WAN and Switching .pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes13 views
A WAN is a network that connects devices over a broad geographic area using common carrier transmission facilities. Components of a WAN include nodes, routers, hosts, and physical links. There are different switching techniques used in WANs, including circuit switching which establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of communication, and packet switching which divides data into packets that can take different paths to the destination. Packet switching includes datagram and virtual circuit approaches, with virtual circuits pre-establishing logical connections between sender and receiver. Frame relay is a virtual circuit WAN technology that uses permanent and switched virtual circuits.
1 of 31
Download to read offline





Ad
Recommended
Unit 1 Circuit and Packet Switching.pptx
Unit 1 Circuit and Packet Switching.pptxVikas Goyal
Ěý
The document covers the principles of circuit switching and packet switching in communication networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path for the entire duration of a connection, while packet switching divides data into packets that can be transmitted independently without reservation of resources. It also discusses virtual-circuit networks, which combine aspects of both techniques, including setup and teardown phases along with dynamic resource allocation.Ch08
Ch08Waleed Awny
Ěý
A circuit-switched network uses dedicated connections between nodes, requiring three phases of connection setup, data transfer, and teardown. Resources are reserved during setup. In contrast, a packet-switched or datagram network divides messages into packets that are routed independently through the network without resource reservation. Each switch uses a routing table to determine the next hop based on the packet's destination address. A virtual-circuit network combines aspects of circuit and datagram switching by establishing virtual circuits with resource reservation but packetizing the data. Switches in these networks use various architectures like crossbar, multistage, time-division, and space-division designs to connect inputs to outputs.Swiching
SwichingMohammed Romi
Ěý
1. The document discusses different types of switched networks including circuit-switched, datagram, and virtual circuit networks. It describes the key characteristics of each type.
2. Circuit switching uses dedicated paths between nodes and has three phases: setup, data transfer, and teardown. Datagram networks treat each packet independently and route using destination addresses in packet headers. Virtual circuit networks combine aspects of circuit and datagram switching.
3. The structures of switches used in different networks are examined, including crossbar switches for circuit switching and various designs for packet switches like Banyan networks.Computer networks-WAN
Computer networks-WANCrystal Rose
Ěý
Wide area networks connect smaller networks over large geographical areas. Packet switching is the dominant switching method used, breaking data into packets that are routed independently to their destination. There are two main types of packet switching: connection-oriented uses virtual circuits to establish dedicated paths for packets to follow, while connectionless treats each packet independently without pre-establishing paths. Packet switching provides more efficient use of network bandwidth compared to circuit switching.Ravi Namboori switching
Ravi Namboori switchingRavi Namboori
Ěý
The document discusses different switching techniques in networking, specifically circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for communication but can be inefficient, while message switching allows for greater channel efficiency without a dedicated path, though it is incompatible with interactive applications. Packet switching combines the advantages of both prior methods, offering cost-effectiveness and improved delay characteristics while introducing some complexities and limitations.Ravi namboori switching
Ravi namboori switchingRavi namboori
Ěý
This document discusses different switching techniques used in digital networks, including circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection between sender and receiver but can have long wait times and inefficient bandwidth usage. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages at each node without dedicated connections, allowing for priority and broadcasting but is incompatible with interactive applications. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that may take different paths to the destination, allowing for more efficient bandwidth sharing but requiring reassembly and possibly retransmission if packets are lost.Ravi Namboori_switching
Ravi Namboori_switchingravi-namboori-babson
Ěý
The document discusses various switching techniques in networking: circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection, while message switching allows messages to be stored and forwarded without a direct path. Packet switching combines the advantages of both by enabling data to be sent in small packets over shared channels, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness, although it may introduce complexities and reliability issues.Switiching by Ravi Namboori Babson University USA
Switiching by Ravi Namboori Babson University USARavi Namboori
Ěý
The document discusses various switching techniques used in networking to manage data transmission. It details circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages, such as dedicated paths in circuit switching and efficiency in packet switching. The document emphasizes the importance of optimizing link usage while managing potential complexities and costs associated with these techniques.Chapter 2 Switches in network.ppt
Chapter 2 Switches in network.pptmonikarawat57
Ěý
This document discusses circuit switching and packet switching in communication networks. It provides details on:
1. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path between two stations but the capacity is wasted if no data is being sent. Packet switching divides messages into packets that are transmitted individually and resources are allocated on demand.
