Vim For Php
- 1. VIM for (PHP) Programmers Andrei Zmievski Outspark, Inc php|works Atlanta â September 14, 2007
- 2. help ~ learn how to get help effectively ~ :help is your friend ~ use CTRL-V before a CTRL sequence command ~ use i_ and v_ preïŽxes to get help for CTRL sequences in Insert and Visual modes ~ use CTRL-] (jump to tag) and CTRL-T (go back) in help window
- 3. intro ~ how well do you know vimâs language? ~ what is the alphabet? ~ look at your keyboard ~ can you name what every key does? ~ modes - what are they? ~ how many do you know? ~ how many do you use?
- 4. intro if you donât like the language, change it example: how do you quit vim quickly? ZZ (exit with saving) ZQ (exit without save) or :nmap ,w :x<CR> :nmap ,q :q!<CR> tip: set showcmd to see partial commands as you type them
- 5. where am i? How do you tell where you are? ~ simple - CTRL-G ~ detailed - gCTRL-G ~ do yourself a favor and set ruler ~ shows line, column, and percentage in status line ~ or conïŽgure it however you want with ârulerformatâ
- 6. moving ~ do you us h/j/k/l for moving? ~ or are you stuck in GUIarrowy world? ~ if you are, re-learn ~ save yourself countless miles of movement between home row and arrows
- 7. moving How do you move to: ~ start/end of buffer? gg and G ~ line n? nG or ngg ~ n% into the ïŽle? n% ~ the ïŽrst non-blank character in the line? ^ ~ ïŽrst non-blank character on next line? <CR> ~ ïŽrst non-blank character on previous line? -
- 8. marks ~ we can bookmark locations in the buffer ~ m<letter> sets mark named <letter> at current location ~ `<letter> jumps precisely to that mark ~ â<letter> jumps to the line with the mark ~ lowercase letter: mark is local to the buffer ~ uppercase letter: mark is global, your buffer will be switched to the ïŽle with the mark ~ :marks shows you your current marks
- 9. marks ~ marks are very handy for changing text ~ set a mark (letâs say ma) ~ then you can do: ~ c`a - change text from cursor to mark a ~ d`a - delete text from cursor to mark a ~ =âa - reformat lines from current one to the one with mark a
- 10. marks ~ letâs say you jump somewhere ~ how do you go back? ~ `` moves you between the last two locations ~ you can set ` (the context mark) explicitly: ~ m`, jump elsewhere, then come back with `` tip: CTRL-O and CTRL-I move between positions in the full jump history, but canât be used as motions â. and `. - jump to the line or exact location of the last modiïŽcation
- 11. insert ~ gi - incredibly handy ~ goes to Insert mode where you left it last time ~ scenario: edit something, exit Insert, go look at something else, then gi back to restart editing
- 12. insert Some more goodies: ~ CTRL-Y and CTRL-E (avoid work if you can) ~ inserts chars from above or below the cursor ~ CTRL-A (oops, i want to do that again) ~ inserts previously inserted text ~ CTRL-R=<expr> (built-in calculator) ~ inserts anything vim can calculate ~ CTRL-T and CTRL-D (tab and de-tab) ~ inserts or deletes one shiftwidth of indent at the start of the line
- 13. delete set your <Backspace> free :set backspace=start,indent,eol lets you backspace past the start of edit, auto- indenting, and even start of the line
- 14. search Search within the line: ~ f/F<char> jumps to the ïŽrst <char> to the right/left and places cursor on it ~ t/T<char> jumps does the same, but stops one character short of it ~ df; - delete text from cursor to the ïŽrst ; to the right ~ cT$ - change text from cursor up to the ïŽrst $ to the left
- 15. search ~ often you want to ïŽnd other instances of word under the cursor ~ */# - ïŽnd next/previous instance of whole word ~ g*/g# - ïŽnd next/previous instance of partial word ~ or ïŽnd lines with a certain word: ~ [I and ]I - list lines with word under the cursor ~ more convenient to use a mapping to jump to a line: :map ,f [I:let nr = input(quot;Which one: quot;)<Bar>exe quot;normal quot; . nr .quot;[tquot;<CR>
- 16. search ~ of course, thereâs always regexp search ~ /<pattern> - search forward for <pattern> ~ ?<pattern> - search backward for <pattern> ~ n repeats the last search ~ N repeats it in the opposite direction ~ vim regexp language is too sophisticated to be covered here
