Vitamin d presentation
- 1. Vitamin D Spikes in testing and miracle cures PFC Eaker
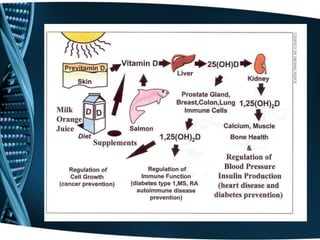
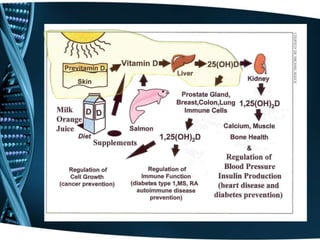
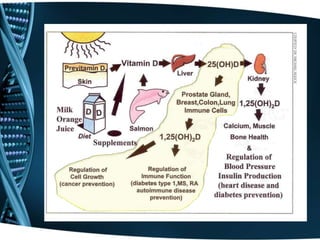
- 2. What is Vitamin D? • Fat Soluble Vitamin • Found in food • Absorbed through sunlight exposure • Converted to hormone form through liver and kidney
- 3. Two Major Forms of Vitamin D • Vitamin D2, ergocalciferol • Vitamin D3, cholecalciferol
- 4. Other Forms of Vitamin D • Vitamin D1: molecular compound of ergocalciferol with lumisterol, 1:1 • Vitamin D4: 22-dihydroergocalciferol • Vitamin D5: sitocalciferol (made from 7- dehydrosisterol)
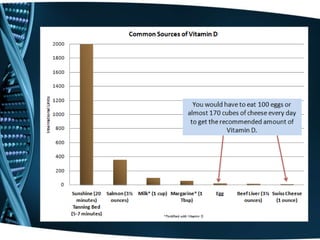
- 9. What are the sources? • Cod Liver Oil, 1 Tbs: 1,360 IU • Salmon, cooked, 3 1/2 oz: 360 IU • Mackerel, cooked, 3 1/2 oz: 345 IU • Sardines, canned in oil, drained, 3 1/2 oz: 270 IU • Milk, nonfat, reduced fat, and whole, vitamin D fortified, 1 c: 98 IU • Margarine, fortified, 1 Tbs: 60 IU • Pudding, 1/2 c prepared from mix and made with vitamin D fortified milk: 50 IU • Dry cereal, Vitamin D fortified w/10% of the recommended daily value, 3/4 c: 40-50 IU (other cereals may be fortified with more or less vitamin D) • Liver, beef, cooked, 3 1/2 oz: 30 IU • Egg, 1 whole (vitamin D is present in the yolk): 25 IU
- 10. Exposure to sunlight • Important source of vitamin D • Season, latitude, time of day
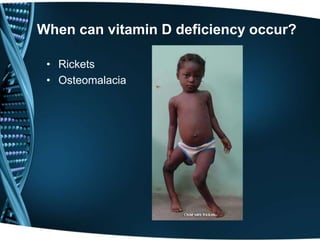
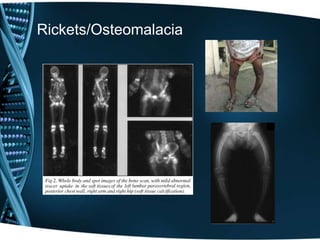
- 11. What does Vitamin D do? • Maintain normal blood levels of Calcium and Phosphorus • Aids in absorption of calcium • Promotes bone mineralization • Prevents rickets in children and Osteomalacia in adults
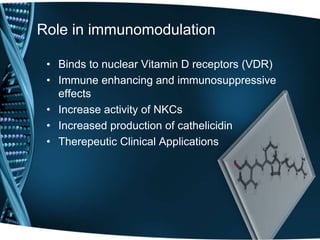
- 12. Role in immunomodulation • Binds to nuclear Vitamin D receptors (VDR) • Immune enhancing and immunosuppressive effects • Increase activity of NKCs • Increased production of cathelicidin • Therepeutic Clinical Applications
- 13. How much Vitamin D do we need? • Ages 19-50: 200 International Units (IU) • Ages 51-69: 400 IU • Age 70 and older: 600 IU
- 15. When can vitamin D deficiency occur? • Rickets • Osteomalacia
- 17. Who may need extra vitamin D to prevent a deficiency? • Older Americans (greater than age 50) • individuals with limited sun exposure • occupations that prevent exposure to sunlight • reduced ability to absorb dietary fat • exclusively breast-fed infants
- 18. What is the health risk of too much vitamin D? • nausea • vomiting • poor appetite • constipation • weakness • weight loss
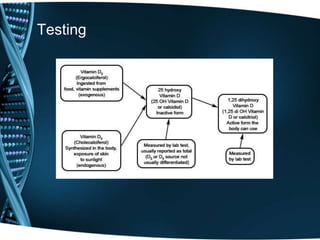
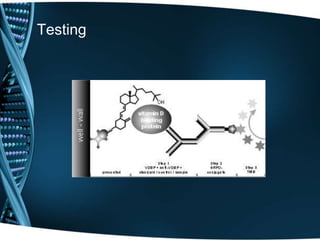
- 19. When is it ordered? • 25 OH Vitamin D test • 1,25 di OH Vitamin D test
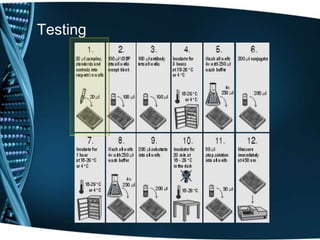
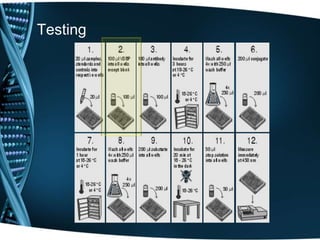
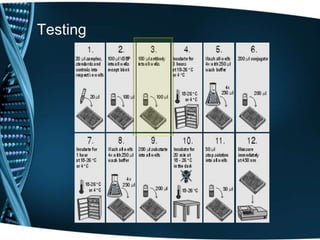
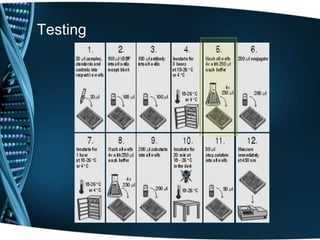
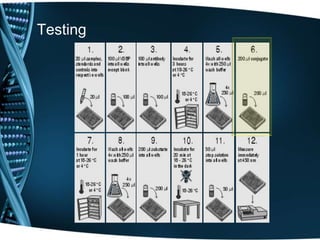
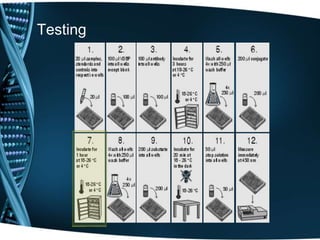
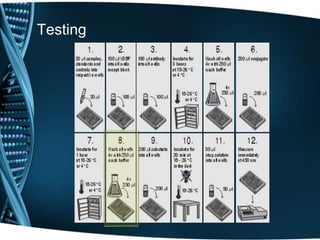
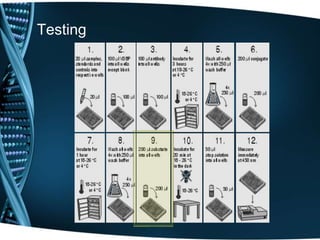
- 20. Testing
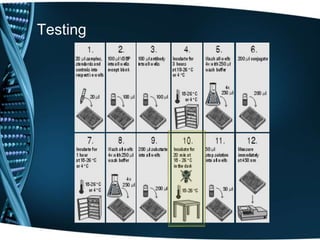
- 21. Testing