2. Circuit switching is used for applications like voice calls where continuous transmission is required. Packet switching provides better line efficiency since the bandwidth is shared between packets.
3. Switches can be implemented using space division or time division techniques. Common switches include crossbar switches, multistage switches, and time-space-time switches.Switching
Switching Abid Ali
Ěý
The document discusses different methods of switching in computer networks, including circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. It provides details on circuit-switched networks, packet-switched networks, and virtual circuit networks. For circuit switching, it describes the setup, data transfer, and teardown phases required to establish and terminate connections. For packet switching, it compares datagram and virtual circuit approaches.DCN-321-Chiwaya_Lesson7_DataElements_Switching.pdf
DCN-321-Chiwaya_Lesson7_DataElements_Switching.pdfOscarKelvinNsitu
Ěý
This document discusses different methods for switching data in communication networks. It describes circuit switching, packet switching, message switching, and fast packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for transmission. Packet switching divides data into packets that are routed independently. Message switching stores data at switches before transmission. Fast packet switching reduces overhead to increase throughput. The document provides details on the characteristics and advantages and disadvantages of each switching method.Switch networking
Switch networking MohikaJamadari
Ěý
The document discusses different network switching techniques including circuit switching, packet switching, datagram switching, virtual circuit networks, and message switching. It provides details on how each technique works, including setup/teardown phases for circuit switching, treating each packet independently for datagram networks, and storing entire messages at intermediate nodes for message switching. Key aspects like bandwidth efficiency and reliability are compared between the different techniques.chapter 5.2.pptx
chapter 5.2.pptxMelkamtseganewTigabi1
Ěý
This document discusses wide area network (WAN) technologies. It begins by defining WAN characteristics such as interconnecting computers over long distances using various media. It then describes different WAN technologies including circuit-switched networks, packet-switched networks, and virtual circuit networks. Specific routing protocols and concepts are explained like distance vector routing, link state routing, static versus dynamic routing. The document concludes by listing various WAN technology options for connecting sites like dial-up, leased lines, frame relay, ATM, microwave links and satellite.Computer network switching
Computer network switchingShivani Godha
Ěý
This document discusses different types of computer network switching, including circuit switching, packet switching, and virtual circuit switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection between nodes for the duration of a call. Packet switching divides messages into packets that are routed independently through a network on a first-come, first-served basis without dedicated connections. Virtual circuit switching combines aspects of circuit switching and packet switching by establishing paths for packets through a three-phase process of setup, data transfer using local addressing, and teardown.CN_Lec 9_Packet_Switching
CN_Lec 9_Packet_SwitchingRijutha Kumar
Ěý
The document discusses packet switching and different types of packet switching networks. It describes how in a packet switching network, data is broken into packets that can take different paths to the destination. There are two main types of packet switching - connectionless datagram switching, where each packet is routed independently, and connection-oriented virtual circuit switching, which establishes connections between nodes like circuit switching but allocates resources dynamically like packet switching. Virtual circuit switching uses two addressing schemes - global addresses and local virtual circuit identifiers assigned within the network. The document provides examples and diagrams to illustrate these different types of packet switched networks.SwitchingTechniques.ppt
SwitchingTechniques.pptShreyasBharati2
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.switchingtechniquesin computer trams.ppt
switchingtechniquesin computer trams.pptShaliniSharma266749
Ěý
The document discusses three main switching techniques for digital traffic: circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for communication, while message switching allows messages to be stored and forwarded through nodes without a dedicated path. Packet switching, which combines features of both, breaks messages into packets, optimizing efficiency and allowing multiple users to share channels, but it comes with greater complexity and potential data loss issues.Switching Techniques - Unit 3 notes aktu.pptx
Switching Techniques - Unit 3 notes aktu.pptxxesome9832
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.switching.ppt
switching.pptswati463221
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.switchingtechniques.ppt
switchingtechniques.pptShoukatRiaz
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.Switching techniques
Switching techniquesGupta6Bindu
Ěý
Circuit switching directly connects the sender and receiver through a dedicated physical path. Message switching transmits entire messages from node to node without establishing a dedicated path. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that can take different routes to the destination and are reassembled, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth but introducing complexity.Switching techniques
Switching techniquesGLIM Digital
Ěý
Circuit switching directly connects the sender and receiver through a dedicated physical path. Message switching transmits entire messages from node to node without a dedicated path. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that can take different routes to the destination and are reassembled, providing more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit switching.Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, Virtual Circuit Networks and Datagram Ne...
Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, Virtual Circuit Networks and Datagram Ne...Kaushik Panta
Ěý
The document compares circuit switching and packet switching in computer networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for data that guarantees delivery but can waste bandwidth, while packet switching divides messages into packets that travel independently without setting up a connection, allowing for faster data transmission but at the cost of reliability. It also covers virtual circuit networks, which combine aspects of both methodologies, and datagram networks, which are connectionless with independent packet treatment.Switching
SwitchingMeenakshi Paul
Ěý
The document discusses different methods of switching in networks, focusing on circuit-switched and packet-switched networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for communication, consisting of three phases: connection setup, data transfer, and connection teardown, whereas packet switching divides messages into packets for more efficient transmission without dedicated paths. The document also highlights the advantages and drawbacks of each method, including resource allocation, efficiency, and delay in data transfer.Packet switching
Packet switchingasimnawaz54
Ěý
Packet switching refers to protocols where messages are divided into packets before being transmitted. Each packet is transmitted individually and can take different routes to the destination. Once all packets arrive, they are recompiled into the original message. There are two main approaches: virtual circuits establish a pre-planned route before transmission, while datagrams treat each packet independently without connection setup. Virtual circuits provide sequencing but are less reliable if a node fails, while datagrams are more flexible but packets may arrive out of order.2b switching in networks
2b switching in networkskavish dani
Ěý
This document discusses different types of switched networks, including circuit-switched networks, datagram networks, and virtual-circuit networks. Circuit-switched networks use dedicated connections between stations that remain in place for the duration of a call. Datagram networks divide messages into packets that are routed independently through the network without dedicated connections. Virtual-circuit networks combine aspects of circuit-switched and datagram networks by establishing virtual circuits for packets belonging to the same data flow. The document also describes the components and operation of packet switches used in these different types of switched networks.Circuit switching in operational research
Circuit switching in operational researchFaizanAli393009
Ěý
The document discusses the differences between circuit-switched and packet-switched networks, explaining their structures, functionalities, and performance characteristics. Circuit switching involves a dedicated path and reserved resources, while packet switching transmits data in packets without dedicated bandwidth, allowing multiple users to share network resources. It also outlines the functionalities of virtual circuits and datagram approaches within packet-switched networks.Stay Safe Women Security Android App Project Report.pdf
Stay Safe Women Security Android App Project Report.pdfKamal Acharya
Ěý
Women’s security is a critical issue in today’s world and it’s very much needed for every individual
to be acting over such an issue. This document describes a GPS based “Women Security System''
that provides the combination of GPS devices as well as provide alerts and messages with an
emergency button trigger whenever somebody is in trouble They might not have so much time, all
that they have to do is generate a distress emergency signal by shaking up their phone. Our system
provides a realizable, cost effective solution to problem detection. Nowdays due to recently
happened cases such as rape by drivers or colleagues, burglary etc., women security, especially
women security has become the foremost priority of the world. System uses the Global Positioning
System (GPS) technology to find out the location of women. The information of women's position
provided by the device can be viewed on Google maps using Internet or specialized software. The
companies are looking for-ward to the security problem and require a system that will efficiently
evaluate the problem of women security working in night shifts, traveling alone. We focus on the
proposed model that can be used to deal with the security issue of women using GPS based tracking
systems.Structured Programming with C++ :: Kjell Backman
Structured Programming with C++ :: Kjell BackmanShabista Imam
Ěý
Step into the world of high-performance programming with the Complete Guidance Book of C++ Programming—a definitive resource for mastering one of the most powerful and versatile languages in computer science.
Whether you're a beginner looking to learn the fundamentals or an intermediate developer aiming to sharpen your skills, this book walks you through C++ from the ground up. You'll start with basics like variables, control structures, and functions, then progress to object-oriented programming (OOP), memory management, file handling, templates, and the Standard Template Library (STL).More Related Content
Similar to WAN and Switching .pptx (20)
Chapter 2 Switches in network.ppt
Chapter 2 Switches in network.pptmonikarawat57
Ěý
This document discusses circuit switching and packet switching in communication networks. It provides details on:
1. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path between two stations but the capacity is wasted if no data is being sent. Packet switching divides messages into packets that are transmitted individually and resources are allocated on demand.
2. Circuit switching is used for applications like voice calls where continuous transmission is required. Packet switching provides better line efficiency since the bandwidth is shared between packets.
