Vitamin a deficiency
- 1. VITAMIN A DEFFICIENCY Prepared by George deogratias MD5 student. Archbishop James university college the constitute of st.augustine university of Tanzania. (biziriko1991@gmail.com) +255656592079 03/25/181
- 2. ContŌĆ” ’éø Vitamin A is a broad term for a number of similar compounds , First recognized fat soluble vitamin ’éø Two forms : a) Preformed vitamin A: retinoids ( from animals) b) Provitamin A: carotenoids (predominantly beta carotene from plants) 03/25/18 Dr george 2
- 3. CONTŌĆ” Preformed vitamin A: Retinoids ’éø Active or usable form ’üČ Four categories of retinoids: ’éøa) retinol (b) retinal ’ü▒c) retinoic acid (d) retinyl esters ’éøAll retinoids are absorbed as retinol. ’éøSources: animal products like liver, fish , fish oils , ’éømilk , eggs etc. ’éø Liver is richest source 03/25/18 Dr george 3
- 4. ContŌĆ” ’éø ProvitaminA: Carotenoids ’éø Precursor of vitamin A ’éø Predominantly beta carotene ’éø Body has to convert it into active vitamin A after ’éø consumption ’éø Sources: plant products like carrot , green leafy ’éø vegetables , papaya , mango , bringal. 03/25/18 george 4
- 5. Functions of Vitamin A (Retinol) ’éø Vitamin A is essential to the normal structure and function of the skin and mucous membranes ’éø It is also required for cell differentiation and therefore for normal growth and development ’éø For normal vision ’éø For the immune system. 03/25/185
- 6. ContŌĆ” ’éø Important in wound healing, bone formation (e.g., teeth), healthy skin and growth and lactation.┬Ā ’éø Further, it may also be a factor in preventing cancers.┬Ā ’éø It has been shown to have antiviral properties. 03/25/186
- 7. Metabolism ’éø Normally, the liver stores 80 to 90% of the body's vitamin A. ’éø To use vitamin A, the body releases it into the circulation bound to prealbumin (retinol-binding protein) ’éø ╬▓-Carotene and other provitamin carotenoids, contained in green leafy and yellow vegetables and deep- or bright-colored fruits, are converted to vitamin A. 03/25/187
- 8. VITAMIN A DEFICIENCY- ’éøCAUSES; ’éø Inadequate intake- ’éø Fat malabsorption- sprue, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic insufficiency, duodenal bypass, chronic diarrhea, bile duct obstruction, giardiasis ’éø liver disorders -cirrhosis 03/25/188
- 9. XEROPHTHALMIA ’éø General term applied to all the ocular manifestations of impaired vitamin A metabolism, from night blindness through complete corneal destruction ’éø Xeros ŌĆō dry ’éø ophthalmia ŌĆō eye ’éø literally means ŌĆ£ dry eye ŌĆ£ ’éø conventionally xerophthalmia has become synonymous ’éø with vitamin A deficiency 03/25/18 Dr george 9
- 10. WHO Classification of xerophthalmia ’éø XN (Night blindness) ’éø X1A ( Conjunctival xerosis) ’éø X1B ( BitotŌĆÖs spots) ’éø X2 ( Corneal xerosis) ’éø X3A ( Corneal ulceration/Keratomalacia affecting less than one third corneal surface) ’éø X3B ( Corneal ulceration/Keratomalacia affecting more than one third corneal surface) ’éø XS ( Corneal scars) ’éø XF ( Xerophthalmic fundus) ’éø Biochemical criterion: Plasma vitamin A < 0.35 ╬╝mol/L 03/25/1810
- 11. ContŌĆ” ’éø Is a major cause of preventable blindness in children and especially in developing countries ’éø It is an inflammation of the cornea that is associated with nutritional deficiency ’éø Risk factors- ’éø general malnutrition, diarrhea, measles, HIV/AIDS, failure to thrive, lack of food diversity ’éø Although xerophthalmia is most prevalent with children, it can also occur in adults with severe malnutrition or in other health problems in which lack of vitamin A in their diets is a factor. 03/25/1811
