funds in equity or equity related instruments of unlisted companies and also in financially weak and sick industries whose shares are listed or unlisted âĒ At least 80% of the funds should be invested in venture capital companies and no other limits are prescribed.
- 16. âĒ SEBI Regulations do not provide for any sectoral restrictions for investment except investment in companies engaged in financial services. âĒ A VCF is not permitted to invest in the equity shares of any company or institutions providing financial services. âĒ The securities or units issued by a venture capital fund shall not be listed on any recognized stock exchange till the expiry of 4 years from the date of issuance .
- 17. âĒ A Scheme of VCF set up as a trust shall be wound up (a) when the period of the scheme if any, is over (b) If the trustee are of the opinion that the winding up shall be in the interest of the investors (c) 75% of the investors in the scheme pass a resolution for winding up or, (d) If SEBI so directs in the interest of the investors
- 18. 1) Those promoted by the Central Government controlled development finance institutions. For example: - ICICI Venture Funds Ltd. - IFCI Venture Capital Funds Ltd (IVCF) - SIDBI Venture Capital Ltd (SVCL) 2) Those promoted by State Government controlled development finance institutions. For example: - Punjab Infotech Venture Fund - Gujarat Venture Finance Ltd (GVFL) - Kerala Venture Capital Fund Pvt Ltd. 3) Those promoted by public banks. For example: - Canbank Venture Capital Fund - SBI Capital Market Ltd
- 19. 4)Those promoted by private sector companies. For example: - IL&FS Trust Company Ltd - Infinity Venture India Fund 5)Those established as an overseas venture capital fund. For example: - Walden International Investment Group - HSBC Private Equity management Mauritius Ltd