3. Switches can be implemented using space division or time division techniques. Common switches include crossbar switches, multistage switches, and time-space-time switches.Switching
Switching Abid Ali
Ěý
The document discusses different methods of switching in computer networks, including circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. It provides details on circuit-switched networks, packet-switched networks, and virtual circuit networks. For circuit switching, it describes the setup, data transfer, and teardown phases required to establish and terminate connections. For packet switching, it compares datagram and virtual circuit approaches.DCN-321-Chiwaya_Lesson7_DataElements_Switching.pdf
DCN-321-Chiwaya_Lesson7_DataElements_Switching.pdfOscarKelvinNsitu
Ěý
This document discusses different methods for switching data in communication networks. It describes circuit switching, packet switching, message switching, and fast packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for transmission. Packet switching divides data into packets that are routed independently. Message switching stores data at switches before transmission. Fast packet switching reduces overhead to increase throughput. The document provides details on the characteristics and advantages and disadvantages of each switching method.Switch networking
Switch networking MohikaJamadari
Ěý
The document discusses different network switching techniques including circuit switching, packet switching, datagram switching, virtual circuit networks, and message switching. It provides details on how each technique works, including setup/teardown phases for circuit switching, treating each packet independently for datagram networks, and storing entire messages at intermediate nodes for message switching. Key aspects like bandwidth efficiency and reliability are compared between the different techniques.chapter 5.2.pptx
chapter 5.2.pptxMelkamtseganewTigabi1
Ěý
This document discusses wide area network (WAN) technologies. It begins by defining WAN characteristics such as interconnecting computers over long distances using various media. It then describes different WAN technologies including circuit-switched networks, packet-switched networks, and virtual circuit networks. Specific routing protocols and concepts are explained like distance vector routing, link state routing, static versus dynamic routing. The document concludes by listing various WAN technology options for connecting sites like dial-up, leased lines, frame relay, ATM, microwave links and satellite.Computer network switching
Computer network switchingShivani Godha
Ěý
This document discusses different types of computer network switching, including circuit switching, packet switching, and virtual circuit switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection between nodes for the duration of a call. Packet switching divides messages into packets that are routed independently through a network on a first-come, first-served basis without dedicated connections. Virtual circuit switching combines aspects of circuit switching and packet switching by establishing paths for packets through a three-phase process of setup, data transfer using local addressing, and teardown.CN_Lec 9_Packet_Switching
CN_Lec 9_Packet_SwitchingRijutha Kumar
Ěý
The document discusses packet switching and different types of packet switching networks. It describes how in a packet switching network, data is broken into packets that can take different paths to the destination. There are two main types of packet switching - connectionless datagram switching, where each packet is routed independently, and connection-oriented virtual circuit switching, which establishes connections between nodes like circuit switching but allocates resources dynamically like packet switching. Virtual circuit switching uses two addressing schemes - global addresses and local virtual circuit identifiers assigned within the network. The document provides examples and diagrams to illustrate these different types of packet switched networks.SwitchingTechniques.ppt
SwitchingTechniques.pptShreyasBharati2
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.switchingtechniquesin computer trams.ppt
switchingtechniquesin computer trams.pptShaliniSharma266749
Ěý
The document discusses three main switching techniques for digital traffic: circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for communication, while message switching allows messages to be stored and forwarded through nodes without a dedicated path. Packet switching, which combines features of both, breaks messages into packets, optimizing efficiency and allowing multiple users to share channels, but it comes with greater complexity and potential data loss issues.Switching Techniques - Unit 3 notes aktu.pptx
Switching Techniques - Unit 3 notes aktu.pptxxesome9832
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.switching.ppt
switching.pptswati463221
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.switchingtechniques.ppt
switchingtechniques.pptShoukatRiaz
Ěý
In large networks, there are multiple paths between senders and receivers. Information can be switched using circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection for the duration of a call. Message switching stores and forwards entire messages without dedicated connections. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that travel over multiple paths and are reassembled at the destination, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit or message switching.Switching techniques
Switching techniquesGupta6Bindu
Ěý
Circuit switching directly connects the sender and receiver through a dedicated physical path. Message switching transmits entire messages from node to node without establishing a dedicated path. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that can take different routes to the destination and are reassembled, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth but introducing complexity.Switching techniques
Switching techniquesGLIM Digital
Ěý
Circuit switching directly connects the sender and receiver through a dedicated physical path. Message switching transmits entire messages from node to node without a dedicated path. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that can take different routes to the destination and are reassembled, providing more efficient use of bandwidth than circuit switching.Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, Virtual Circuit Networks and Datagram Ne...
Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, Virtual Circuit Networks and Datagram Ne...Kaushik Panta
Ěý
The document compares circuit switching and packet switching in computer networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for data that guarantees delivery but can waste bandwidth, while packet switching divides messages into packets that travel independently without setting up a connection, allowing for faster data transmission but at the cost of reliability. It also covers virtual circuit networks, which combine aspects of both methodologies, and datagram networks, which are connectionless with independent packet treatment.Switching
SwitchingMeenakshi Paul
Ěý
The document discusses different methods of switching in networks, focusing on circuit-switched and packet-switched networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated path for communication, consisting of three phases: connection setup, data transfer, and connection teardown, whereas packet switching divides messages into packets for more efficient transmission without dedicated paths. The document also highlights the advantages and drawbacks of each method, including resource allocation, efficiency, and delay in data transfer.Packet switching
Packet switchingasimnawaz54
Ěý
Packet switching refers to protocols where messages are divided into packets before being transmitted. Each packet is transmitted individually and can take different routes to the destination. Once all packets arrive, they are recompiled into the original message. There are two main approaches: virtual circuits establish a pre-planned route before transmission, while datagrams treat each packet independently without connection setup. Virtual circuits provide sequencing but are less reliable if a node fails, while datagrams are more flexible but packets may arrive out of order.2b switching in networks
2b switching in networkskavish dani
Ěý
This document discusses different types of switched networks, including circuit-switched networks, datagram networks, and virtual-circuit networks. Circuit-switched networks use dedicated connections between stations that remain in place for the duration of a call. Datagram networks divide messages into packets that are routed independently through the network without dedicated connections. Virtual-circuit networks combine aspects of circuit-switched and datagram networks by establishing virtual circuits for packets belonging to the same data flow. The document also describes the components and operation of packet switches used in these different types of switched networks.Circuit switching in operational research
Circuit switching in operational researchFaizanAli393009
Ěý
The document discusses the differences between circuit-switched and packet-switched networks, explaining their structures, functionalities, and performance characteristics. Circuit switching involves a dedicated path and reserved resources, while packet switching transmits data in packets without dedicated bandwidth, allowing multiple users to share network resources. It also outlines the functionalities of virtual circuits and datagram approaches within packet-switched networks.Recently uploaded (20)
Stay Safe Women Security Android App Project Report.pdf
Stay Safe Women Security Android App Project Report.pdfKamal Acharya
Ěý
Women’s security is a critical issue in today’s world and it’s very much needed for every individual
to be acting over such an issue. This document describes a GPS based “Women Security System''
that provides the combination of GPS devices as well as provide alerts and messages with an
emergency button trigger whenever somebody is in trouble They might not have so much time, all
that they have to do is generate a distress emergency signal by shaking up their phone. Our system
provides a realizable, cost effective solution to problem detection. Nowdays due to recently
happened cases such as rape by drivers or colleagues, burglary etc., women security, especially
women security has become the foremost priority of the world. System uses the Global Positioning
System (GPS) technology to find out the location of women. The information of women's position
provided by the device can be viewed on Google maps using Internet or specialized software. The
companies are looking for-ward to the security problem and require a system that will efficiently
evaluate the problem of women security working in night shifts, traveling alone. We focus on the
proposed model that can be used to deal with the security issue of women using GPS based tracking
systems.Structured Programming with C++ :: Kjell Backman
Structured Programming with C++ :: Kjell BackmanShabista Imam
Ěý
Step into the world of high-performance programming with the Complete Guidance Book of C++ Programming—a definitive resource for mastering one of the most powerful and versatile languages in computer science.
Whether you're a beginner looking to learn the fundamentals or an intermediate developer aiming to sharpen your skills, this book walks you through C++ from the ground up. You'll start with basics like variables, control structures, and functions, then progress to object-oriented programming (OOP), memory management, file handling, templates, and the Standard Template Library (STL).Proposal for folders structure division in projects.pdf
Proposal for folders structure division in projects.pdfMohamed Ahmed
Ěý
Proposal for folders structure division in projectsIntroduction to Python Programming Language
Introduction to Python Programming Languagemerlinjohnsy
Ěý
This PPT covers features, applications, variable, data types and statements in PythonLearning – Types of Machine Learning – Supervised Learning – Unsupervised UNI...