- 17. search Control your search options ~ :set wrapscan - to make search wrap around ~ :set incsearch - incremental search, <Enter> accepts, <Esc> cancels ~ :set ignorecase - case-insensitive search, or use this within the pattern: ~ c - force case-insensitive search ~ C - force case-sensitive search
- 18. search ~ remember that every search/jump can be used as a motion argument ~ d/^# - delete everything up to the next comment ~ y/^class/;?function - copy everything from current point to the ïŽrst function before the ïŽrst class
- 19. replace ~ :[range]s/<pattern>/<replace>/{flags} is the substitute command ~ used mainly with range addresses ~ range addresses are very powerful (read the manual) ~ but who wants to count out lines and do something like :-23,âts/foo/bar/ ~ in reality you almost always use a couple of shortcuts and Visual mode for the rest
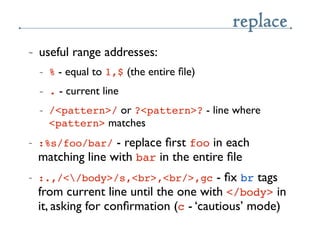
- 20. replace ~ useful range addresses: ~ % - equal to 1,$ (the entire ïŽle) ~ . - current line ~ /<pattern>/ or ?<pattern>? - line where <pattern> matches ~ :%s/foo/bar/ - replace ïŽrst foo in each matching line with bar in the entire ïŽle ~ :.,/</body>/s,<br>,<br/>,gc - ïŽx br tags from current line until the one with </body> in it, asking for conïŽrmation (c - âcautiousâ mode)
- 21. replace ~ & - repeat last substitution on current line ~ :&& - repeat it with the ïŽags that were used ~ g& - repeat substitution globally, with ïŽags
- 22. text objects ~ better know what they are ~ since they are fantastically handy ~ can be used after an operator or in Visual mode ~ come in âinnerâ and âambientâ ïŽavors ~ inner ones always select less text than ambient ones
- 23. text objects ~ aw, aW - ambient word or WORD (see docs) ~ iw, iW - inner word or WORD (see docs) ~ as, is - ambient or inner sentence ~ ap, ip - ambient or inner paragraph ~ a{, i{ - whole {..} block or text inside it ~ a(, i( - whole (..) block or just text inside it ~ a<, i< - whole <..> block or just text inside it
- 24. text objects ~ there are some cooler ones ~ aâ, iâ - single-quoted string or just the text inside ~ aâ, iâ - double-quoted string or just the text inside ~ note that these are smart about escaped quotes inside strings ~ at, it- whole tag block or just text inside (HTML and XML tags)
- 25. text objects examples: das - delete the sentence, including whitespace after ci( - change text inside (..) block yat - copy the entire closest tag block the cursor is inside gUiâ - uppercase text inside the single-quoted string vip - select the paragraph in Visual mode, without whitespace after
- 26. copy/delete/paste ~ you should already know these ~ y - yank (copy), d - delete, p - paste after, P - paste before ~ ]p, ]P - paste after/before but adjust the indent ~ Useful mappings to paste and reformat/reindent :nnoremap <Esc>P P'[v']= :nnoremap <Esc>p p'[v']=
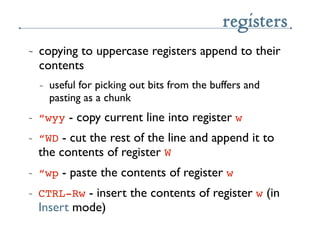
- 27. registers ~ registers: your multi-purpose clipboard ~ you use them without even knowing ~ every y or d command copies to a register ~ unnamed or named ~ â<char> before a copy/delete/paste speciïŽes register named <char>
- 28. registers ~ copying to uppercase registers append to their contents ~ useful for picking out bits from the buffers and pasting as a chunk ~ âwyy - copy current line into register w ~ âWD - cut the rest of the line and append it to the contents of register W ~ âwp - paste the contents of register w ~ CTRL-Rw - insert the contents of register w (in Insert mode)
- 29. registers ~ you can record macros into registers ~ q<char> - start recording typed text into register <char> ~ next q stops recording ~ @<char> executes macro <char> ~ @@ repeats last executed macro ~ use :reg to see whatâs in your registers
- 30. undo ~ original vi had only one level of undo ~ yikes! ~ vim has unlimited (limited only by memory) ~ set âundolevelsâ to what you need (1000 default)
- 31. undo ~ simple case: u - undo, CTRL-R - redo ~ vim 7 introduces branched undo ~ if you undo something, and make a change, a new branch is created ~ g-, g+ - go to older/newer text state (through branches)
- 32. undo ~ you can travel through time ~ :earlier Ns,m,h - go to text state as it was N seconds, minutes, hours ago ~ :later Ns,m,h - go to a later text state similarly ~ :earlier 10m - go back 10 minutes, before I drank a can of Red Bull and made all these crazy changes. Whew.
