Video enc basic_p_pt_type
- 1. Video encoding: basic principles Felipe Portavales Goldstein portavales@gmail.com ? ?
- 2. Video encoding: basic principles Color coding ? ?
- 3. Video encoding: basic principles Color coding Human eye color perception ? ?
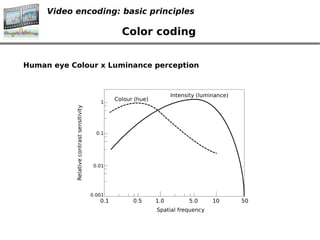
- 4. Video encoding: basic principles Color coding Human eye Colour x Luminance perception ? ?
- 5. Video encoding: basic principles Color coding Human eye Colour x Luminance perception R (8 bits) G (8 bits) B (8 bits) Each color is coded separately Y (8 bits) Cb (4 bits) Cr (4 bits) Y : Luminance Cb : Blue color Cr : Red color Green color is presense of luminance and absence of Blue and Red color ? ?
- 6. Video encoding: basic principles Digital signals / sampling ? ?
- 7. Video encoding: basic principles Digital signals / sampling ? ?
- 8. Video encoding: basic principles Digital signals / sampling Sampling Aliasing: Sample rate must be twice as input bandwidth ? ?
- 9. Video encoding: basic principles Digital signals / sampling Sampling images ? ?
- 10. Video encoding: basic principles Quantizing 7 possible quantized amplitude values: need 3 bits to represent ? ?
- 11. Video encoding: basic principles Multiplexing ? ?
- 12. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform ? ?
- 13. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform ? ?
- 14. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform The transform must consider the complete signal history to get the exact frequencies in the signal. To apply the transform we must known the signal behavior since -°fi to +°fi Is it possible ? And, what if the signal behaves like this : ? ?
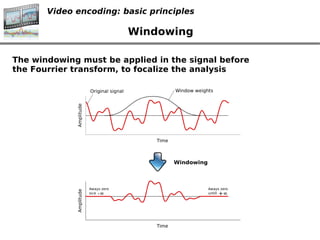
- 15. Video encoding: basic principles Windowing The windowing must be applied in the signal before the Fourrier transform, to focalize the analysis ? ?
- 16. Video encoding: basic principles Windowing The windowing can be used to divide the signal in small pieces, and transform them separately ? ?
- 17. Video encoding: basic principles Windowing Another way to view: ? ?
- 18. Video encoding: basic principles Windowing The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that: the knowledge of the position of a particle is inversely proportional to the knowledge of its energy It is the same to say: knowledge about time is inversely proportional to knowledge about frequency Position knowledge is relative to time Energy knowledge is related to frequency ? ?
- 19. Video encoding: basic principles Windowing ? ?
- 20. Video encoding: basic principles Pre-echo ? ?
- 21. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform in a image ? ?
- 22. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform in a image ? ?
- 23. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform in a image ? ?
- 24. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform in a image ? ?
- 25. Video encoding: basic principles Fourrier Transform in a image ? ? This picture is the cover of book: MPEG-2 , John Watkinson , Focal Press
- 26. Video encoding: basic principles Wavelet transform Wavlet dont use endless sine wave functions as its basis, but instead, use functions that are finite on time axis. The window lenght is variable and is inversely proportional to the frequency. High frequencies are transformed with short basis functions and therefore are accurately located. Low frequencies are transformed with long basis functions which have good frequency resolution. ? ?
- 27. Video encoding: basic principles Frame subdivision ? ?
- 28. Video encoding: basic principles Frame subdivision Subdivision of a Frame into blocks and super blocks Each color plane has its own set of blocks and super blocks ? ?
- 29. Video encoding: basic principles Intra Frame Intra-coding explores redundancy within a picture ? ?
- 30. Video encoding: basic principles Inter Frame Inter-coding explores redundancy between pictures ? ?
- 31. Video encoding: basic principles Inter Frame Golden Frame (intra) Inter Frames Inter Frames Coded frame ? ?
- 32. Video encoding: basic principles Inter Frame ? ?
- 33. Video encoding: basic principles References °Ò Theora I Specification; Xiph.org Foundation °Ò John Watkinson; MPEG-2 ; Focal Press °Ò Martin Ruckert; Understanding MP3: Syntax, Semantics, Mathematics, and Algorithms ; Viewg °Ò http://www.animemusicvideos.org/guides/avtech/video3.htm °Ò http://www.complextoreal.com/tutorial.htm °Ò http://cns-alumni.bu.edu/~slehar/fourier/fourier.html ? ?