Learning – Types of Machine Learning – Supervised Learning – Unsupervised UNI...23Q95A6706
Ěý
Learning – Types of Machine Learning – Supervised Learning – Unsupervised Learning- semi supervised learning - The Brain and the Neuron – Design a Learning System – Perspectives and Issues in Machine Learning – Concept Learning Task – Concept Learning as Search – Finding a Maximally Specific Hypothesis – Version Spaces and the Candidate Elimination Algorithm
FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTUREShabista Imam
Ěý
FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
By : Mostafa Abd-El-Barr & Hesham El-Rewini:: wiley
A complete guidance bookModern multi-proposer consensus implementations
Modern multi-proposer consensus implementationsFrançois Garillot
Ěý
Multi-proposer consensus protocols let multiple validators propose blocks in parallel, breaking the single-leader throughput bottleneck of classic designs. Yet the modern multi-proposer consensus implementation has grown a lot since HotStuff. THisworkshop will explore the implementation details of recent advances – DAG-based approaches like Narwhal and Sui’s Mysticeti – and reveal how implementation details translate to real-world performance gains. We focus on the nitty-gritty: how network communication patterns and data handling affect throughput and latency. New techniques such as Turbine-like block propagation (inspired by Solana’s erasure-coded broadcast) and lazy push gossip broadcasting dramatically cut communication overhead. These optimizations aren’t just theoretical – they enable modern blockchains to process over 100,000 transactions per second with finality in mere milliseconds​ redefining what is possible in decentralized systems.
Complete University of Calculus :: 2nd edition
Complete University of Calculus :: 2nd editionShabista Imam
Ěý
Master the language of change with the Complete Guidance Book of Calculus—your comprehensive resource for understanding the core concepts and applications of differential and integral calculus. Designed for high school, college, and self-study learners, this book takes a clear, intuitive approach to a subject often considered challenging.Fundamentals of Digital Design_Class_21st May - Copy.pptx
Fundamentals of Digital Design_Class_21st May - Copy.pptxdrdebarshi1993
Ěý
Basics of Number Systems and Logic GatesFundamentals of Digital Design_Class_12th April.pptx
Fundamentals of Digital Design_Class_12th April.pptxdrdebarshi1993
Ěý
Boolean Algebra and Combinational Logic CircuitDavid Boutry - Mentors Junior Developers
David Boutry - Mentors Junior DevelopersDavid Boutry
Ěý
David Boutry is a Senior Software Engineer in New York with expertise in high-performance data processing and cloud technologies like AWS and Kubernetes. With over eight years in the field, he has led projects that improved system scalability and reduced processing times by 40%. He actively mentors aspiring developers and holds certifications in AWS, Scrum, and Azure.Tesla-Stock-Analysis-and-Forecast.pptx (1).pptx
Tesla-Stock-Analysis-and-Forecast.pptx (1).pptxmoonsony54
Ěý
this is data science ppt for tesla stock (linear regression)Machine Learning - Classification Algorithms
Machine Learning - Classification Algorithmsresming1
Ěý
This covers traditional machine learning algorithms for classification. It includes Support vector machines, decision trees, Naive Bayes classifier , neural networks, etc.
It also discusses about model evaluation and selection. It discusses ID3 and C4.5 algorithms. It also describes k-nearest neighbor classifer.Ad
WAN and Switching .pptx
- 1. Dr. SUHAIL Q. MIR suhailmir@uok.edu.in M Sc. IT (2022 Batch) Directorate of Information Technology & Support Systems University of Kashmir WIDE AREA NETWORK & SWITCHING IN NETWORKS
- 2. A WAN is a data communications network that covers a relatively broad geographic area and that often uses transmission facilities provided by common carriers, such as telephone companies. What is a Wide Area Network (WAN) ? These networks are often established by service providers that then lease their WAN to businesses, schools, governments or the public.
