Virtual LAN
- 2. Index âĒ LAN âĒ VLAN âĒ Implementation of VLAN âĒ Types Of VLAN âĒ Benefits of VLAN âĒ Bibliography
- 3. âĒ A Local Area Network (LAN) was originally defined as a network of computers located within the same area. âĒ Local Area Networks are defined as a single broadcast domain. This means that if a user broadcasts information on his/her LAN, the broadcast will be received by every other user on the LAN. âĒ Broadcasts are prevented from leaving a LAN by using a router. The disadvantage of this method is routers usually take more time to process incoming data compared to a bridge or a switch LAN
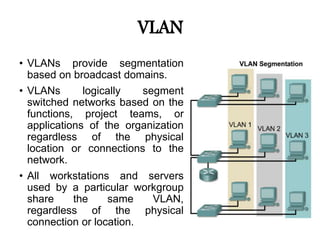
- 4. VLAN âĒ VLANs provide segmentation based on broadcast domains. âĒ VLANs logically segment switched networks based on the functions, project teams, or applications of the organization regardless of the physical location or connections to the network. âĒ All workstations and servers used by a particular workgroup share the same VLAN, regardless of the physical connection or location.
- 5. Implementation of VLAN Statically âĒ Network Administrator configure port-by-port. âĒ Each port is associate with a specific VLAN. âĒ The network administrator is responsible keying in the mappings between the port and VLANs. Dynamically âĒ The port are able to dynamically work out their VLAN configuration. âĒ Uses a software database of MAC address to VLAN mappings (Which the network administrator must set up first).
- 6. 1 2 3 4 5 6 . 1 2 1 2 2 1 . Port VLAN âĒ Static membership VLANs are called port-based and port-centric membership VLANs. âĒ As a device enters the network, it automatically assumes the VLAN membership of the port to which it is attached.
- 7. âĒ Dynamic membership VLANs are created through network management software. (Not as common as static VLANs) âĒ CiscoWorks 2000 or CiscoWorks for Switched Internetworks is used to create Dynamic VLANs. âĒ Dynamic VLANs allow for membership based on the MAC address of the device connected to the switch port. âĒ As a device enters the network, it queries a database within the switch for a VLAN membership.
- 8. Types Of VLAN Port Base: âĒ Most common configuration method. âĒ Port assign individually, in group, in rows, or across 2 or more switches. âĒ Simple to use. MAC Address: âĒ Rarely implemented today. âĒ Each address must be entered into the switch and configured individually. âĒ User find it useful. Protocol Base: âĒ Configured like MAC address, but instead uses a logical or IP address. âĒ No longer common because of DHCP.
- 9. Benefits of VLANs âĒ The key benefit of VLANs is that they permit the network administrator to organize the LAN logically instead of physically. âĒ This means that an administrator is able to do all of the following: ïž Easily move workstations on the LAN. ïž Easily add workstations to the LAN. ïž Easily change the LAN configuration. ïž Easily control network traffic. ïž Improve security.