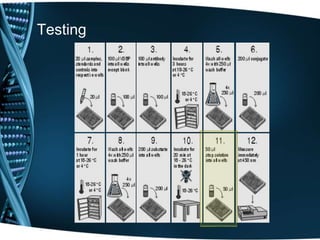
- 22. Testing
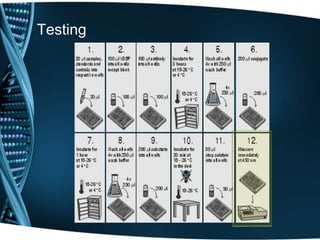
- 23. Testing
- 24. Testing
- 25. Testing
- 26. Testing
- 27. Testing
- 28. Testing
- 29. Testing
- 30. Testing
- 31. Testing
- 32. Testing
- 33. Testing
- 34. Testing
- 35. What does the test result mean? • 25 OH Vitamin D test Low blood levels = not getting enough exposure to sunlight problem with absorption from the intestines High levels = supplementation from vitamin pills or other nutritional supplements • 1,25 di OH Vitamin D test Low levels = kidney disease one of the earliest changes to occur in persons with early kidney failure. High levels = excess parathryoid hormone diseases such as sarcoidosis or some lymphomas, that can make 1,25 di OH Vitamin D outside of the kidneys
- 36. Spike in Vitamin D testing • ABC NEWS - NEW YORK, NY, USA “Sunshine Vitamin May Cut Death Risk” • BBC NEWS - UNITED KINGDOM “Pain Linked With Low Vitamin D” • BLOOMBERG.COM “Death May Be Nearer For People Who lack Vitamin D” • BRITTANIA RADIO “Vitamin D Can Heal Tuberculosis?”
- 37. Current Research • Cancers • Heart Disease • Stroke • Diabetes • Depression • Muscle Weakness • Birth Defects • Obesity
- 38. Role in cancer prevention and recovery • Calcitriol – Induces death of cancer cells • Regulates Cell growth, Differentiation etc. • Daily intake of 1,000IU/day reduces risks
- 39. Vitamin D and Obesity • Seasons • Altitude • Calcium • Link between other diseases • Treatable
- 40. Vitamin D and Diabetes • Low serum levels at greater risk • Lack of Vitamin D interferes with insulin secretion
- 41. Vitamin D and depression • SAD • 130 patients • 600 or 4,000 IU supplements • Re-evaluated 1 year later
- 42. Conclusion • Vitamin D – The wonder drug? • LabCorp – Testing volume doubled every ear for the past four years • Quest Diagnostics – Testing volume tripled between May 2006 and May 2008
- 43. Questions?
Editor's Notes
- #43: Thanks to these studies and national headlines praising its apparent cancer-fighting properties it appears many people now consider vitamin d their wonder drug and are rushing to labs to have their levels tested. The patients requesting these tests through their physicains represent an increasingly health conscious-public. These patients want greater control over managing their own health, they have greater access to information related to health promotion and illness prevention, and there are a growing number of media stores that address their demand for news and information about personal health issues. Spikes are often seen when these three drivers come together – as in the case of vitamin d There is no count on how many people get their vitamin d checked. But at testing giant LabCorp, the volume of vitamin D tests doctors order has, on average, doubled every year for the past four. So far this year, test orders are up another 90%. At competitor Quest Diagnostics, the volume of D tests approximately tripled between may 2006 and last may. http://www.virginiahopkinstestkits.com/vitamindtest.html http://abcnews.go.com/video/playerIndex?id=5563319 Vitamin D video