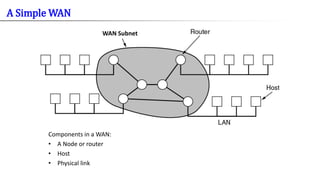
- 3. WAN Subnet Components in a WAN: • A Node or router • Host • Physical link A Simple WAN
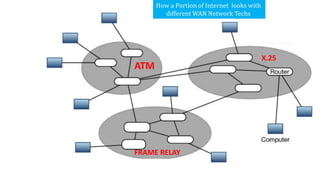
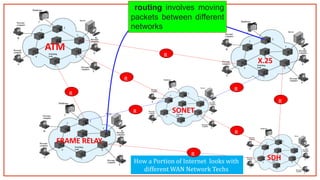
- 4. ATM FRAME RELAY X.25 How a Portion of Internet looks with different WAN Network Techs
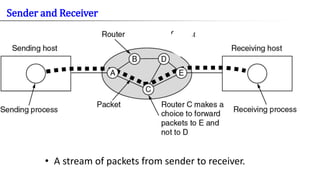
- 5. • A stream of packets from sender to receiver. Sender and Receiver
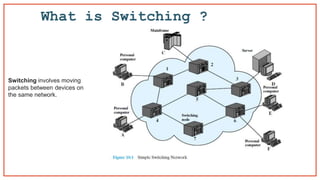
- 6. What is Switching ? Switching involves moving packets between devices on the same network.
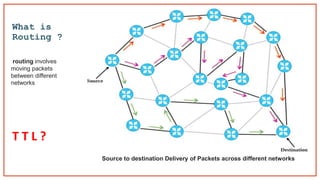
- 7. What is Routing ? T T L ? routing involves moving packets between different networks Source to destination Delivery of Packets across different networks
- 8. ATM FRAME RELAY X.25 SONET SDH How a Portion of Internet looks with different WAN Network Techs R R R R R R R R routing involves moving packets between different networks
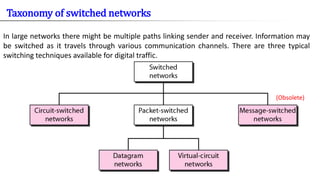
- 9. (Obsolete) In large networks there might be multiple paths linking sender and receiver. Information may be switched as it travels through various communication channels. There are three typical switching techniques available for digital traffic. Taxonomy of switched networks
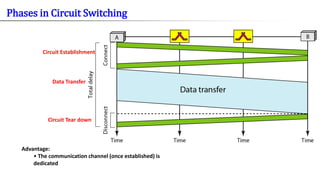
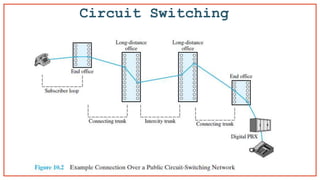
- 10. Dedicated communication physical path between two stations • Circuit switching implies the need to first set up a dedicated, end-to- end path for the connection before the information transfer takes place. • Communication via circuit switching involves three phases: — Circuit Establishment — Data Transfer — Circuit Tear down • Once the connection is made the only delay is propagation time. Circuit Switching
- 11. Advantage: • The communication channel (once established) is dedicated Circuit Establishment Circuit Tear down Data Transfer Phases in Circuit Switching
- 13. • Inefficient —Channel capacity dedicated for duration of connection —If no data, capacity wasted • Set up (connection) takes time • Once connected, transfer is transparent • Developed for voice traffic (phone) Problems with Circuit Switching
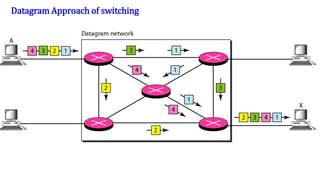
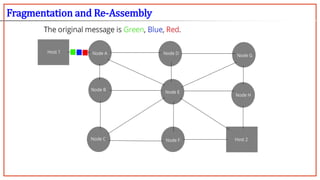
- 14. Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data into suitably sized blocks, called packets, which are transmitted via a medium that may be shared by multiple simultaneous communication sessions. The packets may choose different paths en-route destination. Routing Algorithm needed Packet Switching is divided into: 1. Datagrams 2. Virtual Circuits. Packet Switching
- 15. Datagram Approach of switching
- 16. COST OR WEIGHTS Three Classes or Routing Algorithms 1. Flooding 2. Static Routing 3. Dynamic Routing
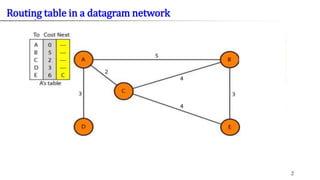
- 17. Routing table in a datagram network
