VIRTUALIZATION.pptx
- 2. TABLE OF CONTENTS Definition of Virtualization Types of Virtualization Comparison Benefits for Virtualization Use Cases for Virtualization Challenges in Virtualization
- 3. DEFINITION OF VIRTUALIZATION â—Ź Virtualization is the technology that allows you to create and manage virtual instances of computer hardware, software, storage, or networks within a single physical infrastructure.
- 4. TYPES OF VIRTUALIZATION BARE-METAL VIRTUALIZATION Also known as Type 1 or hypervisor-based virtualization, runs directly on the hardware. Key Features: • No underlying operating system. • Hypervisor controls hardware resources. • High performance and resource efficiency.
- 5. BARE-METAL VIRTUALIZATION To built a Type I Hypervisor: • Data Cabinet • Install Motherboard, CPU, RAM and Storage Devices. Installing a Type I Hypervisor: Example. • Vmware ESXI/PROXMOX VE.
- 6. BARE-METAL VIRTUALIZATION Create 3 Virtual Machine • Allocating the server’s hardware resources. • Install Operating System. • Installing Applications.
- 7. TYPES OF VIRTUALIZATION HOSTED OPERATING SYSTEM VIRTUALIZATION Hosted virtualization, also known as Type 2 or OS-level virtualization, relies on an underlying operating system. Key Features: • Requires a host operating system. • Multiple virtual environments run on top of the host. • Simplicity and ease of setup.
- 8. HOSTED VIRTUALIZATION A Type II Hypervisor runs on top of an Existing Operating System. Typically used on personal computers. • To test new software • Try out different operating system Type II hypervisor • Oracle VM VirtualBox • Vmware Workstation • Microsoft Virtual PC
- 9. HOSTED VIRTUALIZATION AVR Ups Host Server MCT MWS 9943 MCT MWS 9943 MCT MWS 9943 MCT MWS 9943 MCT MWS 9943 MCT MWS 9943
- 10. COMPARISON - PERFORMANCE BARE-METAL HOSTED • Higher performance due to direct hardware access. • Ideal for resource-intensive workloads. • Slightly reduced performance due to the additional OS layer. • Suitable for lightweight workloads and development environments.
- 11. COMPARISON – RESOURCE ISOLATION BARE-METAL HOSTED ■Strong isolation between virtual machines. ■Each VM has dedicated resources. ■Limited isolation; VMs share the host OS resources. ■Less secure for multi-tenant or critical environments.
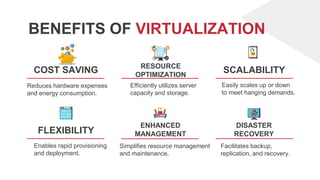
- 12. FLEXIBILITY COST SAVING ENHANCED MANAGEMENT SCALABILITY Enables rapid provisioning and deployment. Simplifies resource management and maintenance. Reduces hardware expenses and energy consumption. Efficiently utilizes server capacity and storage. Easily scales up or down to meet hanging demands. Facilitates backup, replication, and recovery. RESOURCE OPTIMIZATION DISASTER RECOVERY BENEFITS OF VIRTUALIZATION
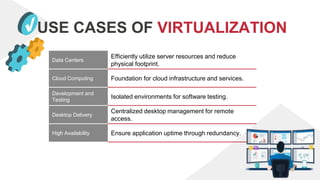
- 13. USE CASES OF VIRTUALIZATION Data Centers Efficiently utilize server resources and reduce physical footprint. Cloud Computing Foundation for cloud infrastructure and services. Development and Testing Isolated environments for software testing. Desktop Delivery Centralized desktop management for remote access. High Availability Ensure application uptime through redundancy.
- 14. CHALLENGES IN VIRTUALIZATION 1. Security: Protecting virtualized environments from threats. 2. Performance: Ensuring adequate performance for virtual workloads. 3. Management Complexity: Properly configuring and monitoring virtual resources.
- 15. CREDITS: This presentation template was created by şÝşÝߣsgo, and includes icons by Flaticon and infographics & images by Freepik THANKS
Editor's Notes
- #6: Type I Hypervisor: Vmware ESXI/vSphere, Citric XenServer, Microsoft Hyper-V and OORACLE VM
- #7: Hardware Resources: CPU, RAM and Storage OS: Windows, Linux and Unix Application: Email, Webserver and Database
- #9: Example VM App: ORACLE VM(VirtualBox) and Vmware Workstation
- #10: Example VM App: ORACLE VM(VirtualBox) and Vmware Workstation