- 33. visual mode ~ use it, it's much easier than remembering obscure range or motion commands ~ start selection with: ~ v - characterwise, ~ V - linewise ~ CTRL-V - blockwise ~ use any motion command to change selection ~ can execute any normal or : command on the selection
- 34. visual mode ~ Visual block mode is awesome ~ especially for table-like text tip: o switches cursor to the other corner, continue selection from there ~ Once you are in block mode: ~ I<text><Esc> - insert <text> before block on every line ~ A<text><Esc> - append <text> after block on every line ~ c<text><Esc> - change every line in block to <text> ~ r<char><Esc> - replace every character with <char>
- 35. abbreviations ~ Real-time string replacement ~ Expanded when a non-keyword character is typed ~ :ab tempalte template - ïŽx misspellings ~ more complicated expansion: ~ :iab techo <?php echo ?><Left><Left><Left>
- 36. windows ~ learn how to manipulate windows ~ learn how to move between them ~ :new, :sp should be at your ïŽngertips ~ CTRL-W commands - learn essential ones for resizing and moving between windows
- 37. tab pages ~ vim 7 supports tab pages ~ :tabe <file> to edit ïŽle in a new tab ~ :tabc to close ~ :tabn, :tabp (or gt, gT to switch) ~ probably want to map these for easier navigation (if gt, gT are too difïŽcult)
- 38. completion ~ vim is very completion friendly ~ just use <Tab> on command line ~ for ïŽlenames, set âwildmenuâ and âwildmodeâ (I like quot;list:longest,fullquot;) ~ :new ~/dev/fo<Tab> - complete ïŽlename ~ :help âcomp<Tab> - complete option name ~ :re<Tab> - complete command ~ hit <Tab> again to cycle, CTRL-N for next match, CTRL-P for previous
- 39. completion ~ CTRL-X starts completion mode in Insert mode ~ follow with CTRL- combos (:help ins- completion) ~ i mostly use ïŽlename, identiïŽer, and omni completion ~ when there are multiple matches, a nice completion windows pops up
- 40. completion ~ CTRL-X CTRL-F to complete ïŽlenames ~ CTRL-X CTRL-N to complete identiïŽers ~ hey, thatâs so useful Iâll remap <Tab> â Insert <Tab> or complete identifier â if the cursor is after a keyword character function MyTabOrComplete() let col = col('.')-1 if !col || getline('.')[col-1] !~ 'k' return quot;<tab>quot; else return quot;<C-N>quot; endif endfunction inoremap <Tab> <C-R>=MyTabOrComplete()<CR>
- 41. completion ~ omni completion is heuristics-based ~ guesses what you want to complete ~ speciïŽc to the ïŽle type youâre editing ~ more on it later
- 42. maps ~ maps for every mode and then some ~ tired of changing text inside quotes? :nmap X ciquot; ~ make vim more browser-like? :nmap <Space> <PageDown> ~ insert your email quickly? :imap ;EM me@mydomain.com ~ make <Backspace> act as <Delete> in Visual mode? :vmap <BS> x
- 43. options ~ vim has hundreds of options ~ learn to control the ones you need ~ :options lets you change options interactively ~ :options | resize is better (since there are so many)
- 44. sessions ~ a session keeps the views for all windows, plus the global settings ~ you can save a session and when you restore it later, the window layout looks the same. ~ :mksession <file> to write out session to a ïŽle ~ :source <file> to load session from a ïŽle ~ vim -S <file> to start editing a session
- 45. miscellaneous ~ gf - go to ïŽle under cursor (CTRL-W CTRL-F for new window) ~ :read in contents of ïŽle or process ~ :read foo.txt - read in foo.txt ~ :read !wc %:h - run wc on current ïŽle and insert result into the text ~ ïŽlter text: :%!sort, :%!grep, or use :! in visual mode ~ i like sorting lists like this: vip:!sort