- 12. ContŌĆ” ’éø Night blindness, is an early symptom ’éø Superficial foamy patches composed of epithelial debris and secretions on the exposed bulbar conjunctiva (Bitot's spots ’éø It involves drying (xerosis) and thickening of the conjunctivae and corneas. ’éø cornea erosions- keratomalacia 03/25/1812
- 13. Other systems ’éø There is keratinization of Skin, drying, scaling, and follicular thickening of the skin ’éø Mucous membranes disorders in the respiratory, GI, and urinary tracts can occur- infections ’éø Immunity is generally impaired 03/25/1813
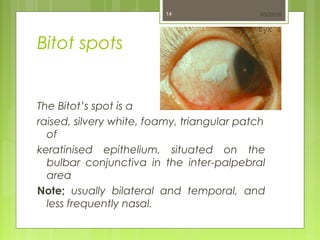
- 14. Bitot spots The BitotŌĆÖs spot is a raised, silvery white, foamy, triangular patch of keratinised epithelium, situated on the bulbar conjunctiva in the inter-palpebral area Note; usually bilateral and temporal, and less frequently nasal. 03/25/1814
- 15. Corneal Xerosis ’éø The earliest change in the cornea is punctate keratopathy . ’éø which begins in the lower nasal quadrant, followed by haziness and/or granular pebbly dryness ’éø Involved cornea lacks lustre. Dr george deogratias 03/25/18 15
- 16. XFC (Xerophthalmic fundus) 03/25/18 Dr george 16 ’éø It is characterized by ’éø typical seed-like, raised, whitish lesions scattered uniformly over the part of the fundus at the level of optic disc
- 17. Treatment-Xerophthalmia ’éø Apply an antibiotic -to prevent secondary bacterial infection. Ointment, e.g. tetracycline or chloramphenicol ’éø Protect the eye with an eye shield in order to prevent trauma. ’éø Vitamin A must be administered orally immediately upon diagnosis- 03/25/1817
- 18. Treatment ’éø 50,000 IU for infants < 6 mo, 100,000 IU for infants 6 to 12 mo, ’éø 200,000 IU for children > 12 mo and adults should be given for 2 days; with a third dose at least 2 wk later. ’éø For pregnant or lactating women, prophylactic or therapeutic doses should not exceed 10,000 IU /day to avoid possible damage to the fetus or infant 03/25/1819
- 19. ContŌĆ” ’éø A. MEDICAL ’éø Antibiotcs, Mydiatrics ’éø Pad specially in X3A, X3B ’éø Avoid Exposure: Antibiotic Ointment ’éø Methyl Cellulose Drops 03/25/18 Dr george 20
- 20. ContŌĆ” B. SURGERY 1. Conjunctivoplasty 2. Keratoplasty a. Prophylactic b. Optical REHABILITATION 03/25/18 Dr george 21
- 21. Prevention ’éø Improve diet- dark green leafy vegetables, deep- or bright-colored fruits (eg, papayas, oranges), carrots, and yellow vegetables (eg, squash, pumpkin). ’éø Vitamin AŌĆōfortified milk and cereals, liver, egg yolks, and fish liver oils are helpful. ’éø Carotenoids are absorbed better when consumed with some dietary fat. ’éø Prophylactic supplements of vitamin A palmitate in oil 60,000 RAE (200,000 IU) po every 6 mo- for all children between 1 - 5 years of age; infants < 6 mo-1year can be given a one- time dose of 15,000 RAE (50,000-100,000 IU), 03/25/1822
- 22. Vitamin A Toxicity ’éø Accidental ingestion by children-more than 300,000IU ’éø or chronic ’éø It usually occurs by taking more that 50,000 IU per day for more than 3 months. ’éø It can lead to dry skin, mouth sores, vomiting, and poor appetite. ’éø Eventually, it can cause increased pressure within the brain, headaches, and problems thinking clearly.┬Ā It may also lead to an enlarged liver or to liver failure. ’éø There is evidence that high levels of retinol may increase the risk of birth defects. 03/25/1823
- 23. , Ahsanteni sana 03/25/18 Dr george deogratias 24