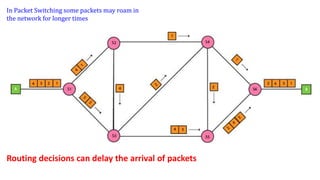
- 19. In Packet Switching some packets may roam in the network for longer times Routing decisions can delay the arrival of packets
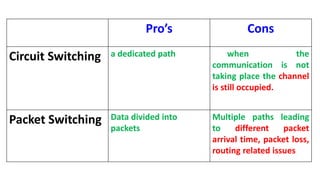
- 20. Pro’s Cons Circuit Switching a dedicated path when the communication is not taking place the channel is still occupied. Packet Switching Data divided into packets Multiple paths leading to different packet arrival time, packet loss, routing related issues
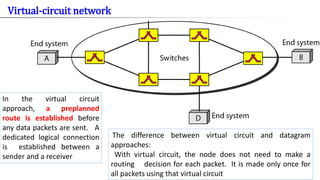
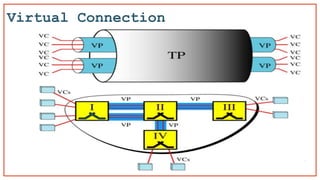
- 21. Virtual-circuit network The difference between virtual circuit and datagram approaches: With virtual circuit, the node does not need to make a routing decision for each packet. It is made only once for all packets using that virtual circuit In the virtual circuit approach, a preplanned route is established before any data packets are sent. A dedicated logical connection is established between a sender and a receiver
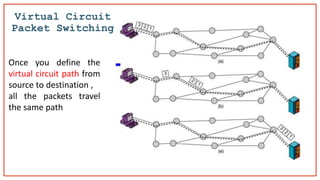
- 22. Virtual Circuit Packet Switching Once you define the virtual circuit path from source to destination , all the packets travel the same path
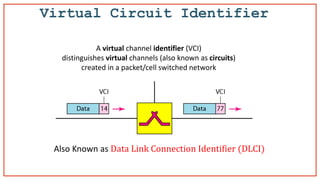
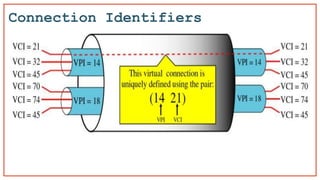
- 23. Virtual Circuit Identifier A virtual channel identifier (VCI) distinguishes virtual channels (also known as circuits) created in a packet/cell switched network Also Known as Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI)
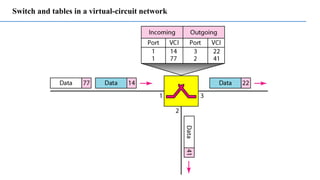
- 24. Switch and tables in a virtual-circuit network
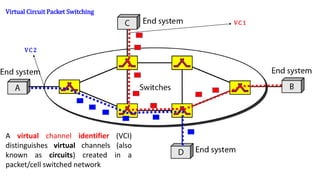
- 25. A virtual channel identifier (VCI) distinguishes virtual channels (also known as circuits) created in a packet/cell switched network Virtual Circuit Packet Switching VC 1 VC 2
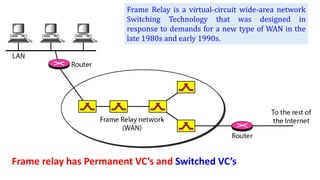
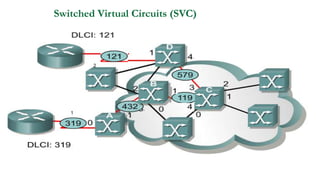
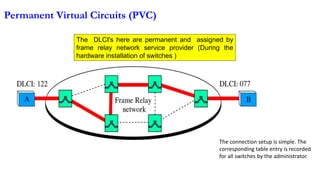
- 28. Frame Relay is a virtual-circuit wide-area network Switching Technology that was designed in response to demands for a new type of WAN in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Frame relay has Permanent VC’s and Switched VC’s
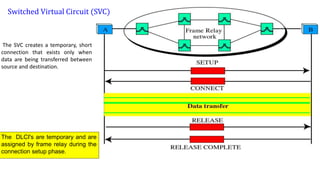
- 29. The SVC creates a temporary, short connection that exists only when data are being transferred between source and destination. The DLCI's are temporary and are assigned by frame relay during the connection setup phase. Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC)
- 30. Switched Virtual Circuits (SVC) 1 2
- 31. Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVC) The connection setup is simple. The corresponding table entry is recorded for all switches by the administrator. The DLCI's here are permanent and assigned by frame relay network service provider (During the hardware installation of switches )