- 46. miscellaneous ~ use command-line history ~ : and / followed by up/down arrows move through history ~ : and / followed by preïŽx and arrows restrict history to that preïŽx ~ q: and q/ for editable history (<Enter> executes, CTRL-C copies to command line)
- 47. miscellaneous ~ CTRL-A and CTRL-X to increment/decrement numbers under the cursor (hex and octal too) ~ ga - what is this character under my cursor? ~ :set number to turn line numbers on ~ or use this to toggle line numbers: :nmap <silent> <F6> set number!<CR> ~ :set autowrite - stop vim asking if you want to write the ïŽle before leaving buffer ~ CTRL-E/CTRL-Y - scroll window down/up without moving cursor
- 48. miscellaneous ~ :set scroloff=N to start scrolling when cursor is N lines from the top/bottom edge ~ :set updatecount=50 to write swap ïŽle to disk after 50 keystrokes ~ :set showmatch matchtime=3 - when bracket is inserted, brieïŽy jump to the matching one ~ in shell: fc invokes vim on last command, and runs it after vim exits (or fc N to edit command N in history) ~ vimdiff in shell (:help vimdiff)
- 49. customization ~ customize vim by placing ïŽles in you ~/.vim dir ~ filetype plugin on, filetype indent on .vimrc - global settings .vim/ after/ - files that are loaded at the very end ftplugin/ plugin/ syntax/ ... autoload/ - automatically loaded scripts colors/ - custom color schemes doc/ - plugin documentation ftdetect/ - filetype detection scripts ftplugin/ - filetype plugins indent/ - indent scripts plugin/ - plugins syntax/ - syntax scripts
- 50. php: linting ~ vim supports arbitrary build/lint commands ~ if we set 'makeprg' and 'errorformat' appropriately.. :set makeprg=php -l % :set errorformat=%m in %f on line %l ~ now we just type :make (and <Enter> a couple of times) ~ cursor jumps to line with syntax error
- 51. php: match pairs ~ you should be familiar with % command (moves cursor to matching item) ~ used with (), {}, [], etc ~ but can also be used to jump between PHP and HTML tags ~ use matchit.vim plugin ~ but syntax/php.vim has bugs and typos in the matching rule ~ i provide my own
- 52. php: block objects ~ similar to vim's built-in objects ~ aP - PHP block including tags ~ iP - text inside PHP block examples: ~ vaP - select current PHP block (with tags) ~ ciP - change text inside current PHP block ~ yaP - copy entire PHP block (with tags) ~ provided in my .vim/ftplugin/php.vim ïŽle
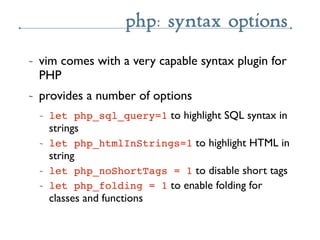
- 53. php: syntax options ~ vim comes with a very capable syntax plugin for PHP ~ provides a number of options ~ let php_sql_query=1 to highlight SQL syntax in strings ~ let php_htmlInStrings=1 to highlight HTML in string ~ let php_noShortTags = 1 to disable short tags ~ let php_folding = 1 to enable folding for classes and functions
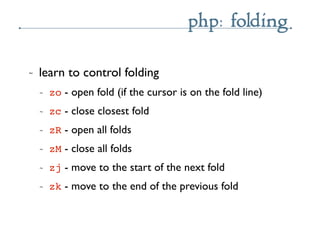
- 54. php: folding ~ learn to control folding ~ zo - open fold (if the cursor is on the fold line) ~ zc - close closest fold ~ zR - open all folds ~ zM - close all folds ~ zj - move to the start of the next fold ~ zk - move to the end of the previous fold
- 55. php: tags ~ for vim purposes, tags are PHP identiïŽers (classes, functions, constants) ~ you can quickly jump to the deïŽnition of each tag, if you have a tags ïŽle ~ install Exuberant Ctags ~ it can scan your scripts and output tags ïŽle, containing identiïŽer info ~ currently does not support class membership info (outputs methods as functions) ~ have to apply a third-party patch to ïŽx
- 56. php: tags ~ use mapping to re-build tags ïŽle after editing nmap <silent> <F4> :!ctags-ex -f ./tags --langmap=quot;php:+.incquot; -h quot;.php.incquot; -R --totals=yes --tag-relative=yes --PHP-kinds=+cf-v .<CR> set tags=./tags,tags ~ all PHP ïŽles in current directory and under it recursively will be scanned
