Vulnerabilities of Different elements exposed to hazard.pptx
- 2. Vulnerabilities of Different Elements Exposed to Hazards
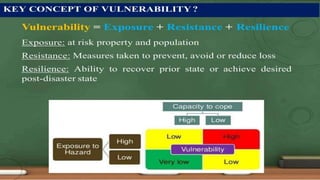
- 4. ŌĆó Vulnerability can determine the ability of a person or a group to predict, cope with, resist and recover from the effects of a natural or human-induced threat. ŌĆó Vulnerability is a state of being at risk. According to Republic Act 10121 also known as ŌĆśPhilippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act of 2010ŌĆÖ, vulnerability is defined as the characteristics and circumstances of a community, system or resource that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard.
- 5. Factors affecting vulnerability of oneŌĆÖs community: A. Population density near a hazard event. The primary consideration is not the population size but the population density.
- 6. B. Capacity and efficiency to reduce Disaster Risk. Community that is less vulnerable has the capacity to reduce disaster risk because; 1. It can provide accessibility and availability of services and facilities during and after disaster. 2. It has the ability to anticipate, adapt, and respond to possible disaster.
- 7. Recognize Vulnerabilities of Different Elements Exposed to Specific Hazards. Vulnerabilities of different elements are determined due to its exposure to particular and specific hazard. Physical vulnerability includes population density levels, place of a settlement, the site design, and materials used for infrastructure and housing.
- 8. Social Vulnerability happens due to inability of people, organization, and societies to prevent severe effects from hazards because of the expected behavior in social interactions, institutions, and system of cultural values.
- 9. ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY - is based on the economic status of individuals, communities, and nations. Social and economic vulnerability can be combined also known as socioeconomic vulnerability.
- 10. Environmental vulnerability is caused by natural resources depletion and destruction. Organisms like humans, animals, and plants are all dependent on the environment for survival. Quantifying vulnerability is used in estimating how much mitigation and preparedness measures will be applied.
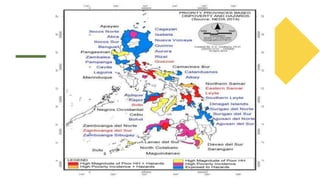
- 11. The Philippines has high vulnerability due to the following reasons: ŌĆó It lies in the Pacific typhoon belt and we are visited by an average of 20 typhoons every year. ŌĆó Rugged nature of the landscape makes it vulnerable to landslide, mudflows, and other disasters. ŌĆó It is an archipelagic country with many small islands where some areas are at below sea level.
- 12. ŌĆó It has the longest shoreline in the world at 32,400 km making it vulnerable to storm surges. ŌĆó It is still a primary agricultural and fishing economy. ŌĆó With poor institutional and social capacity to manage, respond, and recover from natural hazard events. ŌĆó With high level of poverty ŌĆó Aside from typhoon, it is also at risk to
- 14. Direction: Identify what factor affects the vulnerability to disaster with the following situations given. Write P if it is due to population density and write C if it is due to sectorŌĆÖs capacity and efficiency to reduce disaster risk. Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper. 2. Use of drones to disinfect the community in Pasig City to prevent the spread of the COVIDD-19 virus. 1. Tondo community during the total lockdown due to COVID-19 pandemic wherein the families are forced to stay inside their houses that are too small for the number of family members.
- 15. 5. The Philippines and Japan are both prone to earthquakes but the latter one is less vulnerable. 3. Insufficient number of rubber boats during super typhoon Yolanda in Malabon City wherein large number of residents were stranded on the top of their roof. 4. Too many casualties during super typhoon Milenyo in Los Ba├▒os due to excessive kaingin practices and illegal settlers in Mt. Makiling.
- 16. Direction: Classify the following phrases and sentences whether it is PHYSICAL, SOCIOECONOMICAL OR ENVIRONMENTAL VULNERABILITY. 1. Shutdown of telecommunication tower 2. Houses built near fault lines 3. Denudation of forests 4. Rest houses near boracay shoreline 5. Twenty-story building constructed on soil mainly made up of clay. 6. Bridges with cracks and crevices 7. Overfertilization of agricultural soil 8. Lost of job due to COVID-19 pandemic. 9. Possible retrenchment of ABS CBN employees due to its shutdown
Editor's Notes
- #5: VULNERABLE - capable of being physically or emotionally wounded. 2 : open to attack or damage╠² With all the identified hazard at home, there is a possibility that some family members might be susceptible or prone to the accident due to the presence of hazard.
- #6: Population density refers to the number of individuals living in an area in relation to the size of an area. If population density is high, it means that the number of individuals is high but the space is very small.
- #7: Is it appropriate to say that The Philippines is less vulnerable to typhoon? Nowadays, our country has advanced technology to predict super typhoon and several municipalities already provided evacuation centers to provide temporary housing for victims when disaster occur
- #8: When hazardous events occur, normally physical elements are severely damaged.
- #9: during typhoon the line of communications were cut off when cell sites shutdown or disruption of transport system due to inability of small vehicles to pass through the flooded areas or unpassable roads and bridges. With some difficulties in the delivery of services such as relief goods and medicines, a lot of problems occurred like shortage of food and spread of infectious diseases. Therefore, when social elements were exposed to hazard, these may lead to disruption of normal processes and activities in the community.
- #10: The poorer the country, the more vulnerable to disasters because they lack the funds or budgets to build sturdy structures and put other engineering measures in place which protect them from being affected by disasters. So, we can say that Philippines is more vulnerable to an event such as earthquake compared to Japan. Though both countries are exposed to earthquake hazard because both are located in the Pacific ring of fire, but due to differences in economic status, Japan is more resilient because of its ability to afford changes in architectural and engineering designs of building and infrastructures to make them less vulnerable to earthquake. Another example is the Covid-19 pandemic wherein the most affected are those who belong to low income and informal workers.
- #11: Human activities like deforestation, burning of fossil fuels, and kaingin affect the natural abilities of the environment to protect itself from any natural hazard due to absence of trees which may cause landslide and flashfloods. Sometimes the effects are irreversible. Computation is based on the previous hazard events and severity of their effects. Vulnerability can be expressed as: 0 = lowest degree of vulnerability and 1 as the highest degree. Vulnerability of people is the ratio of casualties or injured to the total population. Vulnerability of buildings is expressed as a repair cost or degree of damage
- #12: The Philippines lies directly on the path of the typhoon belt in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
- #17: P C C P C SE Physical E P P P E SE SE E