Visual Literacy: Part 1
- 1. Visual Literacy and Nonlinguistic Representations: Part 1 March 10, 2011 Jessica Fries-Gaither Terry Shiverdecker Beyond Penguins is funded by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0733024.
- 2. A – Classroom Teacher B – Librarian C – Administrator D – Higher Education E - Other What best describes your professional position? Answer using the poll buttons underneath the participant window!
- 3. What grade(s) do you teach? A – Grades K-2 B – Grades 3-5 C – Grades 6-8 D – Grades 9-12 E - Other Answer using the poll buttons underneath the participant window!
- 4. From where are you joining us today? Answer using the stamping tool to the left of the whiteboard!
- 5. Visual Literacy and Nonlinguistic Representations Download these slides at: http://slidesha.re/ visuallit1
- 6. Today ’s presenters Jessica Fries-Gaither Education Resource Specialist The Ohio State University College of Education and Human Ecology School of Teaching and Learning [email_address] Terry Shiverdecker Science Content Specialist Ohio Resource Center Ohio State University College of Education and Human Ecology School of Teaching and Learning [email_address]
- 7. About Beyond Penguins and Polar Bears Online magazine Professional and instructional resources Science and literacy integration Aligned to national standards Multimedia http://beyondpenguins.nsdl.org
- 8. Today’s Agenda Review terminology Types of infographics Why focus on infographics? Strategies for interpreting infographics Children’s literature and online sources of infographics
- 9. What does this mean to you? CNN Health
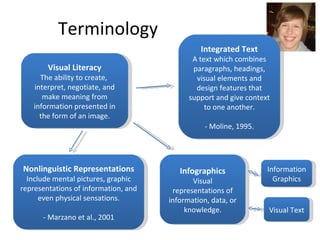
- 10. Terminology Visual Literacy The ability to create, interpret, negotiate, and make meaning from information presented in the form of an image. Nonlinguistic Representations Include mental pictures, graphic representations of information, and even physical sensations. - Marzano et al., 2001 Infographics Visual representations of information, data, or knowledge. Integrated Text A text which combines paragraphs, headings, visual elements and design features that support and give context to one another. - Moline, 1995. Information Graphics Visual Text
- 11. Types of infographics Diagrams Timelines Flowcharts Webs Maps Word Clouds Graphs Tables
- 12. Diagrams University of Arizona Earth Cutaway Amazing Super Powers Scale Teach Engineering Cross-section Labeled Cutaway
- 13. Timelines TN History for Kids Word Clouds Google Images Search Maps Garmin Custom Maps Northern Michigan University Campus Map Ohio Department of Natural Resources
- 14. Tables Houghton Mifflin Math Background Flowcharts and Webs Science in English Research Tools>Concept Web Graphs Google Image Search
- 15. Let ’s pause for questions from the audience….
- 16. Why focus on infographics? “ Students of all ages encounter these visual texts as frequently as adults do and are expected to understand them, both in school work and in everyday living. To reflect the range of literacies, a classroom program needs to include explicit instruction in how these texts work.” - Steve Moline, I See What You Mean
- 17. Why focus on infographics? Information is accessible to all readers. Very young children English Language Learners Struggling readers Visual learners
- 18. Why focus on infographics? We are consumers of larger numbers of infographics and integrated texts due to online media. Daily Infographic
- 19. Teaching Strategies “ Because a diagram can provide many layers of information and because a statistical graph can often be misinterpreted, it is necessary to provide explicit instruction in what these texts do and don’t mean and how these texts make their meaning.” - Steve Moline, I See What You Mean
- 20. Teaching Strategies Explicitly discuss the purpose of different types of infographics.
- 21. Teaching Strategies Focus on one type at a time. Ask questions that help students focus on the components of the infographic and their purposes.
- 22. Teaching Strategies As a class, examine an infographic and list all the information that it conveys. This might take several pages! Check for understanding by challenging students to translate an infographic into text.
- 23. Teaching Strategies Give students strategies to attack infographics. Provide guided practice in applying the strategies.
- 24. Ěý
- 25. Teaching Strategies Have students collect examples from newspapers, books, and online media. What features do they have in common? Evaluate and critique – which convey their information the best and why? Have students revise an infographic to make it more effective.
- 26. Let ’s pause for questions from the audience….
- 28. Online Sources of Infographics Released test items Google Images USGS (maps) wunderground.com NOAA Illuminations Smithsonian Science Net Links
- 29. For More Information I See What You Mean: Children at Work with Visual Information . Steve Moline. Stenhouse Publishers, 1995. Classroom Instruction that Works: Research-Based Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement . Robert Marzano, Debra Pickering, and Jane Pollock. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, 2001. Visual Literacy K-8 k-8visual.info Teaching with Infographics: Places to Start http://learning.blogs.nytimes.com/2010/08/23/teaching-with-infographics-places-to-start/
- 30. Coming Soon! Thursday, April 14, 2011: Visual Literacy and Nonlinguistic Representations: Part 2 ** 3 p.m. – 4 p.m.** Join us as we explore how to help students become proficient at creating maps, charts, diagrams, and other infographics. Presenters: Jessica Fries-Gaither and Terry Shiverdecker http://wiki.nsdl.org/index.php/BeyondPenguins/Seminars
- 31. Thank you! Jessica Fries-Gaither: [email_address] Terry Shiverdecker: [email_address] Today ’s slides available at: http://slidesha.re /visuallit1 Archived recording at: http://wiki.nsdl.org/index.php/BeyondPenguins/Seminars






![Today ’s presenters Jessica Fries-Gaither Education Resource Specialist The Ohio State University College of Education and Human Ecology School of Teaching and Learning [email_address] Terry Shiverdecker Science Content Specialist Ohio Resource Center Ohio State University College of Education and Human Ecology School of Teaching and Learning [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/visualliteracyp1-110310094714-phpapp02/85/Visual-Literacy-Part-1-6-320.jpg)























![Thank you! Jessica Fries-Gaither: [email_address] Terry Shiverdecker: [email_address] Today ’s slides available at: http://slidesha.re /visuallit1 Archived recording at: http://wiki.nsdl.org/index.php/BeyondPenguins/Seminars](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/visualliteracyp1-110310094714-phpapp02/85/Visual-Literacy-Part-1-31-320.jpg)