- 57. php: tags ~ CTRL-] - jump to tag under cursor ~ CTRL-W CTRL-] - jump to tag in a new window ~ :tag <ident> - jump to an arbitrary tag ~ :tag /<regexp> - jump to or list tags matching <regexp> ~ if multiple matches - select one from a list ~ :tselect <ident> or /<regexp> - list tags instead of jumping ~ CTRL-T - return to where you were ~ See also taglist.vim plugin
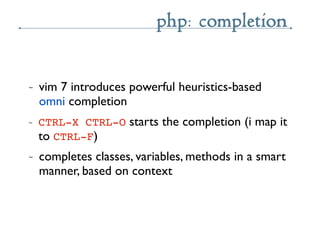
- 58. php: completion ~ vim 7 introduces powerful heuristics-based omni completion ~ CTRL-X CTRL-O starts the completion (i map it to CTRL-F) ~ completes classes, variables, methods in a smart manner, based on context
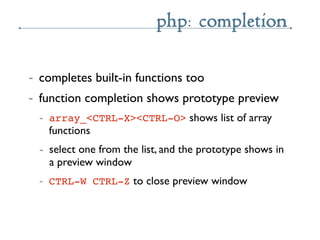
- 59. php: completion ~ completes built-in functions too ~ function completion shows prototype preview ~ array_<CTRL-X><CTRL-O> shows list of array functions ~ select one from the list, and the prototype shows in a preview window ~ CTRL-W CTRL-Z to close preview window
- 60. php: completion ~ switches to HTML/CSS/Javascript completion outside PHP blocks ~ see more: ~ :help ins-completion ~ :help popupmenu-completion ~ :help popupmenu-keys
- 61. plugins ~ vim can be inïŽnitely customized and expanded via plugins ~ there are thousands already written ~ installation is very easy, usually just drop them into .vim/plugin ~ read instructions ïŽrst though
- 62. netrw ~ makes it possible to read, write, and browse remote directories and ïŽles ~ i usually use it over ssh connections via scp ~ need to run ssh-agent to avoid continuous prompts for passphrase ~ don't use passphrase-less keys! ~ once set up: ~ vim scp://hostname/path/to/file ~ :new scp://hostname/path/to/dir/
- 63. NERDTree ~ similar to netrw browser but looks more like a hierarchical explorer ~ does not support remote ïŽle operations ~ :nmap <silent> <F7> :NERDTreeToggle<CR>
- 64. taglist ~ provides an overview of the source code ~ provides quick access to classes, functions, constants ~ automatically updates window when switching buffers ~ can display prototype and scope of a tag ~ requires Exuberant Ctags
- 65. taglist ~ stick this in ~/.vim/after/plugin/general.vim let Tlist_Ctags_Cmd = quot;/usr/local/bin/ctags-exquot; let Tlist_Inc_Winwidth = 1 let Tlist_Exit_OnlyWindow = 1 let Tlist_File_Fold_Auto_Close = 1 let Tlist_Process_File_Always = 1 let Tlist_Enable_Fold_Column = 0 let tlist_php_settings = 'php;c:class;d:constant;f:function' if exists('loaded_taglist') nmap <silent> <F8> :TlistToggle<CR> endif
- 66. snippetsEmu ~ emulates some of the functionality of TextMate snippets ~ supports many languages, including PHP/HTML/ CSS/Javascript ~ by default binds to <Tab> but that's annoying ~ need to remap the key after it's loaded ~ put this in ~/.vim/after/plugin/general.vim if exists('loaded_snippet') imap <C-B> <Plug>Jumper endif inoremap <Tab> <C-R>=MyTabOrComplete()<CR>
- 67. php documentor ~ inserts PHP Documentor blocks automatically ~ works in single or multi-line mode ~ doesnât provide mappings by default ~ read documentation to set up default variables for copyright, package, etc ~ put this in ~/.vim/ftplugin/php.vim inoremap <buffer> <C-P> <Esc>:call PhpDocSingle()<CR>i nnoremap <buffer> <C-P> :call PhpDocSingle()<CR> vnoremap <buffer> <C-P> :call PhpDocRange()<CR> let g:pdv_cfg_Uses = 1
- 68. xdebug-ger ~ allows debugging with xdebug through DBGp protocol ~ fairly basic, but does the job ~ vim needs to be compiled with +python feature ~ see resources section for documentation links
- 69. vcscommand ~ provides interface to CVS/SVN ~ install it, then :help vcscommand
- 70. conclusion ~ vim rules ~ this has been only a partial glimpse ~ from my very subjective point of view ~ donât be stuck in an editor rut ~ keep reading and trying things out
- 71. resources ~ vim tips: http://www.vim.org/tips/ ~ vim scripts: http://www.vim.org/scripts/index.php ~ Exuberant Ctags: http://ctags.sourceforge.net ~ PHP patch for ctags: http://www.live-emotion.com/memo/index.php? plugin=attach&refer=%CA%AA%C3%D6&openïŽle=ctags-5.6j-php.zip ~ article on xdebug and vim: http://2bits.com/articles/using-vim-and- xdebug-dbgp-for-debugging-drupal-or-any-php-application.html ~ more cool plugins: ~ Surround: http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1697 ~ ShowMarks: http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=152 ~ Vim Outliner: http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=517 ~ Tetris: http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=172
- 72. quot;As with everything, best not to look too deeply into this.quot;


![help
~ learn how to get help effectively
~ :help is your friend
~ use CTRL-V before a CTRL sequence command
~ use i_ and v_ preïŽxes to get help for CTRL
sequences in Insert and Visual modes
~ use CTRL-] (jump to tag) and CTRL-T (go back)
in help window](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-2-320.jpg)












![search
~ often you want to ïŽnd other instances of word
under the cursor
~ */# - ïŽnd next/previous instance of whole word
~ g*/g# - ïŽnd next/previous instance of partial word
~ or ïŽnd lines with a certain word:
~ [I and ]I - list lines with word under the cursor
~ more convenient to use a mapping to jump to a line:
:map ,f [I:let nr = input(quot;Which one: quot;)<Bar>exe
quot;normal quot; . nr .quot;[tquot;<CR>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-15-320.jpg)



![replace
~ :[range]s/<pattern>/<replace>/{flags}
is the substitute command
~ used mainly with range addresses
~ range addresses are very powerful (read the
manual)
~ but who wants to count out lines and do
something like :-23,âts/foo/bar/
~ in reality you almost always use a couple of
shortcuts and Visual mode for the rest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-19-320.jpg)





![copy/delete/paste
~ you should already know these
~ y - yank (copy), d - delete, p - paste after, P -
paste before
~ ]p, ]P - paste after/before but adjust the
indent
~ Useful mappings to paste and reformat/reindent
:nnoremap <Esc>P P'[v']=
:nnoremap <Esc>p p'[v']=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-26-320.jpg)










![completion
~ CTRL-X CTRL-F to complete ïŽlenames
~ CTRL-X CTRL-N to complete identiïŽers
~ hey, thatâs so useful Iâll remap <Tab>
â Insert <Tab> or complete identifier
â if the cursor is after a keyword character
function MyTabOrComplete()
let col = col('.')-1
if !col || getline('.')[col-1] !~ 'k'
return quot;<tab>quot;
else
return quot;<C-N>quot;
endif
endfunction
inoremap <Tab> <C-R>=MyTabOrComplete()<CR>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-40-320.jpg)









![php: match pairs
~ you should be familiar with % command (moves
cursor to matching item)
~ used with (), {}, [], etc
~ but can also be used to jump between PHP and
HTML tags
~ use matchit.vim plugin
~ but syntax/php.vim has bugs and typos in the
matching rule
~ i provide my own](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-51-320.jpg)


![php: tags
~ CTRL-] - jump to tag under cursor
~ CTRL-W CTRL-] - jump to tag in a new window
~ :tag <ident> - jump to an arbitrary tag
~ :tag /<regexp> - jump to or list tags matching
<regexp>
~ if multiple matches - select one from a list
~ :tselect <ident> or /<regexp> - list tags instead
of jumping
~ CTRL-T - return to where you were
~ See also taglist.vim plugin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vimforphp-1222245164531885-9/85/Vim-For-Php-57